Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematicszuhairusnizam.uitm.edu.my/phy094/03_LectureOutline … · ·...
-
Upload
duonghuong -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
4
Transcript of Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematicszuhairusnizam.uitm.edu.my/phy094/03_LectureOutline … · ·...

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 2
One-Dimensional Kinematics

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Units of Chapter 2• Position, Distance, and Displacement
• Average Speed and Velocity
• Instantaneous Velocity
• Acceleration
• Motion with Constant Acceleration
• Applications of the Equations of Motion
• Freely Falling Objects

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-1 Position, Distance, and Displacement
Before describing motion, you must set up a coordinate system –define an origin and a positive direction.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-1 Position, Distance, and Displacement
The distance is the total length of travel; if you drive from your house to the grocery store and back, you have covered a distance of 8.6 mi.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-1 Position, Distance, and Displacement
Displacement is the change in position. If you drive from your house to the grocery store and then to your friend’s house, your displacement is 2.1 mi and the distance you have traveled is 10.7 mi.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-2 Average Speed and Velocity
The average speed is defined as the distance traveled divided by the time the trip took:
Average speed = distance / elapsed time
Is the average speed of the red car 40.0 mi/h, more than 40.0 mi/h, or less than 40.0 mi/h?

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-2 Average Speed and Velocity
Average velocity = displacement / elapsed time
If you return to your starting point, your average velocity is zero.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-2 Average Speed and Velocity
Graphical Interpretation of Average Velocity
The same motion, plotted one-dimensionally and as an x-t graph:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
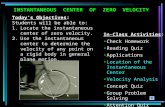
2-3 Instantaneous Velocity
Definition:
(2-4)
This means that we evaluate the average velocity over a shorter and shorter period of time; as that time becomes infinitesimally small, we have the instantaneous velocity.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-3 Instantaneous VelocityThis plot shows the average velocity being measured over shorter and shorter intervals. The instantaneous velocity is tangent to the curve.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-3 Instantaneous VelocityGraphical Interpretation of Average and Instantaneous Velocity

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-4 Acceleration
Average acceleration:
(2-5)

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-4 AccelerationGraphical Interpretation of Average and Instantaneous Acceleration:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-4 Acceleration
Acceleration (increasing speed) and deceleration (decreasing speed) should not be confused with the directions of velocity and acceleration:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-5 Motion with Constant Acceleration
If the acceleration is constant, the velocity changes linearly:
(2-7)
Average velocity:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-5 Motion with Constant Acceleration
Average velocity:
(2-9)
Position as a function of time:
(2-10)
(2-11)
Velocity as a function of position:
(2-12)

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-5 Motion with Constant AccelerationThe relationship between position and time follows a characteristic curve.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-5 Motion with Constant Acceleration

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-6 Applications of the Equations of MotionHit the Brakes!

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-7 Freely Falling Objects
Free fall is the motion of an object subject only to the influence of gravity. The acceleration due to gravity is a constant, g.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-7 Freely Falling Objects
An object falling in air is subject to air resistance (and therefore is not freely falling).

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2-7 Freely Falling Objects
Free fall from rest:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Chapter 2
• Distance: total length of travel
• Displacement: change in position
• Average speed: distance / time
• Average velocity: displacement / time
• Instantaneous velocity: average velocity measured over an infinitesimally small time

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Chapter 2• Instantaneous acceleration: average acceleration measured over an infinitesimally small time
• Average acceleration: change in velocity divided by change in time
• Deceleration: velocity and acceleration have opposite signs
• Constant acceleration: equations of motion relate position, velocity, acceleration, and time
• Freely falling objects: constant acceleration g = 9.81 m/s2

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 4
Two-Dimensional Kinematics

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Units of Chapter 4
• Motion in Two Dimensions
• Projectile Motion: Basic Equations
• Zero Launch Angle
• General Launch Angle
• Projectile Motion: Key Characteristics

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-1 Motion in Two Dimensions
If velocity is constant, motion is along a straight line:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-1 Motion in Two Dimensions
Motion in the x- and y-directions should be solved separately:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-2 Projectile Motion: Basic Equations
Assumptions:
• ignore air resistance
• g = 9.81 m/s2, downward
• ignore Earth’s rotation
If y-axis points upward, acceleration in x-direction is zero and acceleration in y-direction is -9.81 m/s2

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-2 Projectile Motion: Basic Equations
The acceleration is independent of the direction of the velocity:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-2 Projectile Motion: Basic Equations
These, then, are the basic equations of projectile motion:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-3 Zero Launch AngleLaunch angle: direction of initial velocity with respect to horizontal

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-3 Zero Launch Angle
In this case, the initial velocity in the y-direction is zero. Here are the equations of motion, with x0 = 0 and y0 = h:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-3 Zero Launch AngleThis is the trajectory of a projectile launched horizontally:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-3 Zero Launch AngleEliminating t and solving for y as a function of x:
This has the form y = a + bx2, which is the equation of a parabola.
The landing point can be found by setting y = 0 and solving for x:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-4 General Launch Angle
In general, v0x = v0 cos θ and v0y = v0 sin θ
This gives the equations of motion:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Solution page 91

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-4 General Launch AngleSnapshots of a trajectory; red dots are at t = 1 s, t = 2 s, and t = 3 s

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-5 Projectile Motion: Key Characteristics
Range: the horizontal distance a projectile travels
If the initial and final elevation are the same:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4-5 Projectile Motion: Key Characteristics
The range is a maximum when θ = 45°:

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Symmetry in projectile motion:
4-5 Projectile Motion: Key Characteristics

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Chapter 4
• Components of motion in the x- and y-directions can be treated independently
• In projectile motion, the acceleration is –g
• If the launch angle is zero, the initial velocity has only an x-component
• The path followed by a projectile is a parabola
• The range is the horizontal distance the projectile travels