Chapter Twelve Communicating Customer Value: Advertising, Sales Promotion, and Public Relations.
Transcript of Chapter Twelve Communicating Customer Value: Advertising, Sales Promotion, and Public Relations.

Chapter Twelve
Communicating Customer Value: Advertising, Sales Promotion, and
Public Relations

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-2
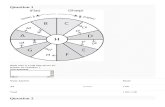
The Marketing Communications (Promotion) Mix
Advertising Sales Promotion Public Relations Personal Selling Direct Marketing

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-3
New Communications Realities
Mass markets have fragmented, leading to a shift away from mass marketing.
Improvements in information technology are speeding movement toward segmented marketing.
These factors have shifted the marketing communications model. – Less broadcasting– More narrow casting

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-4
Integrated Marketing Communications
Using IMC, the company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communication channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its brands.– Several factors influence the choice of
promotional tools.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-5
Advertising
Can reach masses of geographically dispersed buyers.
Can repeat a message many times. Is impersonal, one-way communication. Can be very costly for some media
types.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-6
Personal Selling
Involves personal interaction between two or more people.
Most effective tool at building preferences, convictions and actions.
Allows relationship building. Most expensive promotion tool;
requires long-term commitment.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-7
Sales Promotion
Wide assortment of tools. Attracts consumer attention. Offers strong incentives to buy. Invites and rewards quick consumer
response. Effects are short-lived.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-8
Public Relations
Very believable. Reaches people who avoid salespeople
and ads. Can dramatize a company or product. Tends to be used as an afterthought. Planned use can be effective and
economical.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-9
Direct Marketing
Many forms that share four primary characteristics:– Nonpublic– Immediate– Customized– Interactive
Well suited to highly targeted marketing.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-10
Promotion Mix Strategies
Push Strategy– Producer directs its marketing activities
toward channel members to induce them to carry the product and promote it to the final consumers.
Pull Strategy– Producer directs its marketing activities
toward final consumers to induce them to buy the product.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-11
Advertising
Advertising has been used for centuries. U.S. advertisers spend more than $264 billion
each year; worldwide spending approaches $550 billion.
Advertising is used by:– Business firms– Nonprofit organizations– Professionals– Social agencies– Government

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-12
Major Advertising Decisions
1. Setting advertising objectives
2. Setting the advertising budget
3. Developing advertising strategy
4. Evaluating advertising campaigns

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-13
1. Setting Advertising Objectives
Advertising Objective:– specific communication task to be
accomplished with a specific target audience during a specific period of time.
Classified by Purpose:– Inform– Persuade– Compare– Remind

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-14
2. Setting the Advertising Budget
Affordable method Percentage-of-sales method Competitive-parity method Objective-and-task method

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-15
Sales Promotion
Sales promotion consists of short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sales of a product or service.
The idea behind sales promotion is to generate immediate sales.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-16
Rapid Growth of Sales Promotion
Sales promotion can take the form of consumer, business, trade, or sales force promotions.
Rapid growth in the industry has been achieved because:– Product managers are facing more pressure to
increase their current sales– Companies face more competition– Advertising efficiency has declined– Consumers have become more deal oriented

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-17
Consumer Promotion
Objectives:– Increase short-term sales – Help build long-term market share
Many tools exist which can help to achieve these objectives.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-18
Consumer Sales Promotion Tools
Patronage rewards Point-of-purchase
displays Demonstrations Contests Sweepstakes Games
Samples Coupons Cash refunds Price packs Premiums Advertising
Specialties

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-19
Public Relations
Public Relations – building good relations with the firm’s
various publics by obtaining favorable publicity, building up a good corporate image, and handling or heading off unfavorable rumors, stories, and events.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-20
Public Relations Functions
Press relations or press agency Product publicity Public affairs Lobbying Investor relations Development

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-21
Public Relations Role & Impact
May strongly impact public awareness at a lower cost than advertising.
Results can be spectacular. Beginning to play an increasingly
important brand-building role.

Copyright 2007, Prentice Hall, Inc. 12-22
Public Relations Tools
Audiovisual materials
Corporate identity materials
Public service activities
Company Web site
News Speeches Special events Buzz marketing Mobile marketing Written materials