Cellular organization of plants and animals
Transcript of Cellular organization of plants and animals
Presented By: Saba Iftikhar and Roha Irfan
Presented To: Miss Hafiza Gulnaz Fatima
Date: 20/11/2015
CELLULAR ORGANIZATION OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS
CELLS• All living things are made of cells.• Cell is the basic unit of structure and function
of all living organisms.• Plants and animals are made of trillions of
cells. • Some plants and animals are made of only
one cell For example: Bacteria.• Cell are of different shapes and sizes.• They have different functions.
MICROSCOPE• An instrument used see small things which
cannot be seen by naked eye.• Microscope use light to show image.STRUCTURE• It has a base, an arm, a tube, a stage and
two adjustment screws• It has two lenses : an eye piece and an
objective
Working• The object to be seen
is placed on glass slide and then on the stage.• To focus the object
adjust the adjustment screws
CELL STRUCTURE
• There are many parts in a cell.• A microscopic study of cell shows different parts
in animal and plant cell.• Cell Structure varies in case of animals as well as
plants.
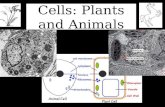
DIFFERENCE B/W ANIMAL AND PLANT CELL
Animal Cell1. It is oval in shape.
2. It has large nucleus and small vacuole.
3. It has centrioles.4. Chloroplast is
absent.5. Cell wall is absent.
Plant Cell1. It is rectangular in
shape.2. It has small nucleus
and large vacuole.3. It has chloroplast.4. Centrioles are
absent.5. Cell wall is present.
CELL ORGANELLES
CELL WALL• Outermost covering of plant cell.• Made of hard material named as cellulose.• Provides support and shape to the cell.• Absent in animal cell. CELL MEMBRANE• Outermost covering of animal cell.• Controls movement of materials.• Present next to cell wall in plant cell.
CYTOPLASM• Jellylike material inside cell membrane.• Contains water and other chemicals.• Tiny cell structures are present in it.• Cell functions takes place in it.
NUCLEUS• Most important part of cell.• Controls all activities of cell.• Control center of cell.• Surrounded by a thin membrane called cell
membrane.• Thread like structures are present in it named as
chromosomes.• 46 chromosomes are present in each cell.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM• Network of channels.• Movement of materials takes place in cell.MITOCHONDRIA
• Provides energy to the cell.• Power house of cell.
CHLOROPLAST• Contain chlorophyll.• Trap energy from sun.• Helps to manufacture food.
VACUOLES• Used to store waste i.e. water, air and food particles.• A large vacuole is present in plant cell.• Many small vacuoles are present in animal cell.
CENTRIOLES• Two in number.• Only in animal cell.• Present near nucleus.• Play important role cell division.
UNICELLULAR AND MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
• Organisms made of only one cell are termed as unicellular organisms.• For example: Bacteria, chlamydomonas, amoeba
and paramecium.• Organisms made of more then one cell are
termed as multicellular organisms.• For example: Things around us which we can see.
TISSUES
• A group of cells performing similar function is known as tissue.• Plants and animals have different tissues in their
bodies. For example: Epidermal tissue, xylem tissue, muscle tissue, blood tissue.
PLANT TISSUES1. EPIDERMAL TISSUES• Covers the root, stem and leaves of a
plant.
2. XYLEM TISSUES• Conduct water and salts from roots to the leaves.
3. PHLOEM TISSUE• Carries prepared food from leaves to
different parts of plantANIMAL TISSUES
1. MUSCLE TISSUE• Helps in movement of animal body.
2. BONE TISSUES• Strong and solid tissues.• Gives shape and support to the body.
3. BLOOD TISSUES• Carries materials from one part to the other.
ORGANS• Different tissues group together to form
organs.• An organ perform one or more functions.• For example: Leaf, flower, heart, brain.
PLANT ORGANS LEAF• They make food.
FLOWER• They produce seeds.• Seeds grow new plants.
ROOTS•Holds plant in soil.•Absorb water and salts for plants
ANIMAL ORGANSHEART
• Pumps blood to all body parts. TONGUE
• Tastes food and helps in digestion.LIVER
• Helps in digestion of food.• Performs many other important function.
ORGAN SYSTEM
• Group of organs which work together.• Do one or more then one special function.
ORGAN SYSTEM IN PLANTS1. ROOT SYSTEM• Helps in absorption of water and salts.2. SHOOT SYSTEM• Includes leaves, branches and flowers.• Make food, produce seeds and transport water.
ORGAN SYSTEM IN HUNANS1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM• Consist of mouth, food pipe, stomach,
intestine and liver.• Helps in digestion of food.2. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
• Consist of nose, windpipe and lungs.• We breath through this system.
3. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM• Consist of heart and blood vessels.• Circulates blood with in the body.
ORGANISMS
• Highest level of organization in living things.• Organ system work in coordination.• If any body system fails to work properly, a living
organism may die.