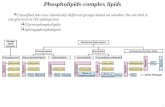
Chapter 4 Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipid - amphipathic molecule.
-
Upload
samantha-thornton -
Category
Documents
-
view
242 -
download
15
Transcript of Chapter 4 Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipid - amphipathic molecule.

Chapter 4Membrane Structure and Function

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ULR79TiUj80&feature=player_embedded
Phospholipid - amphipathic molecule

Membrane Lipids - phospholipid & cholesterol
Membrane Proteins - integral & peripheral

FLUID• due to lipid content
• unsaturated fats = more fluidity• hydrocarbon tails wiggle; move laterally
Why don't phospholipid molecules flip laterally??
• cholesterol• keeps membrane from freezing at decreased temperatures• stiffens the membrane at increased temperatures

MOSAIC• due to protein content
• number and types of proteins vary
• proteins in no set position

Carbohydrates• glycolipids & glycoproteins
• only occur on outside surface
glycocalyx• protection• facilitates adhesion between cells• reception of signaling molecules• cell-to-cell recognition




Aquaporins


DIFFUSION
physical process due to the random motion of particles

OSMOSISwater moves from an area of HIGH water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of LOW water concentration (high solute concentration)


Tonicity - the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Osmotic Pressure - measure of difference in solute concentrations; force needed to stop osmotic flow
Hydrostatic Pressure - pressure of the cytoplasm pushing against the plasma membrane


cytolysiscrenation
plasmolysisturgor pressure



Maintaining Osmotic Balance
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4z98WIeNtjM


Active Transport• needs ATP• moves UP the concentration
gradient• uses highly selective protein
carriers


Cotransport

Endocytosis and Exocytosis

Exocytosis• vesicle fuses with plasma membrane =
secretion• Plants - export materials to construct
cell wall• Animals - secrete hormone,
neurotransmitters and digestive enzymes

Endocytosis• take in substances by vesicle formation• viruses, food, another cell, liquid
A is a bacterium
B is a WBC



EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX
• meshwork of proteins and polysaccharides • collagen resists stretching• elastin gives resilience• fibronectin (adhesive) binds to
integrin• integrin makes contact with
cytoskeleton - plays role in cell signaling
• proteoglycans help resist compression; play role in cell signaling


CELL JUNCTIONS• allows coordination of cells
• adhesive junctions• attach adjacent cells
• tight junctions• plasma membrane proteins attach to
each other
• gap junction• allows cells to communicate

Plasmodesmata• pass through cell wall• allows water and small solutes to pass
freely