Cells Test bank. 1 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? B. Robert...
-
Upload
godwin-bennett -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
1
Transcript of Cells Test bank. 1 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? B. Robert...

Cells Test bank

1• 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork
cells?
• B. Robert Hooke

2• 2 The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by
saying that:
• D. All plants and animals are made of cells

3• Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory:
• C. Very Few Cells Reproduce

4• The cell theory applies to:
• D. All of the above

5• Electron Microscopes can reveal details :
• D. 1000 times smaller than those visible in light microscopes

6• Which type(s) of microscopes can produce three-dimensional
images of cells:
• B. Scanning electron microscopes

7• Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to:
• C. follow molecules moving through the cells

8• Prokaryotes lack:
• C. a nucleus

9• Which of the following contain a nucleus:
• C. Eukaryotes

10• Eukaryotes usually contain:
• D. All of the above

11• Which of the following organisms are prokaryotes:
• C. Bacteria

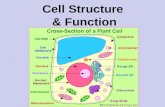
12• Which of the following is a function of the nucleus?
• D. All of the above

13• Which of the following is NOT found in the nucleus:
• A. Cytoplasm

14• Which of the following statements explains why the nucleus is
important to cells:
• C. The nucleus contains coded instructions for making proteins

15• Which of the following structure are found in the cytoplasm:
• B. Ribosome

16• Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can
use:
• B. Lysosome

17• Which structure makes protein using coded instructions that
come from the nucleus:
• D. Ribosome

18• Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food
compounds that are more convenient for the cells to use:
• D. Mitochondrion

19• Which organelles help provide the cell with energy?
• A. Mitochondrion and Chloroplasts

20• Which sequence correctly traces the path of a protein in the
cells:
• A. Rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, rele3ased from the cell.

21• Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells, but
not animal cells?
• C. Chloroplast

22• Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton?
• A. Helps a cell keep its shape

23• Which structures carry out cell movement?
• C. Microtubules and Microfilaments

24• Which of the following is NOT a function of the cytoskeleton?
• C. Prevent chromosomes from separating

25• The main function of the cell wall is to:
• A. Support and protect the cell.

26• Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is:
• D. Usually made of though fibers

27• You will NOT find a cell wall in which of these kinds of
organisms:
• B. Animals

28• Which of the following structure serves as the cell’s boundary
from its environment?
• B. Cell Membrane

29• Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane?
• D. Regulates which materials enter and leave the cell

30• The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help
move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of?
• B. Lipids

31• Diffusion is the movement of molecules from:
• B. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration

32• Diffusion occurs because:
• A. Molecules constantly move and collide with each other.

33• When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a
membrane is the same, the molecules will:
• C. Move across the membrane in both directions

34• Which means of particle transport requires input of energy
from the cell?
• D. Active transport

35• The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable
membrane is called:
• B. Osmosis

36• An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst
because the osmotic pressure causes:
• A. Water to move into the cell

37• Which term refers to cells having different jobs in an
organism?
• B Cell specialization

38• The cells of multicellular organisms are:
• C. Specialized to perform different tasks

39• All of the following are examples of cell specialization EXCEPT:
• C. A prokaryotic cell that carries out photosynthesis

40• Which of the following is an example of an organ?
• A. Heart

41• All of the following are types of tissues EXCEPT:
• C. Digestive

42• A group of similar cells that perform a particular function is
called a(an)L
• C. Tissue

43• Which of the following is an organ of the digestive system?
• A. Stomach

44• An organ system is a group of organs that:
• C. Work together to perform a specific function

45• Which list represents the levels of organization in a
multicellular organism from the simplest level to the most complex level?
• D. Cell, tissue, organ, organ system

46• True or False:• If a cell contains a nucleus, it must be a prokaryote.
• False. If a cell contains a nucleus, it must be a eukaryote