Chapter 6SectionMain Menu Price per slice Equilibrium Point Finding Equilibrium Price of a slice of...
-
Upload
madeleine-tyler -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 6SectionMain Menu Price per slice Equilibrium Point Finding Equilibrium Price of a slice of...

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
Pri
ce
pe
r s
lic
e
Equilibrium Point
Finding Equilibrium
Price of a slice
of pizza
Quantity demanded
Quantity supplied
Result
Combined Supply and Demand Schedule
$ .50 300 100
$3.50
$3.00
$2.50
$2.00
$1.50
$1.00
$.50
Slices of pizza per day
050 100 150 200 250 300 350
Supply Demand
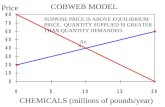
The point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied come together is known as equilibrium.
$2.00
$2.50
$3.00
150
100
50
250
300
350
Surplus from excess supply
$1.50 200 200 Equilibrium
Equilibrium Price
a
Eq
uili
briu
m
Qu
an
tity
$1.00 250 150
Shortage from excess demand
Balancing the Market

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
If the market price or quantity supplied is anywhere but at equilibrium, the market is in a state of disequilibrium
Interactions between buyers and sellers will always push the market back towards
equilibrium.
Market Disequilibrium
Excess Demand
• occurs when quantity demanded is more than quantity supplied.
Excess Supply
• occurs when quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
In some cases the gov steps in to control prices.
Price Ceilings
• A price ceiling is a max price that can be legally charged for a good.
• An example of a price ceiling is rent control, a situation where a government sets a maximum amount that can be charged for rent in an area.
@&$#
@&$#

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
Price Floors
• A price floor is a minimum price, set by the gov, that must be paid
• One price floor is the minimum wage, which sets a minimum price that an employer can pay a worker

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
Shifts in Demand• Excess Demand
– A shortage is a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
• Search Costs
– Search costs are the financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when searching for a good or service.
• A Fall in Demand
– When demand falls, suppliers respond by cutting prices, and a new market equilibrium is found.

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
$800
$600
$400
$200
0
Pri
ce
Output (in millions)
Graph A: A Change in Supply
1 2 3 4 5
Analyzing Shifts in Supply and Demand
• Graph A shows how the market finds a new equilibrium when there is an increase in supply.
• Graph B shows how the market finds a new equilibrium when there is an increase in demand.
Original supply
Demand
a
New supply
b
c
Graph B: A Change in Demand
Output (in thousands)
$60
$50
$40
$30
$20
$10
0
900800700600500400300200100
Pri
ce
Supply
Original demand
a
New demand
c
b

Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
Signals
Think of prices as a traffic light.
Red - low price telling producers to make less.
Green - high price telling producers to make more
Spillover costs, or externalities, are costs of production, such as air and water pollution, that “spill over” onto people who have no control over how much is produced.
Advantages of Prices