Chapter 8. Energy Intake Energy Output Energy Equilibrium Positive Energy Balance Negative Energy...
-
Upload
cornelius-spencer-montgomery -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 8. Energy Intake Energy Output Energy Equilibrium Positive Energy Balance Negative Energy...

Chapter
8

•Energy Intake
•Energy Output
•Energy Equilibrium
•Positive Energy Balance
•Negative Energy Balance


Increasing Increasing Prevalence of Prevalence of Obesity in U.S. Obesity in U.S. AdultsAdults

Regulation of intake◦ Hunger Prompts eating; physiological desire
◦ Satiation Signals to stop eating
◦ Satiety Lack of hunger
◦ Appetite Psychological desire


A Cascade of Regulation: HungerAppetiteSatiation and Satiety

Diet Composition Gastrointestinal Sensations Temperature Neurological and Hormonal Factors Environmental and Social Factors


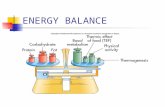
1. Maintain basic physiological functions: breathing, blood circulation, etc.
2. To power physical activity3. To process food you eat

Major components of energy expenditure◦Resting energy expenditure (REE)
Energy for basic body functions Affected by body size, composition, age, gender
◦Physical activity Highly variable Affected by body size, fitness level, type of activity
◦Thermic effect of food (TEF) Energy to digest, absorb, metabolize food


Components of Energy ExpenditureComponents of Energy Expenditure

Fever* Stress Total body weight Smoking * Caffeine High Lean Body Mass Rapid growth Hot & cold ambient
temp Pregnancy, lactation Hyperthyroidism Large body surface
area
Aging Female Fasting/Starvation Sleep Hypothyroidism

Estimating REE from body weight, gender, and age
Estimating Total energy expended from REE and physical activity
Harris-Benedict equation◦ w: 655.1 + 9.56 (wt:kg) + 1.85(ht:cm) - 4.68
(age:yrs)◦ m: 66.47 + 13.75 (wt:kg) = 5.0 (ht:cm) - 6.76
(age:yrs) RDA for energy

Estimating REE from body weight, sex and age:REE for female, age 18-30= (14.7 x weight (kg)) + 496wt=130 lbs..=59 kg = (14.7 x 59) + 496 =1363Harris-Benedict equation655.1 + 9.56 (kg) + 1.85 (cm) - 4.68 (yrs)655.1 + 9.56 (59) + 1.85 (167.64) - 4.68 (22)655.1 + 564 + 310 - 103=1426REE x activity level = total energy expenditureREE x 1.3-1.45 (light activity level) = 1363 x 1.3-1.45 = 1771-1976 = 1800-2000 kcals1426 x 1.3-1.45 = 1853-2067 = 1850-2050 kcals
RDA (women age 19-50) = 2,200 kcals (wt. of 121 lbs.)



Assessing body weight◦ Height-weight tables◦ Men: 106 lbs + 6 lbs per inch◦ Women: 100 lbs. + 5 lbs per inch◦ Body mass index (BMI)
Weight (kg) height2 (m)

Definitions◦ Overweight: BMI between 25-30◦ Obesity: BMI > 30◦ Underweight: BMI < 18.5
Health risks of overweight and obesity◦ Heart disease and stroke◦ Hypertension --Gallbladder disease◦ Diabetes ---Sleep apnea◦ Cancer ◦ Osteoarthritis




Women = 20-25% Men = 12-20% Underwater (or hydrostatic) weighing BodPod Skinfold thickness Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis DEXA

Average Body Average Body CompositionComposition


Visceral Fat and Subcutaneous Fat

Android◦ greater health risk◦ high blood lipids, glucose
intolerance, insulin resistance, and high blood pressure
Gynoid Waist circumference
◦ assess abdominal fatness◦ BMI 25-34.9, waist >40 inches
in men and > 35 inches in women is sign of increased health risk


Early theories of weight regulation◦ Fat cell theory
Obesity increases number and size of fat cells◦ Set point theory
Influences on weight gain and obesity◦ Heredity and genetic factors◦ Sociocultural influences◦ Age and lifestyle factors◦ Gender and ethnicity◦ Socioeconomic factors◦ Psychological factors




Weight management is the adoption of healthful and sustainable eating and exercise behaviors indicated for reduced disease risk and improved feelings of energy and well-being

Perception of weight Setting realistic goals Weight management lifestyle
◦ Diet and eating habits Reduce total calories Reduce fat calories Increase complex carbohydrates Improve eating habits
◦ Increase physical activity◦ Stress management◦ Self-acceptance


Weight management approaches◦Self-help books and manuals
Watch for signs of a fad diet
◦Self-help groups◦Commercial programs◦Professional counselors◦Prescription drugs◦OTC drugs and dietary supplements
◦Surgery

Obesity Promoting EnvironmentObesity Promoting Environment

Fitness Promoting EnvironmentFitness Promoting Environment

15
Medications
• Sibutramine (Meridia); www.4meridia.com
• Orlistat (Xenical); www.xenical.com
• Metformin (Glucophage); Bristol Myers-Squibb; glucophage.com


22
GastricBypass

Prefer sweets?
3 Hershey's Kisses Brand Special Dark Chocolate, 60 calories1 package Original Apple Nature Valley Fruit Crisps, 50 calories1 Late July Organic Dark Chocolate Sandwich Cookie, 50 calories 1 Hostess 100 Calorie Pack: Chocolate Cupcake, 100 calories30 plain M&M's, 100 calories (one Fun Size packet)1 package Back to Nature Honey Graham Sticks, 120 calories12 gummi bears, 120 calories1/2 banana rolled in 1 tbsp frozen semisweet chocolate chips, 123 calories1/3 cup dried fruit, 134 calories3 Oreos, 160 calories1 McDonald’s Fruit 'n Yogurt Parfait, 160 calories

Want a savory snack?5 olives (any kind), 45 calories1 small Martin's pretzel, 50 calories2 oz Applegate Honey and Maple Turkey Breast wrapped
around 2 bread-and-butter pickles, 80 calories1/4 cup hummus and 3 carrot sticks, 80 calories1 Laughing Cow Light Swiss Original wedge, 3 pieces Kavli Crispy Thin, 85 calories 1 oz buffalo mozzarella, 1/2 cup cherry or grape tomatoes, 94 calories1 cup unshelled edamame, 120 calories50 Eden's Vegetable Chips, 130 caloriesOne 1-oz package of Planters NUT-trition almonds, 130
calories15 Terra Blues Potato Chips, 130 calories1/2 cup pumpkin seeds in shell, 143 calories2 pieces (30 grams) prosciutto, 4 dried figs, 154 calories

Definition◦ BMI < 18.5
Causes and assessment◦ Illness◦ Eating disorders◦ Metabolic factors
Weight-gain strategies◦ Small, frequent meals◦ Fluids between meals◦ High-calorie foods and beverages

WebMD: http://www.webmd.com/diet/evaluate-latest-diets
Weight Watchers No diet just life