Mixtures Unit 1: Measurement & Matter. 2 Categories of Matter Pure Substances Mixtures.
Chapter 3 Classification of Matter Objectives: Define and give examples of 3 states of matter (3.1 &...
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 3 Classification of Matter Objectives: Define and give examples of 3 states of matter (3.1 &...

Chapter 3Classification of
MatterObjectives:
Define and give examples of 3 states of matter (3.1 & 3.2)Distinguish between substances and mixtures (3.3 & 3.12)Understand what elements are (3.4-3.7)Distinguish between metals, nonmetals and metalloids (3.8)Define compounds and diatomic molecules (3.9 & 3.10)Be able to write chemical formulas (3.11)

What is Matter?What is Matter? Anything that has mass and occupies space
Composed of atoms Exists in three states on earth
Exists in fourth state in space

Solids Definite Particles tightly packed Crystalline –
Amorphous solids –

Liquids Definite volume Not a
Particles have Particles can

Gases Indefinite volume No Particles have
Particles


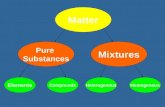
Substances and Mixtures Pure Substance: a particular kind of
matter with a definite, fixed composition
Mixture:

Matter
Pure substances (homogeneous composition)
Mixtures of two or more substances
Elements Compounds
Solutions (homogeneous
composition – one phase)
Heterogeneous mixtures
(two or more phases)
Figure 3.2 (page 48)

Types of Mixtures Heterogeneous mixtures
Chocolate chip cookies; granite
Homogeneous mixtures

Separating Mixtures Do NOT cause chemical
changes Heterogeneous Mixtures

Separating Mixtures Homogeneous Mixtures

Separating Mixtures Homogeneous Mixtures

Separating Mixtures Homogeneous
Mixtures

Pure Substances Elements
Compound

Elements ~111 presently known elements
At room temperature:
Figure 3.3 – distribution of elements in the

Elements Names of the elements
Greek Latin Location where discovered

Elements Arranged in the Periodic Table (inside
front cover) Symbols
Some symbols are Latin/Greek name (Table
3.4)

Elements Classification
Metal Nonmetal Metalloid
See Table 3.5

Elements Metals:
Usually solid at room temperature
High luster Malleable Usually don’t combine with each
other

Elements Nonmetals:
Solids ( ); Liquid ( ); Gases (all others)
Poor conductors
Low melting point; Will combine Will combine
Some found uncombined in nature

Elements Metalloids
Have properties of
Some used for semiconductors in electronics

Compounds Two or more elements
New properties Can be chemically
separated

Compounds Molecular
Held together with Molecule:
Water is an example

Compounds Ionic
Ion:
Cation – Anion –
Held together by ionic bond –

Compounds Diatomic Molecules
Always only 2 atoms 7 naturally occurring

Chemical Formulas Abbreviations for compounds Sodium Chloride (NaCl)

Chemical Formulas Subscript indicates # of
atoms present H2O has 2 Hydrogen atoms and 1
Oxygen atom NaOH has

Chemical Formulas Parentheses are used to show
when a compound contains more than one group of atoms that occurs as a unit

Chemical Formulas Show only number and kind
of atom Do not show arrangement of
the atoms or how chemically bonded