Chapter 5 - Precision. Accuracy and Tolerance
description
Transcript of Chapter 5 - Precision. Accuracy and Tolerance

SPA204/Appendix 6.0 /Notes PRECISION, ACCURACY AND TOLERANCE
Exact Value and Nearest Value
Exact Value Nearest Value
Obtain when we start counting.
Known as discrete quantity (Kuantiti diskret)
Example:1. Number of student in a
classroom.2. Number of pencils in a
box.3. Number of chairs in
stadium.4. Number of fans in an artist
concert.
Obtain when we start measuring.
Known as (Kuantiti selanjar)
Example:1. Height of a student.2. Length of highway in
Malaysia.3. Areas of a classroom.4. Volume of water in a
bottle.5. Depth of a hole.
Precision and Tolerance
Precision: The ability of measuring equipment taking reading consistently every time measurement
was made. Precision of measuring equipment depends on the smallest unit available on that
equipment. < Unit available > precise the measuring equipment. To determine the preciseness of measuring equipment repeated readings should be
taken. Precision also determined by looking at relative deviation. < Relative deviation > precise the measuring equipment.
Relative deviation = Mean deviation x 100% Mean reading
Tolerance: The probability of the largest error in a measurement. Half of the different between largest measurements with smallest measurements.
Tolerance = ½ (Largest measurement – smallest measurement) = ½ (Upper limit – lower limit)= ½ (Smallest measurement unit)
Tolerance specification = (Measurement + Tolerance)Upper Limit, Lower Limit and Tolerance Range
Kolej Komuniti Kepala Batas, Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysia Prepared by: Rosiadi Bin Tajudin

SPA204/Appendix 6.0 /Notes PRECISION, ACCURACY AND TOLERANCE
Upper limit: Largest value of a measurement
(Measurement quantity + Tolerance)
Lower limit: Smallest value of a measurement
(Measurement quantity – Tolerance)
Tolerance range = (Upper limit – Lower limit)
Accuracy
The ability of measuring equipment taking exact reading as in real value. The accuracy of measuring equipment is determined by the smallest unit available on
that equipment. It also determined by errors value (Ralat) in which < errors > exact the value given by
measuring equipment.
Errors = (Real measurement – Obtainable measurement)
Conclusion
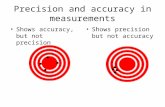
Precision and accuracy of measuring equipment can be simplified as on figure below.
Class Activity (Examples and exercise)
Kolej Komuniti Kepala Batas, Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysia Prepared by: Rosiadi Bin Tajudin
Dart board
Centre
Dart
> Precise, < accuracy < Precise, > accuracy > Precise, > accuracy

SPA204/Appendix 6.0 /Notes PRECISION, ACCURACY AND TOLERANCE
Examples
1. Identify the quantity below as exact value or nearest value.a. Amount of curtains.b. Length of 50 chairs arrange in a rows.c. Number of books in a book shelves.d. Height of a building in a town.e. Areas of a mosque.
2. The table below show the mass of nails in gram obtained after four times reading.
Num. of reading Nails mass (gm)1 4.02 3.73 4.24 3.9
Get the relative deviation for the above readings to determine the precision of measuring equipment used.
3. Given, diameter of a ball is between 3.54cm and 3.60cm, what is its tolerance.
4. Given, length of a wood is 10 cm. what is its,a. Toleranceb. Largest valuec. Smallest value andd. Tolerance range
5. Determine the preciseness for 2 rulers by differentiate its relative deviation for the readings taken as shown on table below.
Num. of reading Ruler A Ruler B1 29.8 30.02 30.1 30.53 30.0 29.84 29.9 28.95 30.2 31.1
6. Calculate largest errors allowed for each value below and get its tolerance specification.a. 3.5 m ≤ Width ≤ 3.6 mb. 1.5 km ≤ Distance ≤ 1.6 kmc. 14.25 cm2 ≤ Areas ≤ 14.56 cm2
7. Calculate the tolerance, upper limit, lower limit and tolerance range for each measurement:
Kolej Komuniti Kepala Batas, Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysia Prepared by: Rosiadi Bin Tajudin

SPA204/Appendix 6.0 /Notes PRECISION, ACCURACY AND TOLERANCE
a. Length = 15 cmb. Mass = 10.5 gmc. Temprature = 32.0 oC
8. Given, 4 ≤ m ≤ 8 and 6 ≤ n ≤ 13, what is its,a. Maximum value for m + nb. Minimum value for m + nc. Maximum value for n – md. Minimum value for n – m
9. Given, s = 4cm and t = 8 cm, what is,a. Maximum value for s + tb. Minimum value for s + tc. Maximum value for t – sd. Minimum value for t – s
Exercise
Kolej Komuniti Kepala Batas, Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysia Prepared by: Rosiadi Bin Tajudin

SPA204/Appendix 6.0 /Notes PRECISION, ACCURACY AND TOLERANCE
1. Identify the quantity below as exact value or nearest value.a. Number of pages in a book.b. Volume of a water tank.c. Highway length.d. Weight of a box.
2. The table below show diameter of a ball obtained after 5 readings taken. What is the relative deviation for that reading.
Num. of reading Diameter (cm)1 2.142 2.133 2.174 2.155 2.17
3. Given diameter of a cylinder is 5.05 cm. what is its,a. Toleranceb. Largest valuec. Smallest value andd. Tolerance range
4. The weight of an apple is between 120.34 g and 120.50 g, what is its tolerance.
5. Given, 3 ≤ x ≤ 5 and 15 ≤ y ≤ 45, what is its,a. Maximum value for x + yb. Minimum value for x + yc. Maximum value for y – xd. Minimum value for y – x
6. Given, a = 20 cm and b = 5 cm, what is,a. Maximum value for a + bb. Minimum value for a + bc. Maximum value for a – bd. Minimum value for a – b
Kolej Komuniti Kepala Batas, Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysia Prepared by: Rosiadi Bin Tajudin