Chapter 2. Chain Structure and Configuration. Polymer chains have three basic properties: 1.The...
-
Upload
jacob-reed -
Category
Documents
-
view
241 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 2. Chain Structure and Configuration. Polymer chains have three basic properties: 1.The...

Chapter 2. Chain Structure and Configuration

Polymer chains have three basic properties:
1. The molecular weight and molecular distribution.2. The conformation of the chains in space.3. The configuration of the chain.
Coil chain conformation

2.1.1 Head-to-head and head-to-tail configurations
2.1 Examples of configurations and conformations
head-to-tail
head-to-head
Thermodynamically and spatially preferred structure is usually the head-to-tail configuration. The H-to-H and H-to-T configurations cannot be interchanged without breaking primary chemical bonds.

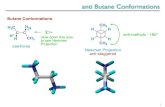
2.1.2 Trans-Gauche Conformations
The trans-gauche conformations of polymer chain can be interchanged by simple rotation about the single bond linking the moieties.

2.2 Theory and instruments2.1.2 Chemical methods of determining
microstructure


2.3 Stereochemistry of repeating units
2.3.1 Chiral centers
*
Chemically identical but they rotated plane-polarized light in opposite directions.

2.3.2 Tacticity in polymers
Polymerization of monosubstituted ethylene
Pseudochiral center

isotactic
syndiotactic
atactic


Stereo-isomers


2.4 repeating unit isomericsm
2.4.1 Optical isomerism

2.4.2 Geometric isomerism
The cis-trans isomerism arises because rotation about double bond is impossible without disrupting the structure.

2.4.3 Substitutional isomerism
1,21,43,4 addition polymerization
Synthesis of diene type polymers
isoprene

2.4.4 Infrared and Raman spectroscopic characterization
C-H bending 823 cm-1
C-O stretching 1164 & 1231 cm-1
C=O stretching 1506 cm-1
Skeletal ring vibration 1776 cm-1


2.5 Common types of copolymers

Copolymers
Terpolymers

Polymer blend Graft copolymer
Block copolymer Semi-IPN
IPN
Cross-linked


Nanoscale ‘microphase’ segregation: N > (N)ODT
with (N)ODT = f(f)
Melt state

‘Solution’ state:Swollen micelles and dissolved single-chains
Blends?

Crystalline state

Block Copolymer (microphase separation)
volume fraction
< 0.20 0.20 ~ 0.35 > 0.35

Transition between mesomorphic phases

Block Copolymer phase diagram
disorder


Representative phase diagram of diblock copolymers(Khandpur et al., Macromolecules 1995, 28, 8796)

3-D TEM micrographs for PS280-PLLA307 (PLLA = 0.37) solution-cast samples sectioned along different planes. As shown, the xy plane is the basal plane normal to helical axes and the yz and zx planes are planes parallel to helical axes


‘Knitting’ pattern

2.8 Conformational states in polymers
tg- g+
Arrhenius type:Exp(-Eact/kT)

2.9 Analysis of polymers during mechanical strain
Far from the neck region
In the neck region

2.10 Photophysics of polymers
A + h = A*
A* + B = A + B*
A* + A = (AA)*
2.10.2 Excimmer formation
(AA)* = 2A + hE
quench

2.10.3 Experimental Studies2.10.3.1 Microstructure of polystyrene



Infrared