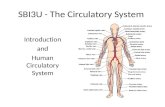
The Circulatory System The Circulatory System Refresh your memory….
Chapter 4-The Circulatory System By Sophie Block B.
-
Upload
buddy-alexander -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Chapter 4-The Circulatory System By Sophie Block B.

Chapter 4-The Circulatory SystemBy Sophie
Block B

The Body’s Transportation SystemSection 1

Moving Materials• Circulatory System carries needed
materials to cells and gets rid of any waste products from cell.
• Also, disease fighting blood cells are transported around to kill disease causing micro-organisms.

The Heart
• Pumps blood• Two upper chambers=atria, two lower
chambers=ventricle
RA
RV LV
LA

Heartbeat• Pacemaker is a group of cells located
in the Right Atrium.• Pacemaker is constantly adjusting
the heart rate to match oxygen needs.
• Exercise=higher heart rate• Artificial pacemakers can replace the
pacemaker if it is damaged.

The Pathway of Blood From the Heart
• Loop #1-– HeartLungsHeart1. Flows into Right Atrium2. Little oxygen, more carbon dioxide3. Blood travels to lungs through arteries4. Comes in contact with capillaries that are close to lungs5. Becomes oxygen rich
• Loop #2-– HeartBlood vessels in bodyHeart1. Blood moves in from left ventricle2. Pumped into Aorta (largest artery)3. Comes in contact with capillaries where oxygen is given to
cells, and carbon dioxide is exchanged

A Closer Look at Blood VesselsSection 2

Arteries• When blood leaves heart, it travels through
arteries.• Coronary arteries carry blood to heart• Each artery branches into smaller arteries• Arteries are very thick• Pulse=a spurt of blood the heart sends through
the arteries• Muscles in the middle wall of artery are
involuntary.– When they contract opening becomes smaller, when
they relax, opening becomes smaller

Capillaries• Materials are exchanged between
blood and body’s cells in Capillaries• Walls are one cell thick• One way the materials are
exchanged is diffusion.

Veins• Veins=larger blood vessels• Have 3 layers like arteries, but are
thinner• Heart has less effect; Contraction of
skeletal muscles moves blood through veins
• Larger veins also have valves that keep from flowing backwards and force blood to heart

Blood Pressure• “Pressure is a force that something
exerts over a given area” pg. 110 in textbook.
• Blood pressure is when ventricles contract.
• Blood flowing in arteries has the most pressure
• Blood pressure is measured with momanometer.

Blood and Lymph
Section 3

Plasma• Materials travel in Plasma• Transports: molecules from broken down
food, vitamins and minerals, chemical messages, wastes from cell processes
• Protein molecules give yellow color• Three groups of plasma proteins– 1-regulates amount of water– 2-helps fight disease– 3- works with platelets to create blood clots

Red and White Blood Cells• Red Blood Cells
– Red blood cells take the oxygen in the lungs– Look like pinched disks– Can bend and twist easily– Made mostly of hemoglobin, a protein containing iron
that mixes with oxygen molecules– Have no nulceus
• White Blood Cells – Fight disease– Fewer than red blood cells– Bigger than red blood cells– Live longer than red blood cells

Platelets• Cell fragments that help produce blood clots• When cut, platelets stick to the vessel where
the wound is• Release chemicals that begin a chain
reaction• After a while, reactions produce chemical
called fibrin• All the platelets and blood cells eventually
get caught in a “net” that creates a blood clot

Blood Types• Figured out types of blood that are tolerated
by original type are the only way for a transfusion to work
• Four types- A, AB, B, O• Type determined by markers on red blood cells• Intolerable types of blood are forced into
clumps that can clog capillaries
❀
Blood Type Intolerable Types
Can be received in transfusion
A B A and OAB N/A AllB A B and OO A and B O

The Lymphatic System• Network of vessels like veins that
returns fluid to bloodstream• While fluid is in lymphatic system,
it’s called lymph• Lymph contains: water, dissolved
materials, some white blood cells• Lymph nodes filter lymph

Cardiovascular Health
Section 4

Cardiovascular Disease• Atherosclerosis= when an artery wall
thickens because of fatty build-up• Can happen in coronary arteries
which can lead to the heart receiving less blood and oxygen, causing a heart attack

Hypertension• Hypertension=high blood pressure• Normal blood pressure-140/90• Makes heart work harder• Heart and arteries can be damaged
badly

Keeping Your Cardiovascular System Healthy
• Eat a good diet• Exercise!• Don’t Smoke!!!!!
All of these will prevent atherosclerosis