Cell Membrane
description
Transcript of Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane11/16/101Cell Membrane
FunctionControls what enters and exits the cell.ImportanceBy regulating this movement it helps the cell to maintain homeostasis.HomeostasisMaintaining a constant internal state in a changing environment.All living things respond to their environment Cells maintain homeostasis by limiting the movement of substances across the cell membraneActs as a gatekeeper
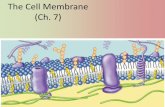
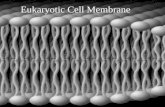
StructurePhospholipid bilayerHydrophilic headsHydrophobic tailsCarrier ProteinsHelp transport through membraneCell MembraneSolutionsIn solutions, moving molecules fill up a space.Equilibrium is when the concentration of a substance is the same throughout a space.When there is a difference in the concentration of a substance, a concentration gradient exists.This concept will be important when talking about some of the vocabulary.Movement Across MembranesTwo types of transportPassive TransportRequires no energy to occurActive TransportRequires energy to occur Boat Analogy
Types of Passive TransportDiffusionMovement of a substance from high concentration to low concentrationDiffusion of water is referred to as osmosis.Facilitated DiffusionUses carrier proteins to help the substances diffuse through the cell membrane.http://www.zerobio.com/flashmx/transport.swf Diffusion
OsmosisPredicting the movement of water depends on the concentration of the cells environmentSolutions can have three different concentrations:Hypertonic: Higher concentration outside the cell.Isotonic: Concentration is the same inside and outside the cell.Hypotonic: Lower concentration outside the cell.http://www.zerobio.com/flashmx/tonicity.swf Osmosis PracticeSaltwater solutionWhat is the solute?What is the solvent?Water is the substance moving through the membrane.Which way will the water move?90% Saltwater98% SaltwaterOsmosis PracticeSaltwater solutionWhat is the solute?What is the solvent?Water is the substance moving through the membrane.Which way will the water move?4% Saltwater2% SaltwaterOsmosis PracticeSugarwater solutionWhat is the solute?What is the solvent?Water is the substance moving through the membrane.Which way will the water move?15% Sugarwater15% SugarwaterActive TransportIn active transport, substances are being transported against their concentration gradient.Requires energyMolecules move from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration
Active TransportCell Membrane PumpsProteins that move molecules through the cell membrane
Active TransportEndocytosisMovement of molecules into the cell through a vesicleExocytosisMovement of molecules out of the cell through a vesicle