Cell Structures
description
Transcript of Cell Structures
-
Introduction toCytology or Cell Biology
-
How do we observe cells?Light microscopeVisible light passes through objectLens magnify image
Electron microscopeScanning - surface of objectTransmission - sees through objects100,000 X to Millions magnification power
-
How do we know what happens in each part of the cell?Radioisotopes are used to "trace" different chemical reactions through a cell.
Separate cellular structures with a blender
Centrifuge material and analyze each layer.
-
People who were important in early cell discovery:
-
Zacharias Jannsen (1590)Helped invent the First compound microscope
-
Robert Hooke (1665) Observed dead cork - called them cellsCompound Microscope
-
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1674) - living cells in pond water; one celled organisms -- animalcules
-
Robert Brown (1831) identifies the nucleus of a cell
-
Mattias Scleiden (1838) stated that plants are made up of cells
-
Theodor Schwann (1839)stated that animals are made up of cells
-
Rudolph Virchow (1858) Studied the pathology of cells. (ability to cause disease)
All cells arise from preexisting cells. New cells can only arise from other living cells by the process of cell division or reproduction
-
Cell TheoryAll living things are composed of cells
Cells are the fundamental building block of life
All cells come from pre-existing cells (life begets life)
-
PROCESSES OF CELLSAll life processes involve energy changes.
1. Nutrition - food is needed for energy and building materials.
2. Digestion - breaking down reactions of food into usable parts.
3. Absorption - water, food, ions and other materials
4. Biosynthesis - cells organize many organic substances for cell activity. 5. Respiration - cell energy is released when certain organic molecules are split - energy is used for cell activity.
-
6. Excretion - waste materials passed from cell to environment
7. Secretion - synthesized molecules which are passed out of a cell and which affect the activities of other cells (vitamins, hormones)
8. Reproduction - cells divide; unicellular - more organisms, multicellular - more cells.
9. Movement - motion of all types; cellular contractions, flowing substances within the cell
10. Egestion - elimination of insoluble compounds and nondigestible particles
-
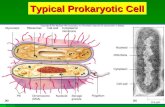
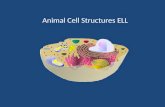
Eukaryotic cells advanced cellsHave nucleusPlasma membraneCytoplasm - everything between plasma membrane and nucleusOrganellesFluidCytoskeleton threads of microtubules and microfilaments in cytoplasm
-
Animal vs Plant CellAnimal cells have unique structuresCentriolesLysosomeFlagellum 1. 2.
3. Plant cells have unique structures Large central vacuoleCell wall 1. 2. Chloroplasts
3.
-
MitochondrionPlasma MembraneCell WallCentral VacuoleVesicleRibosomesEnvelopeDNA NucleolusCytoskeleton FibresChloroplast Pore Golgi BodySmooth ER Rough sdfERMitochondrion
-
Centriole
-
Plasma Membrane
Protein Marker
Sugar Chain Lipid BilayerCholesterol ProteinsEmbedded ProteinOUTSIDE OF CELLINSIDE OF CELL
-
Cell Membrane Side Profile
-
Different membranes
All have similar functions & structuresPlasma membrane separates inside of cell from outside of cellOther membrane define organelles to form compartments of eukaryotic cells
Forms a selectively permeable layerLets some things in or out but not allLike a window screen
-
Nucleus
-
EnvelopeDouble membranePores to get messages in and outChromatinDNA threadsProtein balls called histones - wrappingNucleolus - site of ribosome production
Nucleus - Structures
-
Nucleolus where rRNA or Ribosomes are made
-
Ribosomes
-
Consists of 2 parts, which are made in nucleus
Make protein in the Cytoplasm
Produce proteins from recipes in the nucleus copied into mRNASome (proteins) will remain in cytoplasmSome will be exported out of cellSome will attach to membranes in cell
Ribosomes are found on the endoplasmic reticulum and in the cytoplasm
-
Endoplasmic ReticulumRough ERSmooth ER
-
Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumRough ER - attached to nucleus
Ribosomes stud surface
Produces Membrane proteins - stay in cellSecretory proteins - exported from cell
-
RER makin Proteins!
-
Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumNo ribosomes, so not protein factoriesMore like transport systemMakes steroids, lipidsLiver cells have lots of smooth ERDetoxify chemicalsSupply and demandIncreases tolerance to drugSo higher doses needed for same effect
-
Golgi apparatus the Post Office of the Cell
-
Refines, stores and marks molecules for shipmentLooks like stack of hollow pancakesProducts of ER arrive & leave via transport vesiclesMoving from one sac to the nextMolecules get modifiedLabeled and / or storedCalled the cell Post office because it marks and directs products in the cell
Golgi apparatus what it does
-
Lysosome
-
Greek for breakdown bodyRecylcerSac of strong digestive enzymesCompartmentalized for safetyCan release to breakdown entire cell suicide sackFunctionsDigest food vacuolesDigest invading bacteriaDigest old organelles
Lysosome
-
Lysosome
-
Lysosomal diseasesGenetic disordersRecipe is messed up so protein doesnt workIf recipe for lysosome enzymeWhat should get broken down doesntEx. Tay Sachs Lipids arent broken downBuild up occursEventually causes deathUsually in before age 5
-
Mitochondria
-
MitochondriaSite of cellular respirationConversion of food into energy (ATP)ATP is what cells use to make things happen (drive chemical reactions)Double membraneBig bag stuffed in smaller bagFolds of inner bag called cristaeSpace inside inner bag called matrixAlso once free living bacteriaEfficiency - gasoline engines converts 25% of energy mitochondria converts 54% of energy
-
contains some of its own DNA (amount varies within organisms) believed to evolved from a primitive cell engulfing it and creating a symbiotic relationship DNA in mitochondria obtained only from mother of organism.
-
Plant Organelles Chloroplasts - in plantsChloroplast1. chlorophyll is green chemical that releases electrons, working like a solar panel in sunlight
2. forms glucose
3. photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2 O ---> C6H12 O6 + 6O2
-
Chloroplasts
-
Structure of ChloroplastDouble membraneGranaStack of thylakoidsHollow diskWhere sunlight energy is captured and converted to chemical energyStromaThick fluid filling chloroplastContains some DNAOnce free-living bacteria
-
Cytoskeleton
-
Actin filamentsMicrotubules
-
Network of fibers
Give shape to cellsAllow movement of cellMove organelles aroundMade of microtubules and microfilaments
Role of the Cytoskeleton
-
Cilia
-
Flagella
-
9+2 Arrangment in Cilia or Flagella
-
Basal Body of a Flagella or CiliaNote the triplet rings of tubulin protein
9+0 arrangementNine sets of rings, with no set in middleUsed to set up 9+2 arrangment in cilia or flagella
-
CentriolesCell reproduction; goes to poles of cell during cell division and helps cell divide
-
Centrioles at Work in Cell Division
-
Cell SpecializationDifferent kinds of cells suited for a different activity.
Division of LaborDifferent cells divide their labor each has a specific function and supports each other.
-
Levels of structure1. Cell2. Tissue3. Organ4. Organ system5. Organism
-
Tissue Level A group of cells that are alike in structure and activity in an organism muscles
- Skeletal muscle cells motion- Cardiac muscle cells heartbeat- Bones - support- Nerve cells - coordination, perception and automatic body functions
-
Organ Level several tissues working as a unitheartAnimalsbrain stomachroots Plantsstemleaf
-
Organ Systemmany organs involved in carrying out a function
digestive nervous skeletal excretory respiratoryendocrine (hormones)circulatory muscularreproductive
-
Organism complete living thingcell tissueorganorgan systemorganismINCREASING SIZE