Cell Structures Movement & Organelles. Diffusion Movement of molecules from an area of high...
-
Upload
stephany-brown -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structures Movement & Organelles. Diffusion Movement of molecules from an area of high...

Cell StructuresCell StructuresMovement & OrganellesMovement & Organelles

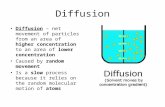
DiffusionDiffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low high concentration to an area of low concentrationconcentration
Move to the lower concentrationMove to the lower concentration

OsmosisOsmosis
Diffusion of waterDiffusion of water

Osmotic ConditionsOsmotic Conditions Hypertonic SolutionHypertonic Solution - contain a - contain a high concentration of solutehigh concentration of solute relative relative
to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell, causing in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell, causing the cell to shrivel the cell to shrivel
Hypotonic SolutionHypotonic Solution - contain a - contain a low concentration of solutelow concentration of solute relative to relative to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water diffuses into the cell, causing the cell a hypotonic solution, the water diffuses into the cell, causing the cell to swell and possibly explode. to swell and possibly explode.
Isotonic SolutionIsotonic Solution – solution where parts are equal in solute and – solution where parts are equal in solute and solvent – water moves across the membrane freelysolvent – water moves across the membrane freely
http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/science/sbi3a1/Cells/Osmosis.htm

Cell MembraneCell Membrane
1. regulates the flow of materials in & out 1. regulates the flow of materials in & out of the cellof the cell
2. selectively permeable – only certain 2. selectively permeable – only certain materials pass thru materials pass thru
3. made up of bilayer of phospholipids 3. made up of bilayer of phospholipids with protein molecules jutting thru the with protein molecules jutting thru the layerslayers

Cell WallCell Wall
Prokaryotic Cell WallProkaryotic Cell Wall Some have a 2Some have a 2ndnd outer layer composed of outer layer composed of
lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharideslipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides Eukaryotic Cell WallEukaryotic Cell Wall 3 parts – primary, middle lamella and secondary 3 parts – primary, middle lamella and secondary
cell wallcell wall Primary cell wallPrimary cell wall – cellulose – cellulose Middle LamellaMiddle Lamella – polysaccharides = pectins – polysaccharides = pectins Secondary cell wallSecondary cell wall – cellulose and lignin – cellulose and lignin

Cell WallCell Wall
Eukaryotic Cell WallEukaryotic Cell Wall Prokaryotic Cell WallProkaryotic Cell Wall

Movement Through MembraneMovement Through Membrane
Simple DiffusionSimple Diffusion Molecules pass thru phospholipids in the Molecules pass thru phospholipids in the
membranemembrane Only occurs for small non-polar moleculesOnly occurs for small non-polar molecules

Movement Through MembraneMovement Through Membrane Passive TransportPassive Transport 1. Protein channels 1. Protein channels
A. Proteins can form tunnels thru which A. Proteins can form tunnels thru which molecules can diffusemolecules can diffuse
B. Polar molecules can travel thruB. Polar molecules can travel thru

Movement Through MembraneMovement Through Membrane
2. 2. Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion A. Carrier proteins bond to a molecule on one A. Carrier proteins bond to a molecule on one
side of the membrane, travel across and side of the membrane, travel across and releases it on the other side.releases it on the other side.
B. Carrier proteins bond with specific B. Carrier proteins bond with specific molecules (like enzymes do)molecules (like enzymes do)

Movement Through MembraneMovement Through Membrane
Active TransportActive Transport Works against a concentration gradientWorks against a concentration gradient Requires an input of energyRequires an input of energy Contractile Vacuole is an example – it Contractile Vacuole is an example – it
forces excess water out of the cell even if forces excess water out of the cell even if it is against osmosisit is against osmosis
http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/library/biology107/bi107vc/fa99/terry/images/ATPpumA.gif

OrganellesOrganelles
Vacuoles Vacuoles – sacs in cell which hold food, – sacs in cell which hold food, water, and enzymeswater, and enzymes
VessiclesVessicles – small vacuoles formed from – small vacuoles formed from part of Golgi bodies to hold proteinspart of Golgi bodies to hold proteins
LysosomesLysosomes – sac contains digestive – sac contains digestive enzymes to break down food or damaged enzymes to break down food or damaged organellesorganelles

Vacuoles and VessiclesVacuoles and Vessicles
VacuoleVacuole VessicleVessicle

OrganellesOrganelles
NucleusNucleus – contains cell’s DNA, controls proteins – contains cell’s DNA, controls proteins and their productionand their production ““Cell’s brain”Cell’s brain” Surrounded by nuclear membrane which has pores to Surrounded by nuclear membrane which has pores to
allow RNA to pass thru into the endoplasmic reticulumallow RNA to pass thru into the endoplasmic reticulum
NucleolusNucleolus – inside nucleus, makes ribosomes – inside nucleus, makes ribosomes Usually each nucleus has several nucleoliUsually each nucleus has several nucleoli

NucleusNucleus

OrganellesOrganelles
RibosomesRibosomes Tiny structure responsible for protein Tiny structure responsible for protein
productionproduction Has its own ribosomal RNAHas its own ribosomal RNA Located in the endoplasmic reticulumLocated in the endoplasmic reticulum

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of tunnels running from nucleus Network of tunnels running from nucleus to Golgi bodiesto Golgi bodies
Rough ER contains ribosomes, Smooth Rough ER contains ribosomes, Smooth ER does notER does not
Function: carry proteins to the Golgi Function: carry proteins to the Golgi bodies and make new cell membranebodies and make new cell membrane

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)

Golgi BodiesGolgi Bodies
Stacks of membranous pouches at the Stacks of membranous pouches at the end of the ERend of the ER
Receive proteins from ER and send them Receive proteins from ER and send them to other organelles by putting them in to other organelles by putting them in vessiclesvessicles

MitochondriaMitochondria
Where cellular respiration occursWhere cellular respiration occurs Eukaryotes have thousands in their cellsEukaryotes have thousands in their cells Inner folded membrane (cristae) where Inner folded membrane (cristae) where
respiration occursrespiration occurs Have their own DNA and can replicate Have their own DNA and can replicate
themselvesthemselves

MitochondriaMitochondria

CytoskeletonCytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers allow the cell to Network of protein fibers allow the cell to change its shape – four typeschange its shape – four types
1. microtubules- involved in cell 1. microtubules- involved in cell reproductionreproduction
2. intermediate filaments – strength/shape2. intermediate filaments – strength/shape 3. microfilaments – cell locomotion3. microfilaments – cell locomotion 4. microtrabeculae 4. microtrabeculae – – connect organellesconnect organelles

PlastidsPlastids((only found in plants)only found in plants)
ChloroplastsChloroplasts green due to chlorophyllgreen due to chlorophyll Have grana and thykaloidsHave grana and thykaloids Photosynthesis occurs in thykaloidsPhotosynthesis occurs in thykaloids

PlastidsPlastids((only found in plants)only found in plants)
ChromoplastsChromoplasts Are like chloroplasts but not greenAre like chloroplasts but not green Allow photosynthesis to occur in different Allow photosynthesis to occur in different
lighting conditionslighting conditions

PlastidsPlastids((only found in plants)only found in plants)
LeucoplastsLeucoplasts Colorless, have no pigmentsColorless, have no pigments Stores starch proteins and lipidsStores starch proteins and lipids Releases them when the cell needs themReleases them when the cell needs them

Unicellular MovementUnicellular Movement
Cilia Cilia Tiny hairs on outside of cell membrane Tiny hairs on outside of cell membrane
used for locomotionused for locomotion

Unicellular MovementUnicellular Movement
FlagellaFlagella Large hair on outside of cell membrane Large hair on outside of cell membrane
used for locomotionused for locomotion Both are composed of microtubulesBoth are composed of microtubules

Unicellular MovementUnicellular Movement
Psudopodia – not truly an organellePsudopodia – not truly an organelle Extension of the cytoplasm which the rest Extension of the cytoplasm which the rest
of the cytoplasm flows toof the cytoplasm flows to Used for movementUsed for movement Surrounds and captures preySurrounds and captures prey