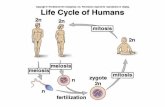
Cell Division—Mitosis Notes Cell Division — process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells
Cell Division— Mitosis Notes. Cell Division — process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells.
-
Upload
whitney-harvey -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Division— Mitosis Notes. Cell Division — process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells.

Cell Division—Mitosis Notes

Cell Division — process by which a cell divides
into 2 new cells

Why do Cells Need to Divide?
• We know cells are microscopic and can only be seen through a microscope.• Cells are small for a reason!

Why do Cells Need to Divide?
• Transport of materials in and out of the cell is MUCH FASTER over short distances. If a cell was too large, the process would take too long.

Why do Cells Need to Divide?
• DNA is responsible for coding the proteins our cells need to survive. The larger the cell, the more protein it would need and DNA could not keep up!

Why do Cells Need to Divide?
• Surface Area to Volume Ratio – the larger the cell, the more volume it has. More is needed and more waste is produced. It would need more surface area than the membrane could provide.

Why do cells need to divide?
• Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in size




Cell Reproduction
• Remember from the cell theory that all cells come from preexisting cells, so genetic information has to be passed from one generation to the next.

Cell Reproduction
• Genetic information is contained in DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid which is in the nucleus of a cell.

Cell Reproduction
• DNA exists in the nucleus as long, threadlike strands called chromatin. THERE is so much DNA material that has to fit inside a tiny little cell! How do we do that?

Cell Reproduction
• Cells pack all of that DNA into a tiny little nucleus by winding it up into coiled structures called chromatin.

Cell Reproduction
• When a cell is going to divide and produce more cells, the chromatin winds up into a double, coiled structure called a chromosome.


Cell Division
• All cells of the body EXCEPT the sex cells are called somatic cells.• Blood cells, nerve cells, skin
cells, etc.

Cell Division
• New somatic cells are made when one parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells

Cell Division
• For example, if you get a cut on your skin, eventually it heals up and new skin forms. This is because skin cells have multiplied and made EXACT copies of themselves for healing.

Cell Division
• So there has to be a way for new cells to form that have the EXACT SAME DNA as the parent cell. There must be DUPLICATION.

Cell Division
• The Cell Cycle: The process somatic cells go through in order to grow and reproduce

The Cell Cycle
• The cell cycle is divided into two main parts:• Interphase• Mitosis (M Phase)

Interphase
• Interphase– this is a time of growth and a time when DNA is replicated (a copy is made) inside the nucleus of the cell

Interphase
• It is divided into 3 parts:
• G1 Phase – G is for GROWTH! The cell is growing and making proteins

Interphase
• S Phase – S is for SYNTHESIS (making something). This is when the DNA is replicated and an identical set of chromosomes is made

Interphase
• G2 Phase – G is for GROWTH. The cell continues to grow and is getting ready for mitosis (division)

Mitosis
• The second part of the cell cycle is mitosis and cytokinesis.• Mitosis is when the nucleus
divides• Cytokinesis is when the entire
cell divides



Mitosis
• Mitosis is divided into 4 phases:• Prophase• Metaphase• Anaphase• Telephase

Prophase
• The chromatin coils up tightly, gets shorter and thicker, and can be seen in the nucleus.

Prophase
• The chromatin is lined up in a way that two sister chromatids are held together at a middle point called a centromere. Each sister is a duplicate of the other (this was done in S phase).


Prophase
• The nuclear membrane disintegrates and a spindle starts to form.• Spindle – Microtubules that line
up in a spindle form in the cell to help division



Metaphase
• Chromatids line up in the MIDDLE.• They attach to the spindle at the
centromere in the middle of the nucleus (equator)


Anaphase
• Chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle. Each chromatid is now its own chromosome


Telophase
• The chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell and start to unwind.• Spindle disappears

Telophase
• Two new nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes to form two new nuclei

Cytokinesis
• The cytoplasm divides during cytokinesis

Plant vs Animal
• In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches inward and gradually separates


Plant vs Animal
• In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the two nuclei and grows out to the edges, dividing the cell in half.


Plant vs Animal
• Remember: In the plant cell, a new cell membrane will form around each cell and a cell wall forms around the outside.


Interphase M Phase (Mitotic)G1-Growth Prophase – Chromatin
Condenses
S-Synthesis-DNA Replication
Metaphase – Chromatids line up in the middle
G2 - Growth Anaphase – Chromatids separate
Telophase – New nuclear membranes

Identify the Following Stages of Mitosis!










What is the longest part of the cell cycle?

Interphase

In which part of interphase are the chromosomes replicated?

S Phase

During what part of interphase does the cell grow and prepare
for mitosis?

G2

What is the division of the nucleus called?

Mitosis

What is the division of the entire cell called?

Cytokinesis

If you are observing a cell and notice that the chromosomes appear to be lined up in the middle of the nucleus, what
stage of mitosis are you observing?

Metaphase

If it looks as though the cell you see through the microscope
has two nuclei, what stage of mitosis are you observing?

Telophase

A cell plate is forming in one of the cells that you are
observing. Which of the following type of cells could
you be viewing?

a. Human skin cellsb. Root tip cellsc. A fly’s eyed. bristles of an earthworm

Root tip cells!

In which of the following circumstances would cells NOT
divide by the process of mitosis?

a. Repairing a cutb. Adding cells for an infant to growc. Creating sex cellsd. Replacing old skin cells

Creating sex cells

How many times do chromosomes separate during
the process of mitosis?

One

http://v7.k12.com/sample_lessons/activities/images/swfs/9-12/ObservingMitosis.swf