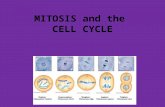
Cell cycle and mitosis. The sequence of events from one division of a cell to the next; consists of...
-
Upload
daisy-manning -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell cycle and mitosis. The sequence of events from one division of a cell to the next; consists of...

Cell cycle and mitosis

The sequence of events from one division of a cell to the next; consists of
mitosis (or division) and interphase.
A progress of a parent cell from creation to cellular division ( it contain
growth, development and DNA synthesis).
Cell cycle Definition
• The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication).
• In cells without a nucleus (prokaryotic), the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission.
• In cells with a nucleus (eukaryotes), the cell cycle can be divided in two brief periods: interphase—during which the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis and duplicating its DNA and the mitosis (M) phase, during which the cell splits itself into two distinct cells, often called "daughter cells".

Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell
separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two
identical sets in two nuclei.
It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis,
which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell
membrane into two cells containing roughly equal
shares of these cellular components.
Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M)
phase of the cell cycle

Cytokinesis: The division of the cytoplasm during cell
division.
Cytokinins: A group of hormones that promote cell
division and inhibit aging of green tissues in plants.
Centriole: Structures in the cytoplasm from which the
spindle apparatus forms during cell division in
eukaryotes.
Centromere: Constriction locted in the chromosome;
serves as an attachment site for sister chromatids and
spindle fibers .
Sister chromatid: Two identical copies of a parent
chromosome which are attached to one another at the
centromere.
Spindle fibers: A protein structures which move the
chromosomes during cell division.
Cell cycle Glossary

Cell cycle

1. Interphase:
which has three phase;
a. First Gap (G1 phase)
b. DNA Synthesis (S phase)
c. Second Gap (G2 phase)
2. Cell division ( Mitosis or Meiosis)
Cell cycle divided to two stages:

First gap is usually longest period of cell
cycle
Cell grows and Size increases
Cytoplasmic growth
Organelle development
Normal metabolism happen
G1 prepares the cell to undergo the next
stage of synthesis
Interphase: First Gap (G1 phase)

All chromosomes are duplicated; the
chromosomes number does not change, but
total amount of DNA doubles.
New proteins synthesized to assemble with
new DNA to form new Chromatid.
replication begins at many sites along the
length of a chromosome
time to complete S phase varies between
different life stages and between species
Interphase: DNA synthesis (S phase)


Cell prepares itself for mitosis by synthesizing
needed components.
Construction of new spindle apparatuses which use
in chromosome movement during cell division.
Condensation of DNA into chromosomes begins.
Interphase: Second Gap (G2 phase)

1. Nuclear division:
which has four phase;
a. Prophase
b. Metaphase
c. Anaphase
d. Telophase
2. Cytoplasm division
(Cytokinesis )
Mitosis divided to:

Mitosis: 1. Prophase
1. The DNA in the nucleus coils and condenses
to form visible chromosomes.
2. Duplicated chromosomes are composed of
two sister chromatids attached by the
centromere.
3. Spindle apparatus completes formation and
centrioles move to opposite poles.
4. Nucleolus disappears.
5. Nuclear membrane disappear.

Prophase

Mitosis: 2. Metaphase Microtubules penetrate the nuclear region and form
the spindle apparatus to attachment with chromosomes at the centromeres.
Chromosomes move to a metaphase plate which is formed along the midline of the cell between the poles
Chromosomes are at their most condensed state now.
Metaphase chromosomes can be stained and will show distinctive banding patterns.

Metaphase

The spindle at metaphase
Centriole
• Sister chromatids
• Kinetochore fibers
• Nonkinetochore fibres

Mitosis: 3. AnaphaseSpindle fibers shorten and attachments between
the two sister chromatids of the chromosomes break.
The two are now separate chromosomes that move to opposite spindle poles.
Each chromosome now has only one chromatid.
Centromere divide to create two chromosomes.
Anaphase results in the exact division of chromosome, distributing one complete diploid complement of genetic information to each daughter cell

Anaphase

Mitosis: 4. Telophase
Chromosomes assemble at the poles.
A new nuclear envelopes reassemble and
surround each set of daughter chromosomes.
Nucleoli reappear inside the newly formed
nuclei.
Chromosomes decondense in the daughter cells
to become chromatin and the cells are once
again in Interphase.

Telophase

Mitosis: Cytoplasm division (Cytokinesis )
Cells separate;
Animals, plant, algal, and fungal cells differ in the way cells separate
Animal cells form a cleavage furrow
Plant cells form a central plate



Which one is a prophase?
11 22 33 44

What are these?

Metaphase or telophase?