THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. Heart Veins Capillaries Arteries Circulatory System.
Circulatory System
-
Upload
nolan-moore -
Category
Documents
-
view
21 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Circulatory System

Circulatory SystemCirculatory System
““Getting Pumped”Getting Pumped”

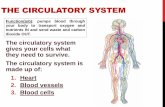
Parts of the Circulatory Parts of the Circulatory SystemSystem
Blood vesselsBlood vessels
1.1. ArteriesArteries
2.2. VeinsVeins
3.3. CapillariesCapillaries
Heart – “Double pump”Heart – “Double pump”

ArteriesArteries
Carry blood away from the heartCarry blood away from the heart Usually carry “oxygenated” blood (OUsually carry “oxygenated” blood (O22). ).
There is one exception to this rule.There is one exception to this rule. Muscular wall allows the vessel to Muscular wall allows the vessel to
constrict (get smaller) and dialate (get constrict (get smaller) and dialate (get bigger)bigger)
Usually found deep in the bodyUsually found deep in the body You can feel a pulse in an arteryYou can feel a pulse in an artery

ArteriesArteries

VeinsVeins
Carry blood towards the heartCarry blood towards the heart Usually carry “deoxygenated” blood Usually carry “deoxygenated” blood
(CO(CO22). ). There is one exception to this There is one exception to this rule.rule.
Walls are weaker than arteries. Walls are weaker than arteries. Veins contain valves that prevent blood Veins contain valves that prevent blood
from running backwards.from running backwards. Found close to the surface of the bodyFound close to the surface of the body Can’t feel a pulseCan’t feel a pulse

VeinsVeins

CapillariesCapillaries
Thinned walled blood vessels that Thinned walled blood vessels that join arteries to veins. join arteries to veins.
Gas exchange between blood and Gas exchange between blood and cells takes place through these cells takes place through these thinned walled vessels. (Othinned walled vessels. (O2 2 into into cells/COcells/CO22 into blood) into blood)

HeartHeart

HeartHeart

HeartHeart
Composed of Cardiac muscle tissueComposed of Cardiac muscle tissue Described as a “double pump”Described as a “double pump” Left side pumps oxygenated blood to all Left side pumps oxygenated blood to all
parts of the bodyparts of the body Right side pumps deoxygenated blood to Right side pumps deoxygenated blood to
the lungsthe lungs 4 chambers 4 chambers Top chambers – AtriaTop chambers – Atria Bottom chambers - Ventricles Bottom chambers - Ventricles

Explanation of HeartExplanation of HeartRight
Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Atrium
Left VentricleValves
The heart has 4 chambers:
2 on the top receive blood and 2 on the bottom pump the blood out
How does the heart pump?
What kind of blood
does each side
pump?
Which side of
the heart is thicker

ValvesValves
Atrioventricular valvesAtrioventricular valves – separate the – separate the atria from the ventricles.atria from the ventricles.
Left side – Bicuspid valve (Mitral)Left side – Bicuspid valve (Mitral) Right side – Tricuspid valveRight side – Tricuspid valve Aortic valve Aortic valve – found at the entrance of – found at the entrance of
the aorta (Semi-lunar valve)the aorta (Semi-lunar valve) Pulmonary valve Pulmonary valve – found at the – found at the
entrance to the pulmonary artery entrance to the pulmonary artery (Semi-lunar valve)(Semi-lunar valve)

Internal structureInternal structure

Blood vesselsBlood vessels
Aorta – largest artery in the bodyAorta – largest artery in the body Exits the left ventricleExits the left ventricle Carries oxygenated blood to all parts Carries oxygenated blood to all parts
of the bodyof the body Vena Cava – large vein that returns Vena Cava – large vein that returns
deoxygenated blood to the right atriumdeoxygenated blood to the right atrium– ““Superior” – returns blood from the top of your Superior” – returns blood from the top of your
bodybody– ““Inferior” – returns blood from the lower parts Inferior” – returns blood from the lower parts
of the body of the body

Blood VesselsBlood Vessels
*Pulmonary Artery * *Pulmonary Artery * - carries - carries deoxygenated deoxygenated blood to the lungsblood to the lungs
Exits the right ventricleExits the right ventricle
*Pulmonary Vein* *Pulmonary Vein* - carries - carries oxygenatedoxygenated blood from the lungs to blood from the lungs to the left ventriclethe left ventricle

Pumping actionPumping action
Pumping animation
The heart makes a “lub-dub” sound when The heart makes a “lub-dub” sound when it beatsit beats
The sounds come from valves closingThe sounds come from valves closing ““Lub” sounds when the ventricles contract Lub” sounds when the ventricles contract
and the AV valves closeand the AV valves close ““Dub” sounds when the atria contract and Dub” sounds when the atria contract and
the aortic and pulmonary valves contractthe aortic and pulmonary valves contract Circulatory systemCirculatory system

Blood pressureBlood pressure Average blood pressure = 110/70Average blood pressure = 110/70 First number – First number – Systolic PressureSystolic Pressure Represents the pressure exerted by your Represents the pressure exerted by your
heart during each contractionheart during each contraction Measured in mm of Hg (mercury)Measured in mm of Hg (mercury)
Second number – Second number – Diastolic PressureDiastolic Pressure Represents the pressure exerted by your Represents the pressure exerted by your
blood inside your blood vessels in between blood inside your blood vessels in between contractions.contractions.
Blood pressureBlood pressure

Heart AttackHeart Attack Most heart attacks are caused by Most heart attacks are caused by
blockages (cholesterol) in the coronary blockages (cholesterol) in the coronary arteries that feed oxygen to the cardiac arteries that feed oxygen to the cardiac muscle tissue.muscle tissue.
A heart attack causes sections of your A heart attack causes sections of your heart muscle to die.heart muscle to die.
The first indication of blockage might be The first indication of blockage might be Angina Angina – chest pain sometimes – chest pain sometimes misdiagnosed as heart burnmisdiagnosed as heart burn
Pain in the left arm may also be presentPain in the left arm may also be present Preventative procedures can help you Preventative procedures can help you
avoid a heart attackavoid a heart attack

Preventative proceduresPreventative procedures
Angioplasty – animationAngioplasty – animation
Bypass – animationBypass – animation
Aneurysm - animationAneurysm - animation

Electrical Circuitry of the Electrical Circuitry of the HeartHeart
Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) – Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) – collection of nerve fibers found in the collection of nerve fibers found in the right atrium.right atrium.
- called the “pacemaker” of the heart- called the “pacemaker” of the heart - stimulates the atria to contract - stimulates the atria to contract and and
stimulates the AV node stimulates the AV node

Electrical Circuitry of the Electrical Circuitry of the HeartHeart
Atrioventricular Node (AV node) Atrioventricular Node (AV node) - once stimulated by the SA node, it - once stimulated by the SA node, it
causes the ventricles to contract causes the ventricles to contract
Electrical circuitryElectrical circuitry

Electrocardiogram (ECG) Electrocardiogram (ECG)
P wave – indicates the contraction of the atriaP wave – indicates the contraction of the atria QRS wave – indicates the contraction of the QRS wave – indicates the contraction of the
ventriclesventricles T wave – indicates the recovery phase as the heart T wave – indicates the recovery phase as the heart
prepares for the next contraction prepares for the next contraction

ECGECG
Inverted T waveInverted T wave
Flatline!Flatline!