Cell Surface Membrane
-
Upload
hanna-elise-de-guzman -
Category
Education
-
view
101 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Surface Membrane

THE CELL SURFACE MEMBRANE…

o Formerly called the plasma membrane.
o Surrounds the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells.
o Forms a permeable barrier, controlling the substances that enter and leave the cell therefore enables the cell to regulate its internal environment.
Cell Surface Membrane...

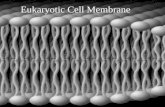
Fluid mosaic
model of the cell surface
membrane

Plasma Membrane Components:Glycoproteins and glycolipids are
proteins/lipids with short chain carbohydrates attached on the extracellular side of the memabrane.

3 types of lipid in the
Cell Surface Membrane:

PHOSPHOLIPIDS:
Make up 75% of the lipid.Are amphipathic molecules- they have a dual nature in that one end
of the phospholipids is hydrophilic whilst the other end of the phospholipid is hydrophobic and non-polar.
* The interaction between the hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends helps give the membrane stability and it is also these lipids which give the membrane selective permeability.

GLYCOLIPIDS: Make up 5% of membrane lipids.
Occur on the external surface of the cell surface membrane and the carbohydrate portion of the glycolipid extends into the intercellular space and is called Glycocalyx .
CHOLESTEROL: A steroid makes up 20% of lipid in animal
membrane but is rarely found in plant cell membranes.


Fluidity- essential in the process such as phagocytosis.
Degree of Fluidity:The length of the fatty acid chains.
The proportion of the fatty acids which are saturated.
The steroid content.

Membrane ProteinsIntrinsic proteins- those which span the entire membrane
-are usually glycoproteins.Four main Functions:• To act as channels.• Transporters.
• Receptors. • Enzymes.

Types of Membrane Proteins:1. Cell-cell recognition proteins
2. Integrins3. Intercellular junction proteins
4. Enzymes 5. Signal transduction proteins
*Aka - Receptor proteins 6. Transport proteins
*Passive and active


Transport across the Cell Surface Membrane:
1. Passive Transport • (Simple) Diffusion • Facilitated diffusion • Osmosis
2. Active Transport
3. Bulk Flow • Endocytosis• Exocytosis

Diffusion: movements of molecules or ions from a region where they are at a high concentration to a region where they are at a lower concentration until the concentrations of the two regions are equal and a dynamic equilibrium is established.Osmosis: diffusion of water molecules from a region where they are at a high concentration to a region where they are at a low concentration through a partially permeable membrane.

Facilitated Diffusion: used to transport molecules such as glucose, fructose, non fat-soluble vitamins, urea and many ions across the membraneActive transport: move substances across the PM against their concentration gradient.• Requires energy (ATP)• Active transport proteins are highly selective• Active transport is needed for proper functioning of
nerves and muscles

Bulk Flow: Vesicles are used to transport large particles across the PM.• Requires energy
Types:Exocytosis:
Endocytosis:Phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-
mediated

Exocytosis: Cytoplasmic vesicle merges with the PM and releases its contentsEndocytosis: PM sinks inward, pinches off and forms a vesicle• Vesicle often merges with Golgi for
processing and sorting of its contents

Phagocytosis – cell eating• Membrane sinks in and captures
solid particles for transport into the cell
Pinocytosis – cell drinking• Cell brings in a liquid

Receptor Mediated Endocytosis:Receptor Mediated Endocytosis: is a highly
specific form of endocytosis.• Receptor proteins on the outside of the cell
bind specific substances and bring them into the cell by endocytosis

1. Receptor proteins on PM bind specific substances (vitamins, hormones..)
2. Membrane sinks in and forms a pit– Called a coated pit
3. Pit pinches closed to form a vesicle around bound substancesCytoskeleton aids in pulling in the membrane and
vesicle formation

FIG. 5-9C
Coatedvesicle
CoatedpitSpecific
molecule
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Coat proteinReceptor
Coatedpit
Material boundto receptor proteins
Plasma membrane


FIG. 5-9Phagocytosis
EXTRACELLULARFLUID
Pseudopodium
CYTOPLASM
Foodvacuole
“Food” orother particle
Pinocytosis
Plasmamembrane
Vesicle
Coatedvesicle
Coatedpit
Specificmolecule
Receptor-mediated endocytosisCoat protein
Receptor
Coatedpit
Material boundto receptor proteins
Plasma membrane
Foodbeingingested

De Guzman, Hanna EliseDipasupil, Ma. Jessica L.Ferrer, Rachelle
_Group1