Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function. Animal Cell 1. cell (plasma) membrane – thin, transparent,...
-
Upload
ambrose-parker -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function. Animal Cell 1. cell (plasma) membrane – thin, transparent,...

Chapter 3
Cell Structure and Function

Animal Cell
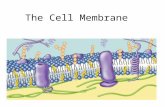
• 1. cell (plasma) membrane –
thin, transparent, 2-layered, semi-permeable
(porous), flexible
-controls what enters and leaves cell
-separates cell from its environment

2. nucleus –
command center of the cell; most cells have only one; some have >1
DNA:
a) chromatin – mass of fibers scattered
through the nucleus (thread-like)
b) chromosomes – compact chromatin
-direct & store instructions for all cell
functions
-control inheritance of traits

c) nuclear membrane –
2-layered, semi-permeable, porous,
surrounds nucleus
d) nucleolus – cell may have 1 or 2; produce
granules rich in RNA, each granule will
become part of a ribosome
e) nucleoplasm - fluid within the nucleus

* 3. cytoplasm – jelly-like fluid outside nucleus, but within cell -transports chemical substances within the cell
4. endoplasmic reticulum – network of interconnected membranes (ER)
-storage, separation, and transport of substances made within the cell (mostly proteins) a) rough ER – dotted with ribosomes b) smooth ER – no ribosomes

5. Golgi apparatus (body) – stack of flattened
membranes where proteins are packaged
and distributed
6. vacuole – clear, fluid-filled sac; used for
storage
7. lysosome – small sac filled with powerful
chemicals which break down food
molecules and digest old organelles;
surrounded by a membrane

8. mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell;
bean-shaped; one of the largest and most
numerous; site of cellular respiration
Cytoskeleton
9. microtubules – long, thin, hollow cylinders;
in cytoplasm, they support cell (shape) or
are arranged in bundles in other structures
(like cilia, flagella, or centrioles* - only in
animal cells)
10. microfilaments – tiny-threadlike fibers made
of protein; contract like muscle cells for
movement

11. ribosomes – tiny, round bodies involved
in protein synthesis from amino acids

Plant Cell
-have a cell wall composed of cellulose (provides structure and support)-contain chloroplasts – function in
photosynthesis (football shaped), starch granules – spherical, function in food storage, and carotens – contain orange pigments;
spherical-plant cells are rectangular in shape (animal
cells are spherical)-have a large water vacuole which provides
turgor pressure