Chapter 7 - Deliver
21
© 2007 Pearson Education 14-1 Supply Chain Operation DELIVER
-
Upload
erum-anwer -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
4
description
Supply chain management
Transcript of Chapter 7 - Deliver
Chopra 2nd Edition, Chapter 14Limiting the distribution to only one
intermediary in the territory
Intensive distribution
Distribute from as many outlets as possible to provide location convenience
Selective distribution
*
When a single outlet is given an exclusive franchise to sell the product in a geographic area, the arrangement is referred to as exclusive distribution
© 2007 Pearson Education
Example of Exclusive Distribution
Products such as specially automobiles, some major appliances, certain brands of furniture eg IKEA,
© 2007 Pearson Education
Enhance product’s image & allow higher markups
Promotes dealers loyalty, better forecasting, better inventory and merchandising control
Restricts resellers from carrying competing brands
*
Betting on one dealer in each market
Only suitable for high price, high margin, and low volume products
© 2007 Pearson Education
Example of Intensive Distribution
Intensive distribution is appropriate for products such as chewing gum, candy bars, soft drinks, bread, film, and cigarettes where the primary factor influencing the purchase decision is convenience
© 2007 Pearson Education
Disadvantages:
Characteristically low price and low-margin products that require a fast turnover
Difficult to control large number of retailers
Intensive Distribution
© 2007 Pearson Education
Selective distribution may be used for product categories such as clothing, appliances, televisions, stereo equipment, home furnishings, and sports equipment.
© 2007 Pearson Education
More control and less cost than intensive distribution
Concentrate effort on few productive outlets
*
May not cover the market adequately
Difficult to select dealers (retailers) that can match your requirement and goals
© 2007 Pearson Education
investment decisions
operating policies
Costs considerations:
Trip-related: labour and fuel
supply chain design
transportation mode choice
Cost considerations:
Facility: e.g. warehouse operating costs
Processing: loading/unloading, invoicing, etc.
Responsiveness; Delivery guarantees
© 2007 Pearson Education
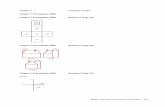
Direct Shipment with Milk Runs
Delivery from single supplier to several retailers
Central Distribution Centre (DC)
Central Distribution Centre with Milk Runs
Tradeoffs? Number and location of DC’s?
© 2007 Pearson Education
© 2007 Pearson Education
Choice of transportation mode
© 2007 Pearson Education
Choice of Transportation Mode
A manager must account for inventory costs when selecting a mode of transportation
A mode with higher transportation costs can be justified if it results in significantly lower inventories
© 2007 Pearson Education
Tailored Transportation
The use of different transportation networks and modes based on customer and product characteristics
Factors affecting tailoring:
Role of IT in Transportation
The complexity of transportation decisions demands to use of IT systems
IT software can assist in:
Identification of optimal routes by minimizing costs subject to delivery constraints
Optimal fleet utilization
Risk that the shipment is delayed
Risk of disruptions
Alternative routings
In case of hazardous materials the use of modified containers, low-risk transportation models, modification of physical and chemical properties can prove to be effective
© 2007 Pearson Education
Design a transportation network that can handle
e-commerce
Intensive distribution
Distribute from as many outlets as possible to provide location convenience
Selective distribution
*
When a single outlet is given an exclusive franchise to sell the product in a geographic area, the arrangement is referred to as exclusive distribution
© 2007 Pearson Education
Example of Exclusive Distribution
Products such as specially automobiles, some major appliances, certain brands of furniture eg IKEA,
© 2007 Pearson Education
Enhance product’s image & allow higher markups
Promotes dealers loyalty, better forecasting, better inventory and merchandising control
Restricts resellers from carrying competing brands
*
Betting on one dealer in each market
Only suitable for high price, high margin, and low volume products
© 2007 Pearson Education
Example of Intensive Distribution
Intensive distribution is appropriate for products such as chewing gum, candy bars, soft drinks, bread, film, and cigarettes where the primary factor influencing the purchase decision is convenience
© 2007 Pearson Education
Disadvantages:
Characteristically low price and low-margin products that require a fast turnover
Difficult to control large number of retailers
Intensive Distribution
© 2007 Pearson Education
Selective distribution may be used for product categories such as clothing, appliances, televisions, stereo equipment, home furnishings, and sports equipment.
© 2007 Pearson Education
More control and less cost than intensive distribution
Concentrate effort on few productive outlets
*
May not cover the market adequately
Difficult to select dealers (retailers) that can match your requirement and goals
© 2007 Pearson Education
investment decisions
operating policies
Costs considerations:
Trip-related: labour and fuel
supply chain design
transportation mode choice
Cost considerations:
Facility: e.g. warehouse operating costs
Processing: loading/unloading, invoicing, etc.
Responsiveness; Delivery guarantees
© 2007 Pearson Education
Direct Shipment with Milk Runs
Delivery from single supplier to several retailers
Central Distribution Centre (DC)
Central Distribution Centre with Milk Runs
Tradeoffs? Number and location of DC’s?
© 2007 Pearson Education
© 2007 Pearson Education
Choice of transportation mode
© 2007 Pearson Education
Choice of Transportation Mode
A manager must account for inventory costs when selecting a mode of transportation
A mode with higher transportation costs can be justified if it results in significantly lower inventories
© 2007 Pearson Education
Tailored Transportation
The use of different transportation networks and modes based on customer and product characteristics
Factors affecting tailoring:
Role of IT in Transportation
The complexity of transportation decisions demands to use of IT systems
IT software can assist in:
Identification of optimal routes by minimizing costs subject to delivery constraints
Optimal fleet utilization
Risk that the shipment is delayed
Risk of disruptions
Alternative routings
In case of hazardous materials the use of modified containers, low-risk transportation models, modification of physical and chemical properties can prove to be effective
© 2007 Pearson Education
Design a transportation network that can handle
e-commerce

















![Chapter 7 [Chapter 7]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/61cd5ea79c524527e161fa6d/chapter-7-chapter-7.jpg)
