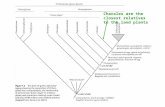
Chapter 26: The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants. Charophytes Green algae Closest ancestor to plants...
-
Upload
juniper-walton -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
4
Transcript of Chapter 26: The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants. Charophytes Green algae Closest ancestor to plants...

Chapter 26: The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants

Charophytes
• Green algae• Closest ancestor to plants• Evidence • Charales and Coleochaetes

Fig. 29-3
40 µm
5 mm Chara species, a pond organism
Coleochaete orbicularis, adisk-shaped charophyte thatalso lives in ponds (LM)

Features of Charophytes that promoted evolution of multicellular land plants
• 1) Cellulose synthesizing complexes nearly identical (during cell wall formation)
• 2) Apical cells – allow filaments to increase in length
• 3) Plasmodesmata – communication between neighboring cells
• 4) Both retain and care for zygote

Adaptations to Life on Land
• Cuticle– Waxy, aerial, prevents desiccation
• Stomata– Pores on surface of leaves, stems Gas exchange
• Gametangia– Multicellular sex organs– Embryo develops within female gametangium
(protected)

7 Characteristics of Plants
• Multicellular, eukaryotic• Photosynthetic• Waxy cuticle• Terrestrial• Stomata and guard cells• Complex fertilization• Cell walls of cellulose and lignin

Alternation of Generations• Switch between haploid and diploid– Both multicellular– Dominant generation
• Haploid (n) = gametophyte– Mitosis – haploid gametes– Antheridia – sperm– Archegonia - egg
• Diploid (2n) = sporophyte– Meiosis – haploid spores
• Zygote (sperm + egg) multicellular embryo (in archegonium)

Fig. 29-5b
EmbryoMaternal tissue
Wall ingrowths
Placental transfer cell(outlined in blue)
Embryo (LM) and placental transfer cell (TEM)of Marchantia (a liverwort)
2 µm
10 µm

Fig. 29-5a
Gametophyte(n)
Gamete fromanother plant
n
n
Mitosis
Gamete
FERTILIZATIONMEIOSIS
Mitosis
Sporen
n
2n Zygote
Mitosis
Sporophyte(2n)
Alternation of generations

• Fertilization zygote embryo mature sporophyte sporogenous cells meiosis spores mature gametophyte archegonia or antheridia egg/sperm

Check your Understanding
• 1. What are the benefits of a lands existence for plants?
• 2. What traits are shared by both charophytes and land plants?
• 3. What is the role of each generation in the alternation of generations life cycle?

4 Major Plant Groups
• Bryophytes– Small, nonvascular, seedless, use haploid spores
• Ferns– Seedless, vascular, spores
• Gymnosperms– Vascular, seeds (unprotected)
• Angiosperms– Vascular, flowering, seed in a fruit

Fig. 29-7
Origin of land plants (about 475 mya)1
2
3
1
2
3
Origin of vascular plants (about 420 mya)
Origin of extant seed plants (about 305 mya)
ANCES-TRALGREENALGA
Liverworts
Hornworts
Mosses
Lycophytes (club mosses,spike mosses, quillworts)
Pterophytes (ferns,horsetails, whisk ferns)
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Seed plantsSeedlessvascularplants
Nonvascular
plants(bryophytes)
Land plants
Vascular plants
Millions of years ago (mya)500 450 400 350 300 50 0

Mosses and other Bryophytes
• Nonvascular – so small• Mosses, liverworts, hornworts• Moist environment – growth and
reproduction• 3 phyla– Bryophyta– Hepaticophyta– Anthocerotophyta

Mosses - Bryophyta
• Dense colonies or beds• Individual plant– Rhizoids (absorb)– Upright, stem like– Leaf like blades
• No true roots, stems or leaves• Alternation of generations• 3 groups: peat moss, granite moss, true moss

Fig. 29-9d
Gametophyte
Seta
CapsuleSporophyte(a sturdyplant thattakes monthsto grow)
Polytrichum commune,hairy-cap moss

Fig. 29-8-3
Key
Haploid (n)Diploid (2n) Protonemata
(n)
“Bud”
“Bud”
Malegametophyte(n)
Femalegametophyte (n)
Gametophore
Rhizoid
Spores
Sporedispersal
Peristome
Sporangium
MEIOSIS SetaCapsule(sporangium)
Foot
Maturesporophytes
Capsule withperistome (SEM)
Femalegametophytes
2 m
m
Raindrop
Sperm
Antheridia
Egg
Archegonia
FERTILIZATION
(within archegonium)Zygote(2n)
Embryo
Archegonium
Youngsporophyte(2n)


Moss Gametophyte

Moss spores

Moss protonema

Fig. 29-9a
ThallusGametophore offemale gametophyte
Marchantia polymorpha,a “thalloid” liverwort
Marchantia sporophyte (LM)
Sporophyte
Foot
Seta
Capsule(sporangium)
500
µm

Moss importance
• Ecological– Form soil, prevent erosion– Rainforest beauty
• Commercial – Peat moss (sphagnum)• Absorb and hold water• Soil conditioner – add to sand• Fuel source – if dried

Fig. 29-11a
(a) Peat being harvested

Liverworts - Hepaticophyta
• Dominant gametophyte• Thallus – body – flattened, lobed– No leaves, stems, roots– Resemble lobes of liver– Underside – rhizoids – anchor– No stomata – some surface pores
• Others – Leafy liverworts – no lobes

THALLOID Liverwort

Fig. 29-9b
Plagiochiladeltoidea,a “leafy”liverwort

Basics of liverwort life cycle
• Sexual - Similar to mosses• Asexual– Form gemmae in gemmae cup

Hornworts - Anthocerotophyta
• Inconspicuous thalloids• Disturbed habitats – fallow fields, roadsides• Cell structure – single chloroplast• Sporophyte projects out of thallus like horn

Fig. 29-9c
An Anthoceroshornwort species
Sporophyte
Gametophyte


Lycophytes: Vascular Tissue
• Seedless vascular plants– Stems, roots, leaves
• Conducting cells• Lignin • Cooksonia = rhyniophyte• Microphylls• Club mosses

Club mosses - Lycophyta
• Coal deposits• True roots, rhizomes, aerial stems– Short, erect branches
• Evergreen

Fig. 29-15a
Lycophytes (Phylum Lycophyta)
Selaginella apoda,a spike moss
Isoetesgunnii,a quillwort
Strobili(clusters ofsporophylls)
2.5 cm
Diphasiastrum tristachyum, a club moss1 cm

Lycophyte

CYU
• 1. Name two features of lycophytes significant to the evolution of land plants.

Seedless Vascular Plants – Pterophyta (Pteridophytes)
• Ferns, horsetails, whisk ferns• Adaptations– Vascular – xylem and phloem• Support• Conduction• larger
– Most – true roots, stems, leaves– Megaphylls

Ferns
• Most abundant – warm, tropics• True roots, stems, leaves• Fronds

Fig. 29-15f
Athyriumfilix-femina,lady fern
25 c
m

Fig. 29-13-3
Key
Haploid (n)Diploid (2n)
MEIOSISSporedispersal
Sporangium
SporangiumMaturesporophyte(2n)
Sorus
Fiddlehead
Spore(n)
Younggametophyte
Maturegametophyte(n) Archegonium
Egg
Antheridium
Sperm
FERTILIZATIONNewsporophyte
Gametophyte
Zygote(2n)



Fern Sorus

Fern – Older sporangium

Fern germinating

Fern Gametophyte

CYU
• How is the life cycle of a fern different from the life cycle of a moss?

Whisk ferns - Psilotophyta
• Simplest vascular– Stems – • horizontal underground• Vertical aerial - photosynthesize
• Lack true roots, leaves• Dichotomous branching – stem divides into 2
equal halves

Fig. 29-15h
2.5
cm
Psilotumnudum,a whiskfern

Horsetails - Sphenophyta
• Ancient – coal deposits• Wet, marshy• True roots (rhizome), stems (aerial), small
leaves– Hollow, jointed stems – silica – gritty– Scouring rushes – pots/pans

Fig. 29-15g
Equisetumarvense,fieldhorsetail
Vegetative stem
Strobilus onfertile stem
1.5
cm

Horsetail

• Homospory – meiosis produces 1 type of spore• Heterospory – meiosis produces 2 different spore
types: microspores and megaspores• Microsporangia – produce microsporocytes
meiosis haploid microspores male gametophyte sperm cells in antheridia
• Megasporangia – make megasporocytes meiosis haploid megaspores female gametophyte eggs in archegonia

Fig. 29-UN3
Homosporous spore production
Sporangiumon sporophyll
Singletype of spore
Typically abisexualgametophyte
Eggs
Sperm
Eggs
Sperm
Heterosporous spore production
Megasporangiumon megasporophyll Megaspore Female
gametophyte
Malegametophyte
MicrosporeMicrosporangiumon microsporophyll

You should now be able to:
1. Describe four characteristics of plants2. Distinguish between the phylum Bryophyta and
bryophytes3. Diagram and label the life cycle of a bryophyte4. Explain why most bryophytes grow close to the
ground and are restricted to periodically moist environments

5. Explain how vascular plants differ from bryophytes
6. Distinguish between homosporous and heterosporous
7. Diagram and label the life cycle of a seedless vascular plant