Cell Theory, Animal Cell Structure, Function, and Processes 8 th Grade Science Mrs. YOO.
-
Upload
jefferson-lacer -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Theory, Animal Cell Structure, Function, and Processes 8 th Grade Science Mrs. YOO.

Cell Theory, Animal Cell Structure, Function, and Processes8th Grade ScienceMrs. YOO

Cell - is the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms.

Scientists and Cell Theory
Robert Hooke – coined the word “cell”
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek- 1st to observe a living cell
“Father of Modern Microscopy”, bacteria, “animalcules”
Hans and Zacharias Janssen- compound microscope
Matthias Schleiden- microscopic studies of plants
Theodor Schwann- concluded that all animals are made of cells.
Rudolph Virchow- cells are produced only by other living cells.

THE CELL THEORY
All living things are composed of one or more cells.
A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things.
All cells come from other living cells.

Unicellular VS Multicellular
Unicellular – organism that is composed of only a single cell.
Most unicellular organisms are of microscopic size, are thus classified as microorganisms. (Bacteria)
*some macroscopic: green alga ( Acetabularia)
o Multicellular- organisms that are composed of more than one cell.
o * often specialized to perform specific functions.
o Examples: human, animals, plants, cyanobacteria,

UnicellularWhat are Ciliates?
Ciliates are unicellular protists that can be recognised by their hairlike 'cilia'. They use them for locomotion and for feeding. Some ciliates are very small, not much larger than the largest bacteria. Others like the 'trumpet animalcule' Stentor can reach a size of two millimetres so it can be seen with the naked eye. Paramecium does not become much larger than 0.3 mm.

Multicellular

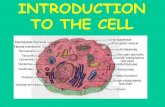
Animal Cell Structure and Cell Function

ANIMAL CELL – STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS
Structure Function
Cell Membrane Controls what enters and leaves the cell
Nucleus Controls all cell activities, stores hereditary information
Mitochondrion Transfers energy from nutrients to ATP
Ribosome Synthesizes proteins
Endoplasmic reticulum Moves molecules within the cell
Golgi Apparatus Modifies and packages protein
Lysosome Digests nutrients and old organelles

PROTISTS (Kingdom Protista)
A. Most are one-celled, but some have many cellsB. Cells have a membrane around the nucleusC. Some get nutrients and energy by eating other organisms
Eukaryotes are organisms that have cells with a deistinct membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Most unicellular protists are microscopic.Some can grow more than 60m a year.
Some protists are animal-like. Do not make their own food and can move independently.

EUGLENA
Unicellular protist that has some characteristics of both plants and animals.
Animal-like - can move freely and feed on other organisms.
Plant-like - has the ability to make their own food.

EUGLENA organelles

Euglena organelles and functions
Chloroplasts- store the chlorophyll and serve as the site for photosynthesis. ( Photosynthesis- a process in which organisms use light energy to join carbon dioxide and water to make food ; Chlorophyll- a green pigment that captures the energy of the sun to drive photosynthesis.
Eyespot or photoreceptor- sensitive to light
Flagellum- a whiplike tail that moves quickly back and forth to propel Euglena through the water.

AMOEBA
A unicellular protist.
Often described as animal-like protists because they are capable of movement and obtain nutrition by feeding other organisms.
Moves using structures called pseudopods.
PSEUDOPODS- an extension of the cytoplasm that forms when cytoplasm extends away from the nucleus. Also used for feeding.


ParameciumA unicellular protist that common in ponds and in slow-moving streams.
Completely covered with hair called cilia- used for movement.
Feeds with the structure called ORAL GROOVE.
Contractile vacuole- pumps water out of the cell to prevent the cell from bursting with excess water.
Contains two nuclei in one single cell. One for cell processes and the other is for sexual reproduction.


VOLVOX
A unicellular protist that has chloroplasts and can carry out photosynthesis.
Volvox DOES NOT live alone.
They form a group of cells known as COLONY.
Colony consists of a hollow sphere that contain from 500- 60, 000 Volvox.
Each of these flagella are used to propel through the water.


Summary features of protists
Protist Structure Locomotion
Food Source
Specialized Cell Structure
EUGLENA Unicellular Flagellum Feeds on other organisms, can make nutrients
Eyespot or photoreceptor
AMOEBA Unicellular Pseudopods
Feeds on other organisms
--------------------
PARAMECIUM Unicellular Cilia Feeds on other organisms
Oral groove and contractile vacuole
VOLVOX Unicellular(lives in colonies)
Flagella Makes nutrients
--------------------

TEST
COACH BOOK
Page 284-285
Page 289
Page 294

Cornell Notes
Read and take Cornell Notes: Lesson 45 pp. 295-302