Normal Probability Distributions. Intro to Normal Distributions the STANDARD Normal Distribution.
Chapter 2 Discrete Distributions - Youngstown State...
Transcript of Chapter 2 Discrete Distributions - Youngstown State...

Normal Distributions
1
1
The Normal Distribution
2
Normal Probability
Density Function
- < x <
Notation: N (, 2) A normal distribution with
mean and standard deviation
2
2
1
2
1)(
-
-
x
exf
The continuous random variable
X has a normal distribution if
its p.d.f. is
3
Normal Distribution
The mean, variance, and m.g.f. of a
continuous random variable X that has a
normal distribution are:
2][
][
XVar
XE
4
Normal Distribution
1. “Bell-Shaped” &
Symmetrical
X
f(X)
Mean
Median
Mode
2. Mean, Median,
Mode Are Equal
3. Random Variable
Has Infinite Range
- < x <
5
Example
N (72, 5) A normal distribution with mean 72
and variance 5.
Possible situations: Test scores, pulse rates, …
6
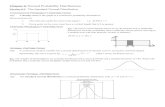
Effect of Varying Parameters ( & )
x
f(x)
A C
B

Normal Distributions
2
7
Normal Distribution
Probability
dxxfdxcPd
c )()(
c dx
f(x)
Probability is
area under
curve!
8
X
f(X)
Infinite Number
of Tables
Normal distributions differ by
mean & standard deviation.
Each distribution would
require its own table.
That’s an infinite number!
9
Standard Normal Distribution
Standard Normal Distribution:
A normal distribution with
mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1.
Notation:
Z ~ N ( = 0, 2 = 1)
0 Z
= 1
Cap letter Z 10
Area under Standard Normal Curve
How to find the proportion of the are under the standard normal curve below z or say P ( Z < z ) = ?
Use Standard Normal Table!!!
0 z
Z
11 12
Standard Normal Distribution
P(Z < 0.32) = F(0.32) Area below .32 = ?
0 .32
0.6255

Normal Distributions
3
13
Standard Normal Distribution
P(Z > 0.32) = Area above .32
0 .32
Areas in the upper tail of the standard normal distribution
= 1 - .6255 = .3745
14
Standard Normal Distribution
P(0 < Z < 0.32) = Area between 0 and .32 = ?
0 .32
= 0.6255 – 0.5 = 0.1255
15
-1.00 0 1.00
P ( -1.00 < Z < 1.00 ) = __?___
.3413 .3413
.6826
0.8413 - 0.5 16
-2.00 0 2.00
P ( -2.00 < Z < 2.00 ) = _____
.4772 .4772
.9544 = .4772 + .4772
.9544
17
-3.00 0 3.00
P ( -3.00 < Z < 3.00 ) = _____
… .4987 .4987
.9974
18
- 1.40 0 2.33
P ( -1.40 < Z < 2.33 ) = ____
.4901 .4192
.9093
.0099 .0808

Normal Distributions
4
19
Normal Distribution
= 0
= 1
= 50
= 3
= 70
= 9
…
Standard Normal
20
Standardize the
Normal Distribution
X
Normal
Distribution
ZX
-
One table!
= 0
= 1
Z
Standardized
Normal Distribution
21
Theorem
If X is N(, 2), then Z = is N(0,1). (X – )
-F-
-F
-
-
ab
bZ
aPbXaP )(
22
N ( 0 , 1)
0
-
-
bZ
aPbXaP )(
Standardize the
Normal Distribution
a b
N ( , )
Normal
Distribution
X
Standard
Normal
Distribution
Z
-a
-b
23
Example 1
Normal
Distribution
For a normal distribution that has
a mean = 5 and s.d. = 10, what
percentage of the distribution is
between 5 and 6.2?
X = 5
= 10
6.2 24
Example 1
X= 5
= 10
6.2
Normal
Distribution
12.10
52.6
-
-
XZ
Z= 0
= 1
.12
Standardized
Normal Distribution P(5 X 6.2)
P(0 Z .12)
010
55
-
-
XZ

Normal Distributions
5
25
Z= 0
= 1
.12
Example 1
Standardized Normal
Distribution Table
Area = .5478 - .5 = .0478 26
Example 1
X= 5
= 10
6.2
Normal
Distribution
12.10
52.6
-
-
XZ
Z= 0
= 1
.12
Standardized
Normal Distribution P(5 X 6.2)
P(0 Z .12)
0.0478 4.78%
010
55
-
-
XZ
27
Example
P(3.8 X 5)
X = 5
= 10
3.8
Normal
Distribution
12.10
58.3-
-
-
XZ
Z = 0
= 1
-.12
Standardized
Normal Distribution
.0478
Area = .0478
P(3.8 X 5) =P(-.12 Z 0)
.0478
28
Example
P(2.9 X 7.1)
5
= 10
2.9 7.1 X
Normal
Distribution
0
= 1
-.21 Z.21
Standardized
Normal Distribution
.1664
Area = .0832 + .0832 = .1664
P(2.9 X 7.1) =P(-.21 Z .21)
.1664
29
Example
P(X > 8)
X = 5
= 10
8
Normal
Distribution
Standardized
Normal Distribution
30.10
58
-
-
XZ
Z = 0
= 1
.30
.3821
Area = .3821
P(X > 8) =P(Z > .30)
=.3821
30
X = 5
= 10
8
Normal
Distribution
62% 38%
Value 8 is the 62nd percentile
Example
P(X > 8)

Normal Distributions
6
31
More on Normal Distribution
The work hours per week for residents in Ohio has a
normal distribution with = 42 hours & = 9 hours.
Find the percentage of Ohio residents whose work hours
are
A. between 42 & 60 hours.
P(42 X 60) =?
B. less than 20 hours.
P(X 20) = ?
32
P(42 X 60) = ?
Normal
Distribution
Standardized
Normal Distribution
X
= 200
2400 Z 0
= 1
2.0
9
42 60 2
P(42 Z 60)
P(0 Z 2)
.4772(47.72%) .4772
33
P(X 20) = ?
Normal
Distribution
Standardized
Normal Distribution
X
= 200
2400 Z 0
= 1
2.0
9
20 42 -2.44
P(X 20) = P(Z -2.44)
= 0.0073 = 0.73%
0.0073
34
Finding Z Values
for Known Probabilities
Standardized Normal
Distribution Table
What is z given
P(Z < z) = .80 ?
0
.80 .20
z = .84
z.20 = .84
Def. za : P(Z ≥ za) = a ; P(Z < za) = 1 – a
35
Finding X Values
for Known Probabilities
Example: The weight of new born
infants is normally distributed with a
mean 7 lb and standard deviation of
1.2 lb. Find the 80th percentile.
Area to the left of 80th percentile is 0.800.
In the table, there is a area value 0.7995
(close to 0.800) corresponding to a z-score
of .84.
80th percentile = 7 + .84 x 1.2 = 8.008 lb 36
Finding X Values
for Known Probabilities
Normal Distribution Standardized Normal Distribution
.80 .80
0 7
( )( ) 008.82.184.7 ZX
X = 8.008 z = .84
80th percentile

Normal Distributions
7
37
Stanine Score
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-1.75 -1.25 -.75 -.25 0 .25 .75 1.25 1.75
4% 4% ? %
38
More Examples
• The pulse rates for a certain population follow a
normal distribution with a mean of 70 per minute
and s.d. 5. What percent of this distribution that is
in between 60 to 80 per minute?
• The weights of a population follow a normal
distribution with a mean 130 and s.d. 10. What
percent of this population that is in between 110
and 150 lbs?
39
The Normal Distribution
Approximation for Discrete Distributions
(Normal approximation to Binomial)
40
Normal Approximation for
Binomial Probability
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
= np = 3.5
2= np(1-p) = 1.75
?)3( bXP
41
)5.2()3( > Nb XPXP
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
= np = 3.5
2 = np(1-p) = 1.75
7764.
)76.(
)75.1
5.35.2(
->
->
ZP
ZP
Binomial Table:
P(Xb ≥ 3) = .7734
Normal Approximation for
Binomial Probability