Cells. Cells and their History All living things are made of cells Cells are microscopic.
Cells
-
Upload
rishabh-jain -
Category
Science
-
view
8 -
download
0
Transcript of Cells
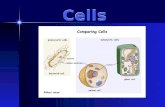
Animal cellAnimal cell Golgi apparatusGolgi apparatus Cell membraneCell membrane NucleusNucleus CentriolesCentrioles Endoplasmic Endoplasmic
reticulumreticulum CytoplasmCytoplasm RibosomesRibosomes LysosomeLysosome MithocondrionMithocondrion Nuclear Nuclear
membranemembrane
Plant cellPlant cell Cell wallCell wall VacuoleVacuole Membrane cellMembrane cell LysosomeLysosome CytoplasmCytoplasm ChloroplastChloroplast NucleusNucleus NucleolusNucleolus MitochondriaMitochondria EndoplasmicEndoplasmic ReticulumReticulum Golgi complexGolgi complex
Specialised cells:Specialised cells:
-Leaf cell-Leaf cell-Root hair cell-Root hair cell-Sperm cell-Sperm cell-Red blood cell-Red blood cell-Egg cell-Egg cell-Nerve cell -Nerve cell
Root hair cellRoot hair cell
Water and Water and mineral ions mineral ions from the soilfrom the soil
Sperm cellSperm cell
FertilisesFertilises Egg cellEgg cell Head gametesHead gametes TailTailmovemove
CellsCellsTissueTissueOrgansOrgansOrgan Organ SystemSystem
Tissue:Tissue:-muscle -muscle -the lining of the intestine -the lining of the intestine -the lining of the lungs -the lining of the lungs --phloem phloem --root hair tissue root hair tissue
Organ systems.Organ systems.-Circulatory system -Circulatory system -Respiratory system -Respiratory system -Digestive system -Digestive system -Nervous system -Nervous system -Reproductive system -Reproductive system -Leaf canopy -Leaf canopy
DiffusionDiffusion Movement of particles Movement of particles
from an area of higher from an area of higher concentration to a area concentration to a area of lowerof lower
Osmosis
Important for plants
Nucleus • Almost all cells contain a single nucleus.• Directs cell activities• Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane• Function-Stores and transmits genetic information in the form of DNA. Genetic
information passes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Nucleolus• Inside nucleus• Contains RNA to build proteins
Nuclear Membrane• Surrounds nucleus• Made of two layers
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pores• Openings allow material to enter and
leave nucleus
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Chromosomes• In nucleus• Made of DNA• Contain instructions for traits &
characteristics
Endoplasmic Reticulum• Moves materials around
in cell• Smooth type (Agranular):
lacks ribosomes. Site of lipid molecule synthesized
• Rough type (Granular): ribosomes embedded in surface. Packaging of proteins to be secreted or distributed.
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Ribosomes
• Composed of proteins and several RNA molecules
• Proteins factories of the cell
• Either bound to the organelle or found free in the cytoplasm
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Golgi Apparatus
• Most cells have single Golgi apparatus.
• Protein 'packaging plant'
• Move materials within the cell
• Move materials out of the cell
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Lysosome• Spherical or oval• Typical cell may contain
several hundreds• Digestive enzyme for
proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
• Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal
• Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html