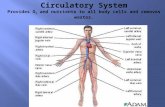
Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System). Functions of the Circulatory System Transport of oxygen,...
-
Upload
theresa-johnston -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
1
Transcript of Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System). Functions of the Circulatory System Transport of oxygen,...

Circulatory SystemCirculatory System(Cardiovascular System)(Cardiovascular System)

Functions of the Circulatory Functions of the Circulatory SystemSystem
Transport of Transport of oxygenoxygen, , nutrientsnutrients and and wastewaste products throughout the body products throughout the body
Helps regulate body temperatureHelps regulate body temperature

ComponentsComponents BloodBlood
– NutrientNutrient rich liquid has everything your cells need rich liquid has everything your cells need to surviveto survive
– It also collects the It also collects the wastewaste products your cells produce products your cells produce
HeartHeart– Primary organ that Primary organ that pumpspumps blood throughout blood throughout bodybody
Blood VesselsBlood Vessels– Vessel throughout the body that carry the blood Vessel throughout the body that carry the blood
1.1. Arteries-carry blood Arteries-carry blood awayaway from heart from heart2.2. Veins- carry blood Veins- carry blood towardstowards the heart the heart3.3. Capillaries- very Capillaries- very smallsmall vessels in between arteries and veins vessels in between arteries and veins
1.1. -very -very thin thin walledwalled2.2. -site of -site of nutrient nutrient and and wastewaste exchange between circ. system and exchange between circ. system and cellscells

THREE TYPES OF CIRCULATION:THREE TYPES OF CIRCULATION:1.1. SystemicSystemic: arteries bring oxygenated blood to body cells and veins : arteries bring oxygenated blood to body cells and veins
return deoxygenated blood back to heartreturn deoxygenated blood back to heart
2. 2. PulmonaryPulmonary: pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated : pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the blood to the lungs lungs to release CO2 and pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to release CO2 and pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood back to the heart back to the heart
3. 3. CoronaryCoronary: arteries supply the heart itself with oxygenated blood and : arteries supply the heart itself with oxygenated blood and veins carry waste products awayveins carry waste products away
© 2014 Getting Nerdy, LLC

Central OrganCentral Organ The Heart The Heart – a fist sized muscular – a fist sized muscular
organ that pumps blood through a organ that pumps blood through a network of blood vesselsnetwork of blood vessels

The Heart The Heart a “double pump”a “double pump”
A septum (wall) vertically divides into two A septum (wall) vertically divides into two sidessides
Right- pumps blood to the lungsRight- pumps blood to the lungs Left- pumps blood to the other parts of the Left- pumps blood to the other parts of the
bodybody
Upper chambers- atriumUpper chambers- atrium– Collect bloodCollect blood
Lower chambers- ventriclesLower chambers- ventricles– Pump blood Pump blood

Heart ValvesHeart Valves Valves- Flap of tissue that open in Valves- Flap of tissue that open in
only one direction. Valves prevent only one direction. Valves prevent blood from flowing backwards.blood from flowing backwards.

Stucture of the HeartStucture of the Heart
Right VentriclePropels oxygen poor blood into Pulmonary arteries towards lungs
Right AtriumCollects oygen poor blood from Vena Cavas
Left AtriumCollects oxygen rich blood from pulmonary veins
Inferior Vena CavaLarge Vein that brings oxygen-poor blood from the lower part of the body
Tricuspid ValvePrevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium after it has entered the right ventricle
Pulmonary ValvePrevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle after it has entered the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary VeinsBring oxygen-rich blood each of the lungs to the left atrium
Superior Vena CavaLarge vein that brings oxygen-poor blood from the upper part of the body
AortaBrings oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the body
Pulmonary ArteriesBring oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
Aortic ValvePrevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle after it has entered the aorta
Mitral (Biscupid)ValvePrevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium after it has entered the left ventricle
Left VentriclePropels Oxygen rich blood into AortaSeptum

99
Simplified flow: print and fill in detailsSimplified flow: print and fill in details

1010
Electrical conduction Electrical conduction system:system:
(Explanation in next slides)
specialized cardiac muscle cells can carry impulses throughout the heart muscle, signaling the chambers to contract in the proper sequence

Conduction Conduction systemsystem
SA node (sinoatrial) SA node (sinoatrial) – Known as the “pacemaker”Known as the “pacemaker”– In dorsal wall Right AtriumIn dorsal wall Right Atrium– Site of connection be nervous system and Site of connection be nervous system and
heartheart– Sets basic rate: 60-80 beats per minuteSets basic rate: 60-80 beats per minute– Impulse sent from SA node to atria causing R. Impulse sent from SA node to atria causing R.
and L. Atrium to contractand L. Atrium to contract– Impulse also sent to AV node (atrioventricular)Impulse also sent to AV node (atrioventricular)

Conduction Conduction systemsystem
AV nodeAV node– Located in the base of the Right Atrium near Located in the base of the Right Atrium near
the Septumthe Septum– Delays the impulse slightly which allows atria Delays the impulse slightly which allows atria
to finish their contraction before the to finish their contraction before the ventricles begin their contractionventricles begin their contraction
Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of His)His)– In Septum (wall between R & L Ventricle)In Septum (wall between R & L Ventricle)– Carries from AV node through to Purkinje Carries from AV node through to Purkinje
Fibers located in the apex of the heartFibers located in the apex of the heart

Conduction Conduction systemsystem
Purkinje FibersPurkinje Fibers– Start at Apex (bottom of the heart)Start at Apex (bottom of the heart)– Relay impulse upward through the Relay impulse upward through the
ventricular wallsventricular walls– Cause ventricles to ContractCause ventricles to Contract

Regulation of Heart BeatRegulation of Heart Beat
Nervous system can speed up or Nervous system can speed up or slow down speed of heart beat slow down speed of heart beat depending on needdepending on need
What do you think the maximum What do you think the maximum beats per minute your heart is caple beats per minute your heart is caple of?of?

BLOODBLOOD

Composition of BloodComposition of Blood55% PLASMA- fluid portion of blood * similar to salt water
-90% water-10% dissolved salts, nutrients,
wastes,hormones ect…
45% SUSPENDED MATERIALS- “free floating” cells/platelets
*Red blood cells = ERYTHROCYTES-carry oxygen-oxygen attaches to hemoglobin
proteinproduced by these cells
*White blood cells = LEUKOCYTES-fight disease and foreign invaders
*platelets = THROMBOCYTES-blood clotting proteins (stop
bleeding)

How much blood does the average How much blood does the average adult have?adult have?
Interesting FactInteresting Fact
Blood cells are made in the bone marrow, the material in the center of the bones. The body will replenish the elements given during a blood donation – some in a matter of hours and others in a matter of weeks.

Antigens- substances, usually Antigens- substances, usually proteins, on surface of cells or proteins, on surface of cells or particles.particles.– Serve as “ID Cards” for living thingsServe as “ID Cards” for living things
Our Immune System will attack cells or Our Immune System will attack cells or particles that do not match cells our own particles that do not match cells our own bodybody
– Create ABo blood groupCreate ABo blood group– Also create Rh+/Rh- blood groupAlso create Rh+/Rh- blood group
Blood GroupingBlood GroupingKey TermKey Term

ABo Blood GroupingABo Blood Grouping
A antigens
ONLY
Bantigens
ONLY
A & B antigen
s
No antigen
s
Abo Groups and Blood Transfusions
Type A- may receive Type A or Type O Blood
Type B- may receive Type B or Type O Blood
Type AB- may receive Type A, Type B, Type AB or Type O Blood
Type O- may only receive Type O Blood

Rh FactorRh Factor Rhesus protein- may or may not be present Rhesus protein- may or may not be present
Rh Factor and Blood Transfusions
Rh+ individuals may receive Rh+ or Rh- blood
Rh- individuals may only receive Rh- blood

Who is a universal donor?Who is a universal donor?
Who is a universal recipient?Who is a universal recipient?

BloodBlood
Blood is 45% cells and 55% plasmaBlood is 45% cells and 55% plasma Blood Cells:Blood Cells:
1.1. Red Blood Cells: carry oxygenRed Blood Cells: carry oxygen
2.2. White Blood Cells: fight diseaseWhite Blood Cells: fight disease
3.3. Platelets: stop bleeding by scabbingPlatelets: stop bleeding by scabbing Blood Plasma:Blood Plasma:
– 90% water90% water– 10% nutrients and hormones10% nutrients and hormones

Blood VesselsBlood Vessels

Blood VesselsBlood Vessels
Vast network that keep the blood Vast network that keep the blood flowing in one directionflowing in one direction
1.1. Arteries and arteriolesArteries and arterioles- carry blood - carry blood awayaway from the heart. from the heart.
Arteries are large, muscular Arteries are large, muscular vessels. They are strong and elastic vessels. They are strong and elastic which allow them to stretch as blood which allow them to stretch as blood enters from the heart. enters from the heart.
2. 2. Arterioles are smaller and less muscular Arterioles are smaller and less muscular in size and turn into capillariesin size and turn into capillaries

Blood VesselsBlood Vessels3. Capillaries3. Capillaries – tiny blood vessels in – tiny blood vessels in
networks that allows exchange of networks that allows exchange of material through diffusion, between blood material through diffusion, between blood and cells in tissueand cells in tissue
4. Veinuoles4. Veinuoles- small blood vessels that - small blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood away from the carry deoxygenated blood away from the capillaries. They turn into veins.capillaries. They turn into veins.
5. Veins5. Veins- large blood vessels that carry - large blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood to the heart. Veins deoxygenated blood to the heart. Veins have valves which prevents blood from have valves which prevents blood from flowing backwards. flowing backwards.

Blood VesselsBlood Vessels
Capillary
VeinArtery

Blood PressureBlood Pressure
Blood pressure is a measure of the Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood on the force exerted by the blood on the wall of the arteries.wall of the arteries.– An example is 120/80 (systolic An example is 120/80 (systolic
pressure/diastolic pressure.pressure/diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the result of the Systolic pressure is the result of the
contraction of the ventricles (normal 110-contraction of the ventricles (normal 110-140)140)
Diastolic pressure is during the ventricle Diastolic pressure is during the ventricle relaxation (normal 70-90)relaxation (normal 70-90)

HypertensionHypertension
High Blood PressureHigh Blood Pressure– Stage 1 Systolic 140-159, Diastolic 90-Stage 1 Systolic 140-159, Diastolic 90-
9999
– Stage 2 Systolic 160+, Diastolic 100+Stage 2 Systolic 160+, Diastolic 100+