Dental Implants Toronto | Aesthetic & Cosmetic Dentistry ...
Classification and impression techniques of implants/ dentistry dental implants
-
Upload
ida-dental -
Category
Education
-
view
301 -
download
34
description
Transcript of Classification and impression techniques of implants/ dentistry dental implants

Classification and Classification and impression techniques impression techniques
of implantsof implantsINDIAN DENTAL ACADEMY
Leader in continuing dental education www.indiandentalacademy.com
www.indiandentalacademy.comwww.indiandentalacademy.com

www.indiandentalacademy.com

ClassificationClassification► Based uponBased upon
1.1. Placement within the tissuesPlacement within the tissues2.2. Materials usedMaterials used3.3. Attachment mechanismAttachment mechanism4.4. Surface coatingSurface coating5.5. ShapeShape6.6. Surgical stageSurgical stage7.7. Mode of insertion Mode of insertion 8.8. Tissue response & systemic toxicity effects of Tissue response & systemic toxicity effects of
implantsimplants www.indiandentalacademy.com

►Subperiosteal implantsSubperiosteal implants
Based upon the placement Based upon the placement within the tissuewithin the tissue
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Subdivision of subperiosteal Subdivision of subperiosteal implantimplant
o UnilateralUnilateralo InterdentalInterdentalo TotalTotalo circumferentialcircumferential
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Unilateral subperiosteal implant
Interdental subperiosteal implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Total subperiosteal implant
Circumferential subperiosteal implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Transosteal implantTransosteal implant
Also known asAlso known as o Staple boneStaple boneo Mandibular stapleMandibular stapleo TransmandibularTransmandibular
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Transosteal implantTransosteal implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Endosteal implantEndosteal implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Root formBlade/plate form
Ramus frame www.indiandentalacademy.com

Intramucosal insertsIntramucosal inserts
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Endodontic stabilizer implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon materials usedBased upon materials used1.Metallic implants-commercially pure titanium1.Metallic implants-commercially pure titanium Titanium alloyTitanium alloy Cobalt chromium molybdenum Cobalt chromium molybdenum alloy alloy
2.Nonmetallic implants-Ceramics2.Nonmetallic implants-Ceramics CarbonCarbon
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Ceramic and titanium alloy implants
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon the attachment Based upon the attachment mechanismmechanism
1.Osseointegration2.Fibro osseous integration
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon their surface Based upon their surface coatingcoating
o Titanium plasma sprayedTitanium plasma sprayedo Hydroxyapatite coatingHydroxyapatite coatingo Grid blasting with TiOGrid blasting with TiOo SLA(sandblasted-largegrid-acidetched)SLA(sandblasted-largegrid-acidetched)o Acid etchedAcid etchedo Machined surfaceMachined surface
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon the shapeBased upon the shape
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd….Contd….o Threaded,nonthreadedThreaded,nonthreadedo Tapered,parallelTapered,parallelo With vent holes,without vent holesWith vent holes,without vent holeso Hollow cylinder,solid screwsHollow cylinder,solid screwso Root form,blade formRoot form,blade form
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon the surgical Based upon the surgical stagestage
Two stage implantsTwo stage implants One stage implant
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon mode of Based upon mode of insertioninsertion
1.Axially inserted 1.Axially inserted (crestal approach)(crestal approach)
www.indiandentalacademy.com

2.Laterally inserted(basal approach)
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Based upon tissue response Based upon tissue response &systemic toxicity effects of &systemic toxicity effects of
implantsimplantso Biotolerant materials-Biotolerant materials-
polmethylmethacrylatepolmethylmethacrylate
o Bioinert materials-titanium and Bioinert materials-titanium and aluminium aluminium oxide oxide
o Bioactive materials-glass and calcium Bioactive materials-glass and calcium phosphate ceramic phosphate ceramic
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Components of implantComponents of implant
Implant body Implant body
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Cover screw Healing abutment
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Healing cap Implant abutment
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Impression posts
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Laboratory analogs
www.indiandentalacademy.com

IMPRESSION MATERIALS
Ideal Requirements
•Complete plasticity before cure
•Fluidity to record fine detail
•Ability to wet oral tissues
•Dimensional accuracy
•Dimensional stability
•Complete elasticity after cure
•Optimal stiffnesswww.indiandentalacademy.com

Materials Used
o Alginateo Agaro Polysulphideo Polyethero Condensation Siliconeo Addition Silicone
www.indiandentalacademy.com

ALGINATE
o Poor dimensional stabilityo Poor dimensional accuracyo Poor tear strength o Poor stiffnesso Interferes with setting of gypsum
www.indiandentalacademy.com

AGAR
o Interferes with setting of gypsumo Dimensional instabilityo Elaborate equipment neededo Low tear resistance
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Polysulphide
o Base-polusulfide polymer, Catalyst- lead dioxideo High tear strengtho Messy,unpleasant odouro Long setting timeo Poor dimensional stabilityo Hydrophobic
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Condensation silicone
o Cheapero Good tear strength, accuracy & elastic propertieso Dimensional instability,due to loss of ethyl alcoholo Poured quickly
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Addition silicone
o Shorter setting timeo Easy to mix- automatic mixing deviceso Adequate tear strengtho Extremely high accuracyo Dimensional stability even after 1 weeko Least distortion on removalo Hydrophilico Good compatibility with gypsum
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Polyether
o Good dimensional stability & accuracyo Short setting timeo Material very rigido Not available in all consistencieso Most expensive
www.indiandentalacademy.com

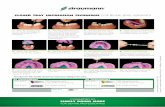
Dispensed as :
Manual mixing
Automixing system
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Manual mixing
o Puttyo Heavy bodyo Monophaseo Light body
www.indiandentalacademy.com

www.indiandentalacademy.com

Automixing equipment & materials
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Two basic impression techniques for implants are
1. indirect technique or closed tray technique
2.direct or pick-up or open tray technique.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Indirect impression technique
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Direct impression technique
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Contd…
www.indiandentalacademy.com

www.indiandentalacademy.com

Indirect method
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Direct method
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Related articles
Tautin(1985)presented a technique to accurately, transfer and reproduce the relationship between implant dentures , in which no preliminary impression or acrylic resin custom tray were needed. He used modeling compound to form a custom tray by adapting it over transfer copings,pressing the compound over the superior aspect of the coping so that its circular outline is seen through the compound.After trimming the outline of the coping showing through the top of the tray an impression plaster is used to record and transfer the coping to the impressions www.indiandentalacademy.com

Loos(1986)presented a detail technique for the fabrication of a fixed prosthesis supported by implants.His technique incorporated plugging the incisal end of the transfer coping with beading wax(to prevent impression material from flowing into it)splinting the transfer copings with orthodontic ligature wire and Duralay acrylic resin,use of a plastic perforated impression tray with incisal window to access the transfer coping and making the final impression with putty light body addition silicone.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Rasmussen(1987)presented a technique in which the existing denture is modified using tissue conditioning material is used instead of healing caps after second stage surgery ,eliminating the use of impression copings at the final impression.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Humphries et al (1990) evaluated the accuracy of implant master casts constructed from transfer impressions using three techniques.The techniques used were splinted square polymer copings,unsplinted square polymer copings and unsplinted hydrocolloid copings.Tapered hydrocolloid copings were more accurate than the other two methods.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Carr (1991) compared impression techniques for five implant mandibular model by both indirect and direct transfer coping techniques and found that for the models used ,the direct method produced more accurate working casts.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Vigolo et al(2000)evaluated the accuracy in transferring the position of the hexagonal head of a single implant to the working cast, and concluded that the sandblasting and coating the roughened surface of the impression coping with an impression adhesive will result in more accurate orientation of the implant replicas in the laboratory master casts in single tooth implant restorations.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Conclusion
Success with implant prosthodontics requires a careful attention to each and every step from diagnosis and treatment planning. Several implant systems are available , selection of appropriate one is mandatory. The prosthesis fit can be accurate only if a proper impression is made. Thus usage of correct impression technique and material are important.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

References
1. contemporary implant dentistry , Carl E. Misch
2. Implants in dentistry , Michael,John and Luis.
3. Implant prosthodontics Stevens & freidrickson
4. Dental implants- Fundamental & advanced laboratory
technology , Robert Winkleman &Kenneth orth.
www.indiandentalacademy.com

References contd…5. Philip’s science of dental materials
6. Contemporary fixed prosthodontics, Rosentiel
7. Principles & practice of implant dentistry, Weiss
8. Theory & practice of ossteointegration, Hobo
9. Carr AB. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1991;6(4):448-55
10. Assif etal. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999;14(6):885-88
11. Loos Larry G. J Prosthet Dent 1986;55:232-42
12. Rasmussen Eric J. J Prosthet Dent. 1987;57:198-203
13. Tautin Francis S. J Prosthet Dent. 1985;54:250-51
14. Vigolo etal. J Proshtet Dent. 2000;83:562-66
www.indiandentalacademy.com

Thank youThank you
Thank you
For more details please visit www.indiandentalacademy.com
www.indiandentalacademy.com