Chapter 7-2Cell Structure and Function Image from: © Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson...
-
Upload
leonard-pope -
Category
Documents
-
view
298 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 7-2Cell Structure and Function Image from: © Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson...

Chapter 7-2Cell Structure and Function
Image from: © Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall; All rights reserved
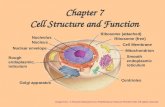
NucleolusNucleus
Nuclear envelope
Ribosome (attached)Ribosome (free)
Cell Membrane
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Smooth endoplasmicreticulum
Centrioles

Image from: http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_membrane.html
A CELL is . . . made of MOLECULES
_______ ___________ ___________ATOMS MOLECULES ORGANELLES

1. All living things are made of _____________.2. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in an organism
(= basic unit of __________)3. New cells are produced from _________________ cells
CELL THEORY CELL SIZE
___________ cells > _________ cells > _____________
Cells
lifeexisting
PLANT ANIMAL BACTERIA

ALL LIVING THINGS ARE MADE OF CELLSCells __________ a _____________ ORORGANELLES surroundedby _______________
= ________________
WITHOUTNUCLEUS
MEMBRANES
Cells __________ a NUCLEUS ANDORGANELLES surroundedby MEMBRANES
= _________________
WITH
PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES
http://www.earthlife.net/prokaryotes/welcome.html
http://summit.k12.co.us/schools/shs/computer/tkelley/types.html
Bacterial Cell

CELL MEMBRANE(also called plasma membrane)
Cell membranes are made mainly of ________________ & __________________ PHOSPHOLIPIDS PROTEINS
Outsideof cell
Insideof cell(cytoplasm)
Cellmembrane
Proteins
Proteinchannel Lipid bilayer
Carbohydratechains
Image from: © Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall; All rights reserved

LIPID TAILS ARE HYDROPHOBIC
HYDROPHILIC
HYDROPHOBIC
Image by Riedell

Oil and water don’t mix!
Image from: http://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch112/lipids/micbilayer.gif

PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
Image from: http://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch112/lipids/micbilayer.gif
SEE HOW MEMBRANES FORMScroll down to animation

CELL MEMBRANE
Proteins that stick on the surface = _____________(either inside or outside of cell)
Proteins that stick INTO membrane = ________________(can go part way in or all the way through)
PERIPHERAL
INTEGRAL

Recognize “self”
GLYCOPROTEINS
GLYCOPROTEINS are PROTEINS with carbohydrates attached
Image from: http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/Michael.Gregory/files/Bio%20101/Bio%20101%20Lectures/Membranes/membrane.htm

TRANSPORT PROTEINShelp move substances across the cell membrane
Animations from: http://bio.winona.edu/berg/ANIMTNS/facdifan.gif
http://www2.uic.edu/~myilma1/ionchannel.gif
More on this in Chapter 7-3

WHAT DOES IT DO?
Acts as a boundaryControls what enters and leaves cell
Images from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/cellmembrane.html http://www.mccc.edu/~chorba/celldiagram.htm

Cell membranes MOVE!
Molecules in cell membranes are
constantly moving and changing
Animation from: http://www.sp.uconn.edu/~terry/images/anim/fluidmem.gif
Click here to seeFluidityAnimation

CYTOPLASM (Between nucleus and cell
membrane)
ORGANELLE-small structure with a specific function (job)
Image from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/cytoplasm.html
Image from: http://faculty.stcc.cc.tn.us/jiwilliams/labprojectsmenu.htm
Organelles suspended in gel-like goo

HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as LIPID ________________ with POLAR heads facing _______ & NON-POLAR tails facing ________
CELL MEMBRANE (PLASMA MEMBRANE)
Made mainly of ____________________ and _________________
MEMBRANE PROTEINS• ____________________- stick on inside or outside surface• ____________________- go part way or all the way through• _________________ - recognize “self” • _______________ PROTEINS- move molecules across membrane
Membranes are _________________________________(=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others
out ___________ what enters & leaves cell
Helps with _________________
__________________ = gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell membrane
GLYCOPROTEINS
phospholipids proteins
BILAYER outin
SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE
cytoplasm
CONTROLS
FUNCTION:
HOMEOSTASIS
TRANSPORT
PERIPHERALINTEGRAL

NUCLEUS
Largest organelle
in animal cells
Image from: http://www.mccc.edu/~chorba/celldiagram.htm

NUCLEUS
Surrounded by NUCLEAR ENVELOPE
(also called NUCLEAR MEMBRANE)
DOUBLE MEMBRANE
Image from: http://www.agen.ufl.edu/~chyn/age2062/lect/lect_06/5_11.GIF

NUCLEUS
NUCLEAR PORES Openings to allow molecules to move in and out of nucleusImage from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html

WHAT DOES IT DO?Contains genetic material (DNA)
DNA is spread out as CHROMATINin non-dividing cells
DNA is scrunched up as CHROMOSOMES
in dividing cells

WHAT DOES IT DO?
Control center of cellImage from:
Genetic code tells the cell’s parts what to do
Image from: http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/12-dna.htm

NUCLEOLUS
Dark spot in nucleus = __________
Makes RNA for ribosomes
Image from: http://lifesci.rutgers.edu/~babiarz/histo/cell/nuc3L.jpg
NUCLEOLUS

NUCLEUS NUCLEOLUSSurrounded by ______________ MEMBRANE called the NUCLEAR __________________ ___________ CENTER OF CELL Nuclear ___________ allow molecules in & out CONTAINS CELL’S GENETIC MATERIAL (_______) Dark spot = NUCLEOLUS
makes ___________________ (RNA) DNA is scrunched up as ______________ in dividing cells.DNA is spread out as ________________ in non-dividing cells.
ENVELOPE
PORESCONTROL
DNA
RIBOSOMES
CHROMOSOMES
CHROMATIN
DOUBLE

CYTOSKELETON• Helps cell maintain
shape
• Help move organelles around
Made of PROTEINS:
MICROFILAMENTS (Actin) & MICROTUBULES (Tubulin)
Image from: http://anthro.palomar.edu/animal/default.htm
Image from: © Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall; All rights reserved

CYTOSKELETONMade of PROTEINS called______________ & _________________
FUNCTION: ____________________________________________________________
MICROTUBULES MICROFILAMENTS
Helps cell maintain shape; Support; Helps in movement

CENTRIOLES
Appear during cell division to guide chromosomes apart

CENTRIOLES/MITOTIC SPINDLE
Made of MICROTUBULES (Tubulin)
Image from: http://www.coleharbourhigh.ednet.ns.ca/library/organelle_worksheet.htm

CENTRIOLESMICROTUBULES
ANIMAL
Made of __________________________
Only seen in _______________ cells during cell division
Function:__________________________________guide chromosomes apart;

MITOCHONDRION (plural=MITOCHONDRIA
)
Look like “little sausages”
Image from: http://instructional1.calstatela.edu/dfrankl/CURR/kin150/Images/mitochondria.jpg

MITOCHONDRIA
Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane
Folded inner membrane increases surface areafor more chemical reactions
Image from: http://www.biologyclass.net/mitochondria.jpe
Has its own DNA

MITOCHONDRIA
Come from cytoplasm in EGG
You inherit your mitochondria from your mother!
http://www.wappingersschools.org/RCK/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/p14%5b1%5d.jpg

WHAT DOES IT DO?
Burns glucose to release energy
Stores energy as ATP
“Powerplant of cell”
Images from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/mito.html
http://www.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookCHEM2.html
Image by: Riedell

MITOCHONDRION (pl. MITOCHONDRIA) Surrounded by _____________ membrane Contains its own ___________ _______________ of cell Burns ____________ Stores energy released as ______
Folded inner membrane = _________________ (increases surface area for more chemical reactions)
DOUBLE
DNAPower plant
GLUCOSEATP
CRISTAE

RIBOSOMES
• Made of PROTEINS and RNA
• Protein factory for cellJoin amino acids to make proteins
Image from: http://www.ust.hk/roundtable/hi-tech.series/1_b1.jpg
Image by: RIedell

RIBOSOMES
Can be attached to Rough ER
OR
free in cytoplasm
Image from: http://www.mccc.edu/~chorba/celldiagram.htm
Image from: http://www.biologyclass.net/endoplasmic.jpe

RIBOSOMESCan be __________________ or __________ to Rough ER
MADE OF ______________ & ________
FUNCTION: _____________________
FREE in cytoplasm ATTACHED
PROTEINS RNA
MAKE PROTEINS

ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
2 KINDS:SMOOTH or ROUGH
Network of hollow membrane tubules
Image from: http://www.agen.ufl.edu/~chyn/age2062/lect/lect_06/5_10B.GIF

ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (Rough ER)
Makes membrane proteins and proteins for export out of cell
Image from: http://www.biologyclass.net/endoplasmic.jpe
Animation from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/er.html

ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
• Has RIBOSOMESattached
• Proteins are made on ribosomes and inserted into Rough ER to be modified and
transportedImage from: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/cells/ER.jpg

SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (smooth
ER)
• Has NO ribosomes attached
• Has enzymes for special tasks
Image from: http://www.science.siu.edu/plant-biology/PLB117/JPEGs%20CD/0073.JPG

SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (smooth
ER)Image from:http://www.accs.net/users/kriel/chapter%20eight/smooth%20er.gif
• Makes membrane lipids (steroids) • Regulates calcium (muscle cells) • Destroys toxic substances (Liver)

ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
ROUGH ER SMOOTH ER (with ribosomes) (no ribosomes)
Internal Network of ___________________ Rough ER: Attached ribosomes make _________________ which are modified and transported to Golgi for export
Smooth ER:
Makes membrane lipids (__________________) Regulates ________________ in muscles
Breaks down _________________ in liver
PROTEINS
STEROIDS
CALCIUM
TOXINS
MEMBRANES

GOLGI APPARATUS (BODY)• Pancake
like membrane stacks
Modify, sort, & packagemolecules from ERfor storage OR transport out of cell
Image from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/golgi.h
Image from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/golgi.h
Image from: http://www.rsbs.anu.edu

Animation from: http://www.franklincollege.edu/bioweb/A&Pfiles/week04.html
See a Golgi movie

GOLGI APPARATUS (BODY)Looks like a “______________________”Made of ______________________
FUNCTION: Modify, sort, & package substances from ER for ______________ or_______________ out of cell
stack of pancakesmembranes
exportstorage

LYSOSOMES
Membrane bound sacs that contain PROTEINScalled digestive enzymes
Animation from: http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/lysosomes.html
Digest food, unwanted molecules, old organelles, cells, bacteria, etc

LYSOSOMES
Image modified from: http://www.people.virginia.edu/~rjh9u/lysosome.html
See lysosomes in action:

LYSOSOMES
Image from: http://www.people.virginia.edu/~rjh9u/lysosome.html
See LYSOSOMEMOVIE

http://www.mgm.ufl.edu/images/bharfe/image3.jpghttp://research.yale.edu/ysm/images/78.3/articles-apoptosis-cells.jpg
“PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH” = ______________________APOPTOSIS
Lysosomes help digest unwanted cells
See animation

Apoptosis plays a role in:
Embryonic developmentNormal body cell
maintenance Immune system responses
CancerAIDS infectionTransplant rejection
http://www.cellsalive.com/apop.htm

LYSOSOMES
Sac containing _________________________
FUNCTION: Digests __________________________________
Plays a role in ____________“Programmed cell death”Cell suicide for the good of the organism
Digestive enzymes
food molecules & unwanted cells/cell parts;
APOPTOSIS

FLAGELLA & CILIA
Made ofPROTEINS called MICROTUBULES
(9 + 2 arrangement)
Image from: http://www.stchs.org/science/courses/sbioa/metenergy/flagella.jpg

FLAGELLA
Help in cell movement

CILIA
Move cell itself
Animation from: http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/13-cells.htm

CILIA
Move substances past cells
http://www.sk.lung.ca/content.cfm?edit_realword=hwbreathe

CILIA• Many• short
FLAGELLA•Few•Long
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
Animation from: http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/13-cells.htm

CILIA & FLAGELLAMade of PROTEINS called _______________organized in a _________ arrangement that help with ___________________
CILIA =________ & __________
FUNCTION: ______________________
________________________________
FLAGELLA =______ & ________
FUNCTION: _________________
MICROTUBULES
9 + 2MOVEMENT
MANY SHORT
move cells; move substances past cells
FEW LONG
Move cells

WHAT’S SPECIAL ABOUT PLANT CELLS?
• Cell wall• HUGE vacuoles• Chloroplasts• No centrioles
Plant vs Animal cells

CELL WALLSupports and
protects cell
Outside of cell membrane
Made of carbohydrates & proteins
Plant cell walls are mainly _____________CELLULOSE
http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/13-cells.htm
http://www.windows.ucar.edu/kids_space/images/brick_wall.jpg

CELL WALLFound OUTSIDE the ____________________Provides ____________ & ________________
___________________ makes plant cells sturdy Bacteria have cell walls made of _______________ instead.
Cell membrane
SUPPORT PROTECTION
CELLULOSE
PEPTIDOGLYCAN

VACUOLES
Storage space
Image from: http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/plant_cell.gif
http://library.thinkquest.org/3564/Cells/cell93.gif

VACUOLES
• Storage space for WATER, salts, proteins (enzymes), carbohydrates, and waste
Vacuoles SMALL in ANIMAL CELLSNO VACUOLES IN BACTERIA
Image from: http://www.metoliusfriends.org/csca/images/tupperware.jpg

Contractile vacuoles control excess water in cells
(HOMEOSTASIS)
1
http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/imgjun99/vidjun1.gif

VACUOLESStorage space for: _______________Proteins, carbohydrates,
water, waste
Huge in __________cells , small in _____________ cells,Not in _________________
plantanimalbacteria

CHLOROPLASTS
• Use energy from sunlight to make own food (glucose)
http://stallion.abac.peachnet.edu/sm/kmccrae/BIOL2050/Ch1-13/JpegArt1-13/04jpeg/04-28_chloroplasts_1.jpg
http://www.seorf.ohiou.edu/~tstork/compass.rose/photosynthesis/chloro_sun_bathing.gif

CHLOROPLASTS
• Surrounded by DOUBLE membrane
• Contains own DNA
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_campbell_essentials_2/cipl/04/HTML/source/04-17-chloroplast-nl.htm
•Thylakoid membrane sacs contain enzymes for photosynthesis

CHLOROPLASTSurrounded by ____________ membrane Has own ________ _____________ =membrane sacs inside
Contain CHLOROPHYLL where _______________________ happens
FOUND ONLY IN _____________ CELLS
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
DOUBLE
DNATHYLAKOIDS
PLANT

Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Nuclearenvelope
Ribosome(attached)
Ribosome(free)
Smooth endoplasmicreticulum
Nucleus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Cell wall
CellMembrane
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells

WHAT’S DIFFERENT ABOUT BACTERIAL CELLS?
• Cell wall • NO NUCLEAR
MEMBRANE• DNA is circular• No membrane
bound organelleshttp://www.eurekascience.com/ICanDoThat/bacteria_cells.htm See video

BACTERIA have a CELL WALL BUT…
IT’S MADE OF DIFFERENT MOLECULES
than plant cell walls!
_______________ NOT CELLULOSE!
More on this in Chapter 18!
Image from: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/procaryotes/images/procaryote.jpg
PEPTIDOGLYCAN

WHICH IS BIGGER?
_________ > _____________ > ___________Plant cell Animal cell bacteria

DIFFERENCES IN ANIMAL CELLS, PLANT CELLS, AND BACTERIA
ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL BACTERIA
Eukaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes
Cell membrane Cell membrane Cell membrane
Nuclear membrane
Nuclear membrane
NO nuclear membrane
NO cell wall Cell wall made of
CELLULOSE
Cell wall made ofPEPTIDOGLYCAN
Has ribosomes Has ribosomes Has ribosomes
DNA in multiple chromosomes
DNA in multiple chromosomes
DNA is a single circular ring
CYTOSKELETON CYTOSKELETON CYTOSKELETON
Small vacuoles Really big vacuole
NO vacuoles
Has lysosomes Has lysosomes NO lysosomes
Has centrioles NO centrioles NO centrioles
NO chloroplasts Chloroplasts NO chloroplasts
SMALLER SMALL SMALLEST

BACTERIA arePROKARYOTES
PLANTS & ANIMALSare EUKARYOTES
No membrane bound organelles
Organelles with membranes

USE WORDS FROM THE WORD BANKS TO COMPLETE THE VENN DIAGRAM COMPARISON


















![Nucleolus vs Nucleus Count for Identifying Spiral Ganglion ... · contain one nucleus (mean diameter: 10 µm) that has a nucleolus inside it (mean diameter: 2.5 µm) [30]. The counting](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/603a23d2e81ba752bc5c64b2/nucleolus-vs-nucleus-count-for-identifying-spiral-ganglion-contain-one-nucleus.jpg)
