Cholesterol
description
Transcript of Cholesterol

Cholesterol & Fat

Cholesterol & Fat
FAT - FACTSFat have a greasy, oily, or waxy consistency, composed of fatty acids
1. Saturated Fatty Acid
2. Monounsaturated
3. Polyunsaturated
Fatty Acids
• Saturated fats are solid at room temperature
• Found in animal fat – milk fat, butter, red meat
• Plant Origin – Coconut and Palm Oils
• Cashew nut
• Unsaturated Fats are soft or liquid
• Polyunsaturated fats will stay in Liquid Form
• Mono-unsaturated fats will become viscous

Cholesterol & Fat
Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Omega – 3 & Omega 6
• Omega - 3
• Found in fish oils – mackerel, tuna, salmon, sardines
• Walnuts, Soya, pumpkin Seeds, and Olives
• Fish Oil reduce Blood Triglycerides
• Anti-Clogging Effect
• Anti-Inflammatory Properties
• Good Vision
• Hormone Production
• Joint Flexibility
• Lower the risk of Alzheimer’s Disease

Cholesterol & Fat
• Omega - 6 Polyunsaturated Fat
• Linolenic Acid found – Vegetable oil – corn oil, safflower and soya bean
• Corn Oil, Cotton Seed Oil, Safflower oil, Sunflower Oil, Soya Bean Oil are Polyunsaturated.
• They prevents clotting
• Relax blood vessels
• Lower blood pressure
• Maintain water balance in the body
• Decrease pain and inflammation
• Improve immune system
• Help insulin to work

Cholesterol & Fat
Mono-Unsaturated Fats : Found in Olive and Canola Oils
• Olive Oil
• Lower the incidence of Heart disease
• Brain Function – Mood controlling brain chemical, Serotonin
• Pregnancy – Omega 3 and Omega 6 for Foetal Brain development
• Decrease Triglycerides, LDH and Increase HDL
• Weight Loss – Increase Metabolic Rate – Heat Production – Energy – Burn more calories
• Skin – Vitamin E

Cholesterol & Fat
Major Food Sources of Trans Fat
Cakes, Cookies, crackers, pies bred, etc
40%
Animal Products 21%Candy 1%
Breakfast Cereal 1%
Salad dressing 3%
Household shortening 4%
Potato Chips, corn chips, popcorn 5%
Fried potato 8%
Margarine 17%

Cholesterol & Fat
Function of Dietary Fats
• Source of Heat and Energy
• Add Flavour and Palatability to diet
• Furnish Essential Fatty Acids
• Spare Burning of Proteins for Energy
• Slow Digestive Process
• Serve as carrier of Fat Soluble, Vitamin A, D, E & K
• Insulate and Control Body Temperature

Cholesterol & Fat
Cholesterol: is a waxy, fat like substance classified as Lipid- found in every cell of human body
• To digest Fat
• To Strengthen Cell Membrane
• To Manufacture Hormones
• Vitamin D
• Bile ( Digestive Juice)
• Skin Oils
• Nerve and Brain Cell Sheath
It is used by the body

Cholesterol & Fat
• Body’s richest concentration of cholesterol is in the
Brain
• Liver and to some extend small intestine make all the
cholesterol that we need
• 1000 mg of Cholesterol is Manufactured in a day
• Cholesterol and other fats in the body cannot dissolve
in the blood
• Transported by the Special Carrier’s of Lipids and
Proteins – Lipoproteins
• Two important ones are – low density Lipoprotein and
High – Density Lipoprotein
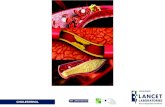
Cholesterol

Cholesterol & Fat
• Major Carrier of Cholesterol in the blood
• LDL Cholesterol have little protein and high levels of cholesterol
• LDL Cholesterol can slowly build up within the walls of arteries while feeding the Heart and Brain - Plaque
• Later causes arteries to harden – “Atherosclerosis”
• Plaque can block the flow of blood and oxygen to heart
• If enough blood and Oxygen cannot reach your heart – suffer chest pain
• When blood supply to a portion of the heart is completely cut off by blockage – Heart Attack
• When blood and oxygen to the brain is cut off-Stroke
• Hence LDL Cholesterol is also known as “Bad Cholesterol”
Low Density Lipoprotein (Bad Cholesterol)

BLOCKAGE OF THE BLOCKAGE OF THE ARTERYARTERY

Cholesterol & Fat
• Carries away bad cholesterol from
the cell and tissue back to Liver
• Hence know as Good Cholesterol
• Has a powerful Anti-oxidant
properties
• It block the oxidation of LDL
Cholesterol
• HDL has lot of Protein and Very
little Cholesterol
High Density Lipoproteins – Good Cholesterol

Cholesterol & Fat
• Over the age of 20, should get their cholesterol level checked at least once every 5 years
What are the symptoms of High Cholesterol?
When to Check for Cholesterol?
• Does not cause any Symptoms
Total CholesterolTotal Cholesterol 150 – 250 mg %150 – 250 mg %
H. D. L.H. D. L. 20 – 60 mg %20 – 60 mg %
L. D. L.L. D. L. Up to 150 mg %Up to 150 mg %
TriglycerideTriglyceride 30 – 180 mg %30 – 180 mg %
NORMAL VLUES

Cholesterol & Fat
Total CholesterolTotal Cholesterol CategoryCategory
Less than 200Less than 200 DesirableDesirable
200 – 239200 – 239 Border LineBorder Line
240 and above240 and above HighHigh
LDL CholesterolLDL Cholesterol CategoryCategory
Less than 100Less than 100 OptimalOptimal
100 - 129100 - 129 Near OptimalNear Optimal
130 -159130 -159 Border Line HighBorder Line High
Bad Cholesterol Level
160 - 189160 - 189 HighHigh
190 and Above190 and Above Very HighVery High
HDL Cholesterol - Above 35 mg / dlHDL Cholesterol - Above 35 mg / dl
Triglyceride - 150 – 199 HighTriglyceride - 150 – 199 High

Cholesterol & Fat
• Main Goal is to lower LDL and raise HDL
• Eat a Heart – Healthy Diet
• Take Cholesterol Lowering Medication
• Goals for Lowering LDL based on the number of risk factors for Heart Disease
• If you have 0-1 Risk factor for Heart Disease – Low to moderate risk – life style change recommended.
• 2 or more risk factors – Moderate risk-life style change with cholesterol lowering drugs
• If you have known heart disease, diabetes or multiple risk factors – High Risk
How is High Cholesterol Treated?

Cholesterol & Fat
• Statins
• Niacin
• Bile Acid Resins
• Fibric Acid Derivatives
Cholesterol Lowering Drugs
Side Effects of Cholesterol Lowering Drugs• Muscle Aches
• Abnormal Liver Function
• Allergic Skin Reaction
• Heart Burn
• Dizziness
• Abdominal Pain
• Constipation
• Decreased Sexual Desire

Cholesterol & Fat
Uncontrollable Risk Factors• Positive Family History of Heart Disease
• Male Sex > 45 years
• Post-menopausal > 55 years
• Older Age
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Controllable Risk Factors• Smoking
• Hypertension
• Diabetes Mellitus
• Sedentary Habit
• Obesity (More than 20% over ones ideal body weight)
• High LDL and Low HDL
• Uncontrollable Stress and Anger
• Increased Plasma Homocysteine Level

Cholesterol & Fat
Prevention of Ischemic Heart Diseaseo Check cholesterol level and be sure it is normal
o Check B.P. regularly, and if high, take treatment
o Diabetes should be treated and brought under control
o Stop Smoking
o Do regular aerobic exercise and brisk walking
o Stick to healthy diet rich in fish, vegetable, fruits, and low in fat
o Maintain an ideal body weight
o Do not indulge in excess of alcohol
o If you are a post-menopausal women consider hormone replacement therapy
o Dietary supplementation of folic acid in combination with Vitamin B6, vitamin B-12, if the plasma homocystene level is high