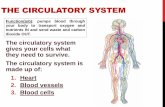
Organ Systems The circulatory system The circulatory system.
Circulatory System
-
Upload
acza-jaimee-kalaw -
Category
Science
-
view
62 -
download
1
Transcript of Circulatory System
- 1. THE HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEM
2. SING -ALONG WARNING: THOSE WHO WILL NOT SING WILL GROW OLD ALONE!!! 3. THE HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEM CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 4. BY GROUP MANILA PAPER K W H What do you know What I want to know How will I learn? NOTE: INDIVIDUAL K-W-H SHOULD ALSO BE WRITTEN IN YOUR CATTLEYA 5. GROUP WORK Trace the pathway of blood from the lungs to the heart to every part of the body by creating an illustration. Note the Oxygen rich blood and Carbon dioxide rich blood by indicating color. Red- O2 rich blood; Blue-CO2 rich blood 6. GUIDE QUESTIONS. a. How do the heart and the lungs work together? b. What takes place in the alveoli when you inhale and exhale? c. What does blood deliver to every part of the body? d. Why is oxygen important to your body? e. How will you describe the circulation of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and blood in your body? 7. GRAPHIC ORGANIZER BY GROUP Complete the concept map that will organize their thoughts about the Circulatory System NOTE: INDIVIDUAL GRAPHIC ORGANIZER SHOULD ALSO BE WRITTEN IN YOUR CATTLEYA 8. POINT OF DISCUSSION PARTS AND FUNCTIONS HEART BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD CIRCULATION FROM THE LUNGS TO THE HEART- TO OTHER ORGAN SYSTEM FROM OTHER ORGAN SYSTEM TO THE HEART- TO THE LUNGS PUMPING MECHANISM 9. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM is the main cooling and transportation system for the human body 10. The body has about 5 LITERS OF BLOOD continuously traveling through it by way of the Circulatory System 11. 13 12. PARTS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM HEART BLOOD VESSEL BLOOD 13. THE HEART PUMPS BLOOD THROUGH MUSCLE CONTRACTION 14. 16 15. THE BLOOD VESSELS NETWORK OF BLOOD PATHWAYS IN THE BODY 16. 18 A.ARTERIES- contains oxygenated blood B.VEINS- contains deoxygenated blood C.CAPILLARIES THE BLOOD VESSELS 17. THE BLOOD CARRIES THE MATERIALS (OXYGEN & NUTRIENTS AS WELL AS WASTE PRODUCTS) THROUGHOUT THE BODY 18. 20 19. BLOOD CIRCULATION 20. PULMONARY CIRCULATION (lungs) CORONARY CIRCULATION (heart) SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION (the rest of the systems processes). 21. The oxygen and CO2 are exchangedin the cells Oxygen Rich Oxygen Rich Oxygen Poor Oxygen Poor TISSUE HEMOGLOBIN in the blood cells let go of the cells oxygen because of the large CO2 (waste) count in the tissue. GAS EXCHANGE OCCURS 22. TRANSACT The oxygen the blood cells are carrying is given to the bodys tissue. And the CO2 (waste) from the tissue is given to the same blood cell to be exhaled. Tissue Tissue HOW IT WORKS Oxy-Rich Blood Cell Oxy-Poor Blood Cell Hemoglobin has an affinity for whichever gas has a greater count. 23. THE PUMPING MECHANISM 24. capillaries 25. THE STORY OF YOUR HEART INTERPRET THE DIAGRAM, AND WRITE A STORY OF HOW IT WORKS TO KEEP YOU ALIVE. FOCUS ON A. MOVEMENT OF BLOOD IN AND OUT OF YOUR HEART B. BLOOD WITH OXYGEN C. BLOOD WITH CARBON DIOXIDE 26. 28 27. This organ is what pumps oxygen rich blood, nutrients, hormones, and the other things your body needs to maintain your health, to your organs and tissues. The pulmonary veins you see on the right side of the diagram come from your lungs, where the blood cells collect oxygen. Its then pumped out to the rest of the body through the Aorta (Top). 28. All of the blue sections show blood cells carrying waste, (C02) moving back to the lungs (where the C02 will be replaced by oxygen) through the Pulmonary Artery (Top, blue) Whenever the blood is pumped from one section of the heart another a valve closes behind it preventing the blood from moving backwards. 29. BLOOD FLOW THROUGH HEART