Chapter 1 Milky Way Galaxy- The Sun
Transcript of Chapter 1 Milky Way Galaxy- The Sun

8/14/2019 Chapter 1 Milky Way Galaxy- The Sun
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/chapter-1-milky-way-galaxy-the-sun 1/2
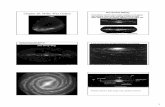
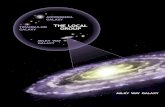
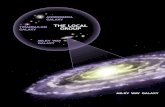
Chapter 1 Milky Way Galaxy- The sun and all the stars that we can see with thenaked eye• Our galaxy is one of the 2 largest of our local groups• Groups of galaxies with more than a few dozen members are often
called galaxy clusters
Universe- encompasses everything all over the joint.• The universe is expanding because average distance between galaxies is
expanding• Nuclear fission- when gravity becomes dense and hot enough to generate
enough energy to create a star• When a massive star dies it is called a Supernovae• KNOW THE VOCABULARY LIST ON PAGE 5
• Astronomical unit(AU) The average distance between Earth and thesUn which is about 150 Million kilometers, more technically, 1 AU isthe length of the semimajor axis of Earth's orbit.
• One light year equals 9.46 Trillion km or about 10 trillion km• Our solar system is about 4.5 billion years old• Speed of light is 300,000 km per second• Because light takes time to travel through space we are led to a
remarkable fact: the farther we look in distance, the further back we lookin time.
• We can only see our observable universe, anything farther, light has nothad enough time to reach us yet.
• Planet• Orbits a stir but itself is neither a star or a moon• Is massive enough for its own gravity to give it nearly round shape• Has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit.
• Earth is on a 23.5 degree axis• Earth's orbital path defines a flat plane that we call the ecliptic plane• The axis tilt happens to be oriented so that it points almost directly at a
star called Polaris, or the north star• Edwin hubble-1920's
• Virtually every galaxy outside the local group is moving away from us• The more distant the galaxy, the faster it appears to be racing away
-We are star stuff, the atoms from which we are made becan as hydrogenand helim in the Big Bang and were later fused together in to heacierelements by massice stars. Stellar deaths released thse atoms into spacewhere our galaxy recycled them into new stars and planets. Our solarsystem formed from such recycled matter some 4.5 bill years ago.
• The earth rotates 1 per day at 1,000 km an hour• Earth orbits the sun each year at 100,000 km an hour• The solar system moves relative to near by stars at typically at a speed of
70,000 km/h• The milky way galaxy rotates carrying our sun around its center once
every 230 million years at about 800,000 km/h

8/14/2019 Chapter 1 Milky Way Galaxy- The Sun
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/chapter-1-milky-way-galaxy-the-sun 2/2
• Out galaxy moves relative to our local group at about 300,000 km/h• The universe expands at nearly the speed of light
-LOOK IN THE BOOK FOR SCALES