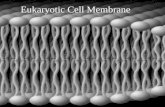
Cell Membrane “Keeping it all Together”. Cell Membrane ► Defines the cell ► About 8 nm thick...
-
Upload
gilbert-palmer -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Membrane “Keeping it all Together”. Cell Membrane ► Defines the cell ► About 8 nm thick...
Cell MembraneCell Membrane
►Defines the cellDefines the cell►About 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the About 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the
thickness of one page of paper)thickness of one page of paper)►Helps to regulate the cell (maintain Helps to regulate the cell (maintain
equilibrium/homeostatic state)equilibrium/homeostatic state)►Selectively permeableSelectively permeable►Fluidity (lipids/proteins can shift Fluidity (lipids/proteins can shift
laterally)laterally)
Cell Membrane ArchitectureCell Membrane Architecture
►Lipids and Proteins – staple ingredients Lipids and Proteins – staple ingredients Most abundant lipids – phospholipidsMost abundant lipids – phospholipids
►Phospholipids are amphipathetic Phospholipids are amphipathetic (philic/phobic)(philic/phobic)
►Fluid Mosaic ModelFluid Mosaic Model
Lipid Bilayer Structure cont…Lipid Bilayer Structure cont…
►Each lipid molecule contains a Each lipid molecule contains a hydrophilic regionhydrophilic region or polar head or polar head regionregion and a and a hydrophobic region hydrophobic region or or non polar tail region.non polar tail region.
The hydrophilic region is attracted to aqueous water conditions while the hydrophobic region is repelled from such conditions
Freeze FractureFreeze Fracture
►A cell membrane can be split (with a A cell membrane can be split (with a knife) into it’s two layers revealing the knife) into it’s two layers revealing the ultrastructure of the membrane’s ultrastructure of the membrane’s interior.interior.
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
►While the lipid bilayer While the lipid bilayer provides the provides the structurestructure for the cell membrane, for the cell membrane, membrane proteins allow for many of membrane proteins allow for many of the interactionsthe interactions that occur between that occur between cells.cells.
►More than 50 kinds of proteins found More than 50 kinds of proteins found (so far) in the plasma membrane of (so far) in the plasma membrane of RBC’s for example. RBC’s for example.
Classifying Membrane Classifying Membrane ProteinsProteins
►Proteins are generally broken down Proteins are generally broken down into the smaller classifications of into the smaller classifications of integral proteins and peripheral integral proteins and peripheral proteinsproteins
Integral ProteinsIntegral Proteins
► Integral proteins are embedded within Integral proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer and partially penetrate the lipid bilayer and partially penetrate the hydrophobic core.the hydrophobic core.
►Many are transmembrane proteinsMany are transmembrane proteins►Example of an integral protein is Example of an integral protein is
“integrins”. These attachments “integrins”. These attachments combine to give animal cells a stronger combine to give animal cells a stronger framework that the plasma membrane framework that the plasma membrane could alone.could alone.
Peripheral ProteinsPeripheral Proteins
►Peripheral proteins are not embedded Peripheral proteins are not embedded in the lipid bilayer at allin the lipid bilayer at all
►They are appendages loosely bound to They are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane, often to the surface of the membrane, often to exposed parts of the integral proteins. exposed parts of the integral proteins.
►Some are attached to the cytoskeleton Some are attached to the cytoskeleton of the cell.of the cell.
Membrane TransportMembrane Transport
► We have discussed how the lipid bilayer acts as an We have discussed how the lipid bilayer acts as an efficient barrier by only allowing a very small efficient barrier by only allowing a very small number of non-polar molecules to freely enter or number of non-polar molecules to freely enter or exit a cell. exit a cell.
► While for the most part this While for the most part this selectivityselectivity is a is a valuable function and allows the cell to maintain its valuable function and allows the cell to maintain its integrity, integrity, cells do need to move certain large, cells do need to move certain large, polar molecules such as amino acids, sugars, polar molecules such as amino acids, sugars, andand nucleotidesnucleotides across their membranes. across their membranes.
► As a result, cell membranes require specific As a result, cell membranes require specific structures that allow for the transport of certain structures that allow for the transport of certain molecules. molecules.
Membrane TransportMembrane Transport
►There are a number of different ways There are a number of different ways that molecules can pass from one side that molecules can pass from one side of a cell membrane to the otherof a cell membrane to the other
► Some such means, like Some such means, like diffusiondiffusion and and osmosisosmosis, are natural processes that , are natural processes that require require no expenditure of energy no expenditure of energy from the cellfrom the cell and are called and are called passive transportpassive transport. .
Membrane TransportMembrane Transport
► Other methods of transport do Other methods of transport do require cellular energyrequire cellular energy and are and are called called active transportactive transport
► In addition to these two forms of In addition to these two forms of transport, there exist other forms of transport, there exist other forms of transport such as transport such as endocytosisendocytosis and and exocytosisexocytosis, which will be discuss , which will be discuss later. later.
Passive TransportPassive Transport
►Diffusion is the natural phenomenon in Diffusion is the natural phenomenon in which nonpolar molecules naturally flow which nonpolar molecules naturally flow from an area of from an area of higher concentration to higher concentration to an area of lower concentration - an area of lower concentration -
►Diffusion DOES NOT require energy!Diffusion DOES NOT require energy!
►OsmosisOsmosis is a similar process, but refers is a similar process, but refers specifically to water molecules. specifically to water molecules.
http://http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/westmin/science/Sbi3a1/science/Sbi3a1/cells/cells/Osmosis.htmOsmosis.htm
Active TransportActive Transport
Requires energy or ATP
Moves materials from LOW to HIGH concentration
AGAINST concentration gradient
Transport ProteinsTransport Proteins►Both of passive and active transport Both of passive and active transport
are mediated with the help of are mediated with the help of transmembrane proteinstransmembrane proteins that that act act as transporters as transporters
►Two main classes of transport Two main classes of transport proteinsproteins are are carrier proteinscarrier proteins and and channel proteinschannel proteins..
Transport Proteins cont…Transport Proteins cont…
►For the most part, carrier proteins For the most part, carrier proteins mediate active transport while channel mediate active transport while channel proteins mediate passive transport proteins mediate passive transport
Transport Proteins cont…Transport Proteins cont…
►Transport proteins are critical to cell life Transport proteins are critical to cell life and cell interactions. and cell interactions. They allow for They allow for the proper distribution of ions and the proper distribution of ions and molecules in multicellular molecules in multicellular organismsorganisms. Additionally, they can help . Additionally, they can help to to maintain proper intra- and extra-maintain proper intra- and extra-cellular pH levels, facilitate cellular pH levels, facilitate communication between cells, and communication between cells, and are involved numerous other are involved numerous other essential functions including protein essential functions including protein sythesissythesis. .
Checkpoint QuizCheckpoint Quiz
►QUESTION 1: QUESTION 1: The cell membrane is made up of a The cell membrane is made up of a _____ bilayer._____ bilayer.
Carbohydrate Carbohydrate Lipid Lipid Protein Protein None of the Above None of the Above
Answer to Question 1Answer to Question 1
►Cell membranes are also described as Cell membranes are also described as lipid bilayers. There are two layers of lipid bilayers. There are two layers of phospholipids with proteins embedded phospholipids with proteins embedded in the layers. The membrane is able to in the layers. The membrane is able to move as needed by the cell. move as needed by the cell.
QuizQuiz
►QUESTION 2: QUESTION 2: All eukaryotic cells are surrounded by All eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell membrane.a cell membrane.
True True False False
Answer to Question 2Answer to Question 2
►Eukaryotic cells have an organized Eukaryotic cells have an organized nucleus and cell organelles. All of nucleus and cell organelles. All of these cells have a membrane. Plant these cells have a membrane. Plant cells have a cell membrane and cell cells have a cell membrane and cell walls. walls.
Quiz Quiz
►QUESTION 3: QUESTION 3: The lipids in the bilayer have tails that The lipids in the bilayer have tails that are...are...
Hydrophilic Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Hydrophobic
Answer to Question 3Answer to Question 3
►The tail end of a phospholipid The tail end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic. The tails do molecule is hydrophobic. The tails do not like to be near water and arrange not like to be near water and arrange themselves so that tails meet tails and themselves so that tails meet tails and the heads face the cellular fluids and the heads face the cellular fluids and exterior of the cell. exterior of the cell.
QuizQuiz
►Question 4: The heads of the lipids in Question 4: The heads of the lipids in the cell membrane are...the cell membrane are...
Hydrophilic Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Hydrophobic
Answer to Question 4:Answer to Question 4:
►The head end of a phospholipid The head end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic. The heads like molecule is hydrophilic. The heads like to be near water and arrange to be near water and arrange themselves so that tails meet tails and themselves so that tails meet tails and the heads face the cellular fluids and the heads face the cellular fluids and exterior of the cell. exterior of the cell.
QuizQuiz
►QUESTION 5: QUESTION 5: Some molecules can pass through a Some molecules can pass through a cell membrane without help.cell membrane without help.
True True False False
Answer to Question 5Answer to Question 5
►Some molecules can pass through the Some molecules can pass through the cellular membrane by a process called cellular membrane by a process called diffusion. Other molecules are too diffusion. Other molecules are too large to pass through the membrane large to pass through the membrane and must be helped across the lipid and must be helped across the lipid bilayer. bilayer.
Answer to Question 6Answer to Question 6
►There are proteins embedded in the There are proteins embedded in the cell membrane. Some of the proteins cell membrane. Some of the proteins pass through the membrane and pass through the membrane and others are only attached to the others are only attached to the surface. The proteins serve several surface. The proteins serve several functions. functions.
QuizQuiz
►QUESTION 6: QUESTION 6: You will also find proteins in the lipid You will also find proteins in the lipid bilayer.bilayer.
True True False False
Overview of Membrane Overview of Membrane TransportTransport
For a visual of the processes discussed, For a visual of the processes discussed, check out:check out:
►http://phschool.com/webcodes10/http://phschool.com/webcodes10/index.cfm?index.cfm?wcprefix=cbe&wcsuffix=3076&fuseactionwcprefix=cbe&wcsuffix=3076&fuseaction=home.gotoWebCode&x=0&y=0=home.gotoWebCode&x=0&y=0
►Assignment:Assignment: Read section 7-3 and Read section 7-3 and answer questions 1-6 on page 189answer questions 1-6 on page 189
►Copy Figure 7-16 into notesCopy Figure 7-16 into notes