Template by Bill Arcuri, WCSD Jeopardy The Cell Cycle Review.
Cell Cycle Review
description
Transcript of Cell Cycle Review

Cell Cycle Review

What limits cell size?– Not enough DNA– Moving materials into and out of the cell

What are the parts of the cell cycle?– Interphase (G1, S, G2)– Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis)

What are the parts of interphase?– G1 – First Growth Phase (organelles synthesized)– S – Synthesis Phase (chromosomes synthesized)– G2 – Second Growth Phase (organelles for cell
division synthesized)

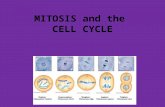
What are the 4 parts of mitosis?– Prophase– Metaphase– Anaphase– Telophase







A.
B.


















The division of the cytoplasm.

A nuclear envelope re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes.

The spindle begins to break apart, and a nucleolus becomes visible.

Chromosomes begins to unwind to form chromatin.

The centromeres that join the sister chromatids split, allowing the sister chromatids to separate and become individual chromosomes.

Chromosomes continue to move until they have separated into two groups near the poles of the spindle.

Chromosome line up in the middle/center of the cell.

Microtubules connect the centromere of each chromosome to the two poles of the spindle.

Chromosomes appear.

Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell.

Spindle fibers become attached to the chromosomes at their centromere.

Nuclear membrane breaks down. Nucleolus disappears.

Includes G1, S and G2 Phase. Cell Grows and Replicates DNA.

Replication of DNA

Normal Cell Growth.

Final preparation for mitosis.

Why do our cells divide? – Pass genetic information to new cells– Reproduction– Growth– Replace old cells/dying cells – Replaced damaged or missing cells.