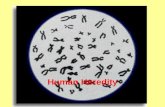
Chapter 14 Human Chromosomes Karyotype: a picture of the chromosomes from a single cell. Used to...
-
Upload
alannah-cain -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
3
Transcript of Chapter 14 Human Chromosomes Karyotype: a picture of the chromosomes from a single cell. Used to...
Human Chromosomes• Karyotype: a
picture of the chromosomes from a single cell.
• Used to determine the sex, or possible genetic disorders of an individual.
• 44 autosomes• 2 sex chromosomes
Determining the sex of a zygote:• Always determined
by the father.• All eggs contain
one X chromosome• Sperm either
contain one X chromosome or one Y chromosome.
Pedigree charts
• Used to show how a particular trait is passed from one generation to the next in a family
Genetic disorders
•Recessive disorders:•Most common•To be afflicted with a
recessive disorder, one must have 2 copies of each recessive allele.
PKU (phenylketonuria)• The body cannot break down the amino
acid phenylalanine• Nutrasweet could be deadly• If not detected early, or if a specific diet
is not followed, serious brain damage can occur.
• 1 in 60 Caucasians are carriers of the gene that causes PKU.
• The gene is found on chromosome 12
Tay-Sachs
• Cannot break down certain fats.• Results in brain damage• The gene is found on
chromosome 15• Mainly affects people of
European Jewish ancestry (1 in 30 are carriers)
Cystic Fibrosis
• Affects digestive system and absorption of fats.
• Causes a build up of mucus in the lungs.
• CF kids are often more likely to develop pneumonia.
• One of the first disorders to be actively studied for gene therapy.
More CF• Sweat test• Gene found on
chromosome 7• 1 in 25 people are
carriers.• Most lethal
autosomal recessive disorder in U.S.
• No cure
Treatment
• Respiratory therapy.
• Enzyme therapy (DNAse)
• Lung transplants.
• Boomer Esiason Foundation
Albinism• Lack of pigment
in skin, hair, and eyes.
• Approx. 1 in 17,000 people
• Dangers:1. Eye problems2. Severe
sensitivity to sunburn.
Autosomal dominant disorders
• These disorders are expressed when the dominant allele is present in the genotype.
Achondroplasia
• A form of dwarfism• The torso is of normal size, but
arms and legs are very short.• Average adult height of 4 feet.• 1 in 25,000 births.• Gene is found on chromosome 4
Huntingtons
• Results in a loss of muscle control and mental function.
The symptoms usually do not appear until after 30 years old.
• Approximately 1 in 10,000 births in Europe and N. America
• Gene on chromosome 4
Sickle cell disease (sickle cell anemia)
• Codominant disorder found in African Americans.
• Red blood cells are misshapen.• Characterized by extreme pain in
legs and arms because the cells get stuck in capillaries.
• Can be fatal• The gene can prevent Malaria
Sickle-cell cont’d• Approx 1000 babies
born each year• 1 in 400 African
Americans• Possible cure: bone-
marrow transplants• Treatment:
– Avoid being overly active
– Watch your diet
Sex-linked genes and disorders
• A situation in which an organism’s sex can affect the chances of inheriting a gene.
• First studied by Morgan with fruit flies
• Most sex-linked genes are found the X chromosome. Why?
• Much larger.
Color blindness gene
• Recessive gene located on the X chromosome.
• Does color blindness affect more men or women?
• Ans: MEN• Men only have one X chromosome,
thus only one copy of the color blind gene.
Hemophilia
• A disorder in which a person’s blood does not clot properly.
• Gene found on X chromosome.
• 1 in 10,000 males born are afflicted.
More hemophilia:
• Main type: hemophilia a. Body cannot manufacture a specific protein needed for proper blood clotting.
• Traditionally treatment: periodic blood transfusions
• Known as the “royal disease”• Why?
ALD (adrenoleukodystrophy)
• Similar to multiple sclerosis.• Body is unable to break down long
chain fatty acids.• Results in destruction of myelin
(insulating material around the nerves)
• Affects only boys. Fatal• Depicted in the movie “Lorenzo’s Oil”
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
• Weakening and loss of muscle tissue.
• 1 out of 3000 males born in U.S.
• Genetic disorder website
Chromosomal disorders
• A disorder resulting from either the loss of or gain of part or a whole chromosome.
• Nondisjuntcion : most common chromosomal mutation.
• When a gamete contains either an extra or one less chromosome.
• Occurs during meiosis.
Down Syndrome
• Also known as Trisomy 21 because of the presence of an extra chromosome 21.
• Symptoms similar to mental retardation
• Approx 1 in 800 babies born in U.S.• Chances of having a baby with
Down Syndrome increases with the age of the mother.
Sex Chromosome Disorders:
• Turner’s syndrome: In females, a person only inherits one X chromosome (45,X)
• Klinefelter’s syndrome: In males, an extra X chromosome is present (47,XXY)
DNA analysis
• Testing for alleles : makes it possible to determine if a person can pass on a particular disorder to his or her children.
• DNA fingerprinting
Human Genome Project
• Began in 1990. • The goal was to analyze the entire
human DNA sequence (6 billion base pairs)
• Originally scheduled to be completed in 2005
• In June 2003, the map was completed
Gene Therapy
• Replacing an absent or faulty gene with a copy of a “good” or working gene.
• Still considered a radical therapy. • Has not been tested thoroughly.