Cell Division by Mitosis. all living things start life as a single cell Growth results when your...
-
Upload
gregory-parrish -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Division by Mitosis. all living things start life as a single cell Growth results when your...

Cell Division by Mitosis

• all living things start life as a single cell
• Growth results when your body forms new cells.
• New cells are formed by cell division

• There are two types of cell division
1. mitosis (division of body cells)
2. mieosis (division of sex cells)

• two cells are formed from one cell
• new cells are similar to old cell
• the new cells replace old cells
• root cells, skin cells, muscle cells are examples

• - for many simple organisms (like bacteria and some algae) mitosis = reproduction

• mitosis is NOT a one step process• as a cell divides some of the cell parts
change• it forms two new cells. The number of
cells increases every time cells divide.• the number of chromosomes in each
cell remains the same


Interphase (resting)• “resting” describes
cells that have not started to divide
• occurs between cell divisions
• longest part of the cell cycle

• chromatin is coiled DNA inside the nucleus,– Later,chromatin
condenses to form chromosomes
• during interphase, the DNA is replicated (copied) and the cell prepares for division

Interphase in an Onion Root Tip

Prophase (mitosis begins)• during this phase the
chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
• The original chromosome and the copied chromosome form a pair, called a chromatid.

• pair of sister chromatids = chromosome
• joined together at a central point called the centromere
• the membrane surrounding the nucleus begins to disappear

Prophase in an Onion Root Tip

Metaphase• membrane
surrounding the nucleus totally disappears
• sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell (metaphase plate)

Metaphase in an Onion Root Tip

Anaphase • chromatids separate
at the centromere and move to opposite ends of the cell– Separate using spindle
fibers
• once separated, the chromatids are now identical daughter chromosomes

Anaphase in Onion Root Tip

Telophase • nucleus forms
around both sets of daughter chromosomes
• cell splits and two new cells are formed (cytokinesis)

Telophase in an Onion Root Tip

• a cell that divides too fast can form a tumor• cells divide too fast because of mutations
(changes) in the cells DNA
- mutations can occur because of
1. genetics
2. environmental factors
- UV radiation from sun
- cigarette smoke

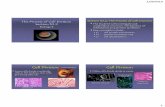
The Cell Cycle and Cancer

The Stages of the Cell Cycle
1. Click on picture for cell cycle animation – will go to www.cancerquest.org)2. Use alt-tab keys to go between website and power point presentation. 3. Click on blank space to proceed to next slide.)

There are several factors that regulate the cell cycle and assure a cell divides correctly.
1.Before a cell divides, the DNA is checked to make sure it has replicated correctly. (If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs.
DNA replication animation:click on DNA picture

2. Chemical Signals tell a cell when to start and stop dividing.
(Target cells animation: click on go sign)

Neighboring cells communicate with dividing cells to regulate their growth also.
(Normal contact inhibition animation: click on petri dish)

Cancer is a disease of the cell cycle. Some of the body’s cells divide uncontrollably and tumors form.
Tumors in Liver
Tumor in Colon

DNA mutations disrupt the cell cycle.
Mutations may be caused by:
1. radiation 2. smoking 3. Pollutants 4. chemicals 5. viruses

While normal cells will stop dividing if there is a mutation in the DNA, cancer cells will continue to divide with mutation.

Due to DNA mutations, cancer cells ignore the chemical signals that start and stop the cell cycle.
2 animations of cancer cells dividing: click on picture

Due to DNA mutations, cancer cells cannot communicate with neighboring cells. Cells continue
to grow and form tumors.
(cancer cells dividing: click on picture.)
Skin cancer

SUMMARY
Normal Cell Division
1. DNA is replicated properly.
2. Chemical signals start and stop the cell cycle.
3. Cells communicate with each other so they don’t become overcrowded.
Cancer Cells
1. Mutations occur in the DNA when it is replicated.
2. Chemical signals that start and stop the cell cycle are ignored.
3. Cells do not communicate with each other and tumors form.

Treating Cancers
Cancer treatments include drugs that can stop cancer cells from dividing.

• 1. In mitosis, how many cells are formed from each dividing cell?
• 2. What is copied in the nucleus before the cells divide?
• 3. If a cell has 46 chromosomes and divides
by mitosis, how many chromosomes will each new cell have?