CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
Transcript of CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
1/49
Lecture 2
Management and decision-making (1)
Introduction to business strategy
Consequences for management decision-making
1
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
2/49
Introduction to the module
Scope of study
What is a Management Support System?
Blog for learning materials Coursework
groups of 4: group membership form
case study: Officionado
need to be preparing underlying database will be developing a management support system
2
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
3/49
Management decision-making what sorts of decisions do business managers need to make?
Business strategy introduction to some strategic planning techniques
Consequences for management decision-making how can strategic planning inform our thinking about key
management decisions?
3
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
4/49
Techniques Porters generic competitive strategies
Porters value chain analysis
SWOT analysis
BCG matrix SCM and CRM
What is strategy?
Strategic planning - process overview
Performance measurement and the balancedscorecard
4
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
5/49
Porter identifies
three generic strategies
for achieving competitive advantage in the context
of the five forces identified below
5
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
6/49
Porters competitive strategies
These are:
Overall cost leadership:
control and reduction of costs across all areas of the business
from the basic premise that:
Profit = Revenue Costs
reduced costsimpliesincreased profit
6
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
7/49
Porters competitive strategies
Differentiation:
involves making the product or service recognisably
differentoruniqueacross the whole industry sector,
thereby enabling an increase in the priceof that product orservice (with a consequent increase inprofit)
7
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
8/49
Porters competitive strategies
Focus:
specialising the product and/or service
for a particular market niche
e.g. by geographical region,
vertical market sector, etc.
8
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
9/49
Porters Value Chain Analysis
Administration and infrastructure
Human Resource Management
Product technology / development
Procurement
Inbound
logistics
Operations Outbound
logistics
Sales and
Marketing
Services
Value
addedcost=
margin
9
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
10/49
Porters Value Chain Analysis
Pearlson & Saunders, 2003
10
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
11/49
Porters Value Chain Analysis
"Porter's value chain is a framework for considering
key activities within an organisation
and how well they add value
as products and services move from conception
todelivery to the customer
(Chaffey, 2003)
11
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
12/49
Supply chain management
The planning and control of materialsfrom identifying the need
through to delivery to the customer
Objective:
to optimise performance in meeting customer requirements
i.e. increasing profit by minimising costs
and making thebest use of resources
12
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
13/49
Supply chain
Administration and infrastructureAdministration and infrastructure
Human Resource ManagementHuman Resource Management
Product technology / developmentProduct technology / development
ProcurementProcurement
InboundInbound
logisticslogisticsOperationsOperations OutboundOutbound
logisticslogisticsSales andSales and
MarketingMarketingServicesServices
ValueValue
addedaddedcostcost==
marginmargin
Administration and infrastructureAdministration and infrastructure
Human Resource ManagementHuman Resource Management
Product technology / developmentProduct technology / development
ProcurementProcurement
InboundInbound
logisticslogisticsOperationsOperations OutboundOutbound
logisticslogisticsSales andSales and
MarketingMarketingServicesServices
ValueValue
addedaddedcostcost==
marginmargin
Administration and infrastructureAdministration and infrastructure
Human Resource ManagementHuman Resource Management
Product technology / developmentProduct technology / development
ProcurementProcurement
InboundInbound
logisticslogisticsOperationsOperations OutboundOutbound
logisticslogisticsSales andSales and
MarketingMarketingServicesServices
ValueValue
addedaddedcostcost==
marginmargin
Raw
materials
Consumer
ManufacturersWholesalers /
DistributorsSales outlets
Each link in the supply chain adds value
by developing products (and/or delivering services);
the margin (or profit) is equivalent to the value added13
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
14/49
Value Chain: Interconnecting relationships between organizations
Pearlson & Saunders, 2003
14
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
15/49
Porters five forces
"Competition is seen as the crux of an industry's profitabilitywhichis determined by the [five] competitive forcesidentified
Each of the competitive forces is identified in depth
firstly to ascertain the extent to which it is relevantto theparticular industry
secondly to ascertain its strengthin the particular situation...
15
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
16/49
Porters five forces
... [However], a sixth force, government regulation,can often be the most important factor in determining
the profitability of an industry"
(Pearson, 1999)
16
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
17/49
Porters five forces
Threat of new
entrants
Threat of
substitutes
Bargainingpower of
buyers
(customers)
Bargainingpower of
suppliers
Rivalry orbasis of
competition
17
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
18/49
18
1. Threat of New Entrantsnew firms that may enter a market
2. Bargaining Power of Buyersability of buyers to use market power to lower a firms
competitive position
3. Bargaining Power of Suppliersability suppliers of inputs to product/service to reduce a firmscompetitive position
4. Threat of Substitutesproviders of equivalent/superior products
5. Industry Competitorscurrent competitors for the same market
Porters five forces
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
19/49
SWOT analysis
Involves a detailed and exhaustive assessment of the
strengthsand weaknessesof the business
and the opportunitiesand threats
presented by its product markets and other environments suchas suppliers and technology developers
(Pearson, 1999)
19
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
20/49
SWOT analysis
Opportunities A B
Threats C D
Externalfactors
Strengths Weaknesses
Internal factors
20
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
21/49
BCG matrix
The Boston Consulting Group analysis technique models therelationshipbetween the currentand futurepotential of aproduct or serviceand how management wants to deal with it.
It is therefore a marketing analysis and it shows theproducts that are cash generatorsand cash consumers.
Each of these will need to be managed differently andsupported by different kinds of systems
(Cadle and Yeates, 2001)
21
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
22/49
BCG matrix
High Wild Cats(or problem
children)
Stars
Low
Dogs Cash Cows
Marketgrowth
Low High
Market Share
22
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
23/49
Customer relationships
Customer relationship management
Marketinghas traditionally been about finding newcustomers
CRMis about maximising the profit from relationships withexistingcustomers through targeting your best customers,repeat-selling, cross-selling, etc.
Putting the customer at the of your business
23
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
24/49
Customer relationships
Custom
er
satisfact
ion
Customer loyalty
Low High
High
Low
Satisfied
stayers
Hostages
Happy
wanderers
Dealers
Source:Piercy (1997),
from Needle
(2004)
24
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
25/49
Even from the crudest SWOT model, [strategy]
frameworks have been concerned largely with the
nature of the organisationand its
environmentand how the two might be
advantageously relatedto each other
(Pearson, 1999)
What is strategy (1) ?
25
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
26/49
The strategic process refers to the way in which
management strategy is formed.
In most organisations this involves amixture of scientific and rational analysis
together with more
subjective and political considerations.
(Needle, 2004)
What is strategy (2) ?
26
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
27/49
What is strategy (3) ?
Mintzberg (1987) considers 5 definitions,
not necessarily mutually exclusive:
Strategy as plan
Strategy as ploy
Strategy as pattern
Strategy as position
Strategy as perspective27
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
28/49
What is strategy (4) ?
Strategy as plan:
a deliberate, intentional approach to achieving
(long-term) results
28
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
29/49
What is strategy (5) ?
Strategy as ploy:
competitive manoeuvres aimed at generating
some positive effect on the basis of competition
29
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
30/49
What is strategy (6) ?
Strategy as pattern:
strategy emerges or is inferred from consistent
natural (i.e. unplanned) behaviour
30
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
31/49
What is strategy (7) ?
Strategy as position:
how the organisation positions itself in its
various environments, particularly its marketand competitive environments
31
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
32/49
What is strategy (8) ?
Strategy as perspective:
distinctive characteristics of an organisation as
perceived both internally and externally
32
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
33/49
What is strategy (summary) ?
Mintzberg (1987) considers 5 definitions, not necessarily mutually exclusive:
Strategy as plan: a deliberate, intentional approach to achieving (long-term) results
Strategy as ploy: competitive manoeuvres aimed at generating somepositive effect on the basis of competition
Strategy as pattern: strategy emerges or is inferred from consistentnatural (i.e. unplanned) behaviour
Strategy as position: how the organisation positions itself in itsvarious environments, particularly its market and competitive
environments
Strategy as perspective: distinctive characteristics of an
organisation as perceived both internally and externally
33
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
34/49
Strategicplanningov
erview
Business Strategy
Strategic planning andmanagement
Analysing theenvironment
Planning thedirection
Planning thestrategy
Implementingthe strategy
SWOT analysis
BCG matrix
Porters fiveforces
Strategy as pattern
Porters generic strategies
Vision
Mission
Objectives
Targets
Organisation Business environment
Organisation structureand culture
Monitor and control
34
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
35/49
Vision, mission, objectives, targets
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
Every business will have some sort of
visionorcore ideologymade up of:
core values
core purpose
visionary goals
35
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
36/49
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
The vision is often captured in a
mission statementoften not more than 50 words
Vision, mission, objectives, targets
36
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
37/49
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
The vision is often captured in a
mission statement
often not more than 50 words
Vision, mission, objectives, targets
The mission can be highlighted in a
strapline
using only a few words
London Metropolitan Universitysstrapline is:
transforming lives
meeting needs
building careers
37
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
38/49
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
The mission statement may beexpanded into key goals or
which should be SMART:Specific and written down
Measurable
Agreed, Aligned, Achievable
Realistic, RelevantTime-framed
Vision, mission, objectives, targets
38
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
39/49
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
Objectives will be supported by
Critical Success Factors (CSFs)
and measurable targets, or
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Vision, mission, objectives, targets
39
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
40/49
Vision, mission, objectives, targets (summary)
Mission
statement
Vision
Objective Objective
KPI KPI KPI
Every business will have some sort ofvision
The vision is captured in a mission statement
The mission can be highlighted in a strapline
The mission may be expandedinto SMART objectives
Objectives will be supported by CSFsand measurable targets as KPIs
40
P f t
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
41/49
Performance measurement
Why measure performance?
Organisations use key performance indicators (KPIs) to: identify success identify whether they are meeting customer requirements help them understand theirprocesses identify where bottlenecks, waste, etc. exist ensure decisions are based on fact
show if planned improvements happened(Parker, 2000)
41
C t l M d l f Add i th G b t
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
42/49
Conceptual Model for Addressing the Gaps betweenPerformance Measurement and Customer Satisfaction
Word of Mouth
and
Communications
Customer Value Past Experience
Expected Service
Perceived Service
Service Delivery
(including previous
and post)
Service
Performance
MeasurementProcesses
Management
perceptions of
customer
expectations
Customer
Satisfaction
CUSTOMER
PROVIDER Contact staff
perceptionsExternal
Communications
Internal
Communications
Gap1
Gap 2
Gap
3
Gap4
Gap
6
Gap5
Alignment of CRMVision and
Strategy through
streamlined
technology
Actual Perception
Level of Customer
Satisfaction
Gap 7
Wood, Page and Webb (2007)
42
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
43/49
Balanced Scorecard
Traditional performance measurement basedmainly on financial measures
Balanced scorecard designed to translateoverall mission and business strategyintospecific, quantifiable goals
Usually divided into 4 key areas:
financial customer
internal business process
learning and growth 43
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
44/49
Strategy triangle
Successful firms have an overriding
business strategy that drives bothorganisational and IS strategy
IS strategy can affect and is affectedby changesin a firms business andorganisational strategy
Changesin anystrategy must beaccompanied by changes in the
others
Source: Pearlson (2001)
Business Strategy
Organisational
Strategy
Information
Strategy
44
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
45/49
source: http://www.soroc.com/Content.aspx?ID=5
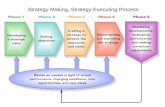
Strategic Planning
45
S i h k i
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
46/49
Starting the coursework assignment
Consider the following:
Detailed requirements identify datato support chosen decision for proposed MSS
Management Information include ERDand data dictionary
describe how you dealt with any problems in the data
Sample queries
relevant to your choice of decision providing information needed by management
46
R d d di f t k
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
47/49
Recommended reading for next weekmanagement decision making
Chaffey, D. (ed.), 2003, Business Information Systems, 2nd ed., FT
Prentice Hall
Data and information: pages 4 - 14 + Decision-making: pages 16 - 28
Laudon, K. & Laudon, J., 2004, Management Information Systems, 8th ed.,
Pearson Prentice Hall
Role of managers: pages 85 - 87 + Decision-making: pages 87 - 90
Lucey, T., 1997, Management Information Systems, 8th edition, Continuum
Decision-making: pages 140 - 151
Turban E. & Aronson J.E., 2001, Decision Support Systems and Intelligent
Systems (6th edition), Prentice Hall Business Publishing
Decision-making: (summary) pages 4 - 13 + (detail) pages 33 - 77
Whiteley, D., 2004, Introduction to Information Systems, Palgrave
Management decision-making: pages 171 -178
or similar
https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/bitstream/1826/2594/1/Creating%20and%
20Managing%20Value%20in%20Collaborative%20Netwo.pdf
47
R f
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
48/49
References
Boston Consulting Group (1968), Growth and Financial Strategies, BCG
Cadle J and Yeates, D, (2001), Project Management for Information Systems, 3rd
edition, PrenticeHall
Chaffey D (2003), Business Information Systems, 2nd edition, FT Prentice Hall
Mintzberg H (1987), The Strategy Concept I: five Ps for strategy, California Management Review,Fall
Needle D (2004), Business in Context, 4th edition, Thomson Learning
Parker C (2000), Performance Measurement, Work Study, MCB University Press
Pearlson K (2001), Managing and Using Information Systems, Wiley Pearlson K & Saunders C (2003), Managing and Using Information Systems: A Strategic
Approach, Wiley
Pearson G (1999), Strategy in Action, Prentice Hall
Porter M E (1979), How competitive forces shape strategy, Harvard Business Review, March/April
Porter M E (1980), Competitive Strategy: Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors,Free Press
Robson W (1997), Strategic Management and Information Systems, Prentice Hall
Wood S, Page S, Webb P (2007) Measurement of Customer Satisfaction & Performance
Measurement within a Local Government Framework (available at:
http://chesterrep.openrepository.com/cdr/handle/10034/37773)
48
-
7/31/2019 CC6052 Lecture Wk02 Strategy 2012
49/49
Any questions?
49