CELLS & the ORGANELLES Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Animal vs. Plant Cells.
Cells and Organelles (Learning Objectives)faculty.sdmiramar.edu/bhaidar/Bio 130/lectures/Cells and...
-
Upload
nguyenduong -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
3
Transcript of Cells and Organelles (Learning Objectives)faculty.sdmiramar.edu/bhaidar/Bio 130/lectures/Cells and...

Cells and Organelles (Learning Objectives)• Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. List their
similarities and differences.• Learn the three domains of living organisms and the 6 emergent
feature of cells and living organisms.• Compare and contrast gamete, zygote, somatic cells, and germ
cells.• Review the structure of membranes and explain the importance of
different proteins for creating intracellular membranous compartments where different cellular functions can take place.
• Learn the structure and functions of each of the following, and where applicable relate to specific known genetic diseases;a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoskeleton c. Nucleus d. Endoplasmic
reticulum (smooth and rough) e. Golgi apparatus & vescilcesf. Lysosomes g. Peroxisomes h. Mitochondria
• Explain the coordination of functions of several organelles that bring about cellular functions such as secretion and flow of genetic information from DNA to protein

Types of Cells on Earth
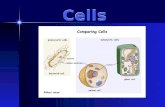
Prokaryotic cells- Lack a nucleus
Eukaryotic cells- Possess a nucleus and other organelles
Figure 2.2

Domains of Life• Three broad categories of organisms
• Archaea – Unicellular prokaryotes
• Bacteria – Unicellular prokaryotes
• Eukarya – Includes both unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes

Atoms/Elements
Molecules
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism(Family)
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biosphere
Chemical world
Biological W
orld
Non-living
Living
Ascending
Descending

Emergent properties of life shared by cells and all levels if the biological organization
• Order• Regulation of internal conditions (Homeostasis)

• Growth and development• Energy use• Response to environmental stimuli• The ability to reproduce

Basic concepts
• Cells Interact: send, receive, respond to signalsaggregate to form tissues, organs and organ systems
• Health state- balance between cell division and cell death
• Specialization of cell function- expression of different subsets of genes.

Human Development
Sperm cell
NucleicontainingDNA
Egg cell
Fertilized eggwith DNA fromboth parents
(Zygote)
Embyro’s cells with copies of inherited DNA
Offspring with traitsinherited fromboth parents
Unspecialized replicating
cells
Different specialized
cells

Human Cells Gametes:
• sperms and eggs• haploid
Zygote• diploid
Somatic cells: • body cells • diploid
Germ cells:• gonad cells that
produce gametes• diploid
Mitosis and development
Multicellulardiploid adults
(2n = 46)
Diploidzygote
(2n = 46) 2n
Meiosis Fertilization
Egg cell
Sperm cell
n
Haploid gametes (n = 23)
n

• Cellular activities and abnormalities underlie our inherited traits, quirks, and illnesses
Lack ofdystrophin
Figure 2.1
Muscular Dystrophy

A animal cell is a living unit greater than the sum of its parts
• Boundary-plasma membrane• Cytoplasm: Compartment (division of labor)
o Cytosol (soluble components) o Organelles surrounded by membranes to
partition functions• Nucleus DNA-information

Smooth endoplasmicreticulum
Roughendoplasmicreticulum
CYTOSKELETON:
NUCLEUS:Nuclear envelopeChromosomesNucleolus
Ribosomes
Golgiapparatus
Plasma membrane
Mitochondrion
Peroxisome
Centriole
Lysosome
MicrotubuleIntermediatefilamentMicrofilament
Figure 2.3

Role of cell membranes in compartmentalization of cellular
functions
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tail
Figure 2.8
A phospholipid bilayer- Phosphate end (hydrophilic)- Fatty acid chains (hydrophobic)

Compartmentalized functions of animal cells
• Manufacturing, processing, and shipping of molecules to appropriate destination: – DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids
• Breakdown of molecules: – large structures, lipids, detoxification of certain substances
• Energy processing: – forming cellular energy form
• Structural support, movement, and communication

Figure 2.3
Plasma Membrane
Forms a selective barrier Contains proteins,
glycoproteins, and glycolipids
- Important to cell function and interactions
- May be receptors- Form channels for ions
Figure 2.9

Figure 2.3
Inherited Diseases caused by Faulty Ion Channels
Sodium channels- Mutations lead to absence or extreme pain
Potassium channels- Mutations lead to impaired heart function and one form of deafness
Chloride channels- Mutations lead to cystic fibrosis
Reading 2.2, page 27

Figure 2.3
CytoskeletonA meshwork of protein
rods and tubulesIncludes three major
types of proteins- Microtubules- Microfilaments- Intermediate filaments
Figure 2.10

Figure 2.3
Cytoskeleton FunctionsMaintain cell shape
Connect cells to each other
Transport organelles and small molecules
Provide cell motility (some cell types)
Move chromosomes in cell division
Compose cilia

A network of protein fibers that functions in cell structural support and motility
Cytoskeleton
Microfilament
Actin subunit
7 nm
Intermediate filament
Fibrous subunits
10 nm
Microtubule
Tubulin subunit
25 nm
Nucleus
Nucleus

Figure 2.3
Inherited Disease caused by faulty connections between the plasma membrane and the
cytoskeleton
Hereditary Spherocytosis page 29

Figure 2.3
The NucleusThe largest structure in a cellSurrounded by a double-layered nuclear
envelopeContains:
- Nuclear pores that allow movement of some molecules in and out - Nucleolus, which is the site of ribosome production- Chromosomes composed of DNA and proteins

Figure 2.3
Figure 2.4
The Nucleus
Figure 2.4

Figure 2.3
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Interconnected membranous tubules & sacs
Winds from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane
Rough ER contains ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis
Smooth ER does not contain ribosomes and is important in lipid synthesis

Figure 2.3
Golgi ApparatusStack of flat membrane-enclosed sacs
Processing center of added sugars that form glycoproteins and glycolipids
Site of final protein folding
Products are released into vesicles that bud off to the plasma membrane

SecretionCoordination of function of organelles
Figure 2.5
Protein Traffickinghttp://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/proteintrafficking/movie-flash.htm

Transport vesiclebuds off
Secretoryproteininside trans-port vesicle
GlycoproteinPolypeptide
Ribosome
Sugarchain
Rough ER
1
2
3
4

Nucleus
VacuoleLysosome Plasma membrane
Smooth ER
Nuclearmembrane
Golgiapparatus
Rough ER
Transportvesicle
Transportvesicle

Figure 2.3
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound sacs containing > 40 types of digestive enzymes
Break down bacteria, cellular debris, and nutrients
Tay-Sachs is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder
http://www.ygyh.org/tay/whatisit.htm Figure 2.6

Lysosomes• Membrane-bounded sacs of hydrolytic enzymes
that digestive enzymes
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter5/animations.html#

Figure 2.3
PeroxisomesSacs with one membrane filled with several types of
enzymes- Break down lipids, rare biochemicals- Synthesize bile acids- Detoxify compounds from free radicals, H2O2, and
alcohol- Abundant in liver and kidney cells
Lorenzo’s oilAdrenoleukodystrophy absence of a peroxisomal enzyme leads
to accumulation of long-chain fatty acids in brain and spinal cord

Figure 2.3
MitochondriaSurrounded by two
membranes Site of ATP (energy)
productionContain their own
circular DNAHuman mitochondrial
DNA is inherited only from the mother
Lou Gehrig Disease
Figure 2.7

Structures and Functions of Organelles
Table 2.1

Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Animal and Plant cellshttp://www.wisc-
online.com/objects/index.asp?objID=AP11604
Secretionhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MrHULUxAsGg