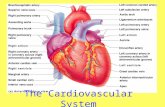
Cardiovascular Physiology 1)Blood 2)Heart 3)Peripheral Circulation The primary function of the...
-
date post
20-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Cardiovascular Physiology 1)Blood 2)Heart 3)Peripheral Circulation The primary function of the...

Cardiovascular Physiology
1) Blood
2) Heart
3) Peripheral Circulation
The primary function of the Cardiovascular system is to
1) deliver nutrients/oxygen and
2)remove wastes/CO2
from the cells in your body
Pump
Solution of Nutrients/Wastes
Tubes

Cardiac Physiology
The primary function of the HEART is
to generate a Pressure gradient in the vascular system
Pressure gradient allows blood to move by BULK FLOW through the body & the
lungs

GradientsGradients
e.g. e.g. Pressure, concentration, temperature, energyPressure, concentration, temperature, energy
Molecules move “down” gradients Molecules move “down” gradients fromfrom “ “HiHi” ” toto “ “LoLo”, ”, spontaneouslyspontaneously
A A GRADIENTGRADIENT is a difference in any parameter over distance is a difference in any parameter over distance

Bulk FlowBulk Flow
Many molecules moving simultaneously in one Many molecules moving simultaneously in one direction, from an area of high P to low Pdirection, from an area of high P to low P
PPATMOS mm Hg ATMOS mm Hg
PPLUNGS mm Hg LUNGS mm Hg
Hi PHi P
InspirationInspiration
Lo PLo P
Lo PLo P
ExpirationExpiration
Hi PHi P

FFB B = k = kBB(P(P11 - P - P22) L/min) L/min
FFB B = Bulk Flow L/min= Bulk Flow L/min
kkB B = bulk flow constant ~ tube diameter= bulk flow constant ~ tube diameter
PP1 1 P P22
If PIf P11 > P > P22, flow goes from 1 to 2, flow goes from 1 to 2
If PIf P11 < P < P22, flow goes from 2 to 1, flow goes from 2 to 1
If PIf P11 = P = P22, no flow occurs, no flow occurs
Poiseulle’s Law of Bulk Flow: Its all about PRESSURE

Bulk Flow: Movement DOWN a Pressure Gradient

Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle links
1) Electrical
2) Contractile
3) Pressure
4) Flow
through the heart!

The Heart is surround by cardiac muscle
Myocardium
Pericardium
Endocardium
Myocardial Fibers

Myocardium Anatomy
Myocardium is very similar to skeletal muscle
Except
• Intercalated discs form Gap junctions between adjacent myocardial fibers
• Myocardial fibers branch
• SR and T-tubules are weakly linked….Ca2+ is slowly released upon excitation

Pacemaker Cells: Heart is Autorhythmic!Heart is Autorhythmic!

How do pacemaker cells spontaneously produce action potentials?
Pacemaker cells have an UNSTABLE resting membrane potential!Pacemaker cells have an UNSTABLE resting membrane potential!
1
1) Prepotential: Few Na+ channels open, Na+ influx = funny current
2) Depolorization: VG Ca2+ channels open INFLUX of Ca2+
3) Repolarization: K+ channels open EFFLUX of K+
2 3
Drugs to treat Arrhythmias sometimes work on Ca2+ channels!

Myogenic signal propagates down Myogenic signal propagates down MyocardiumMyocardium

Electrical Properties of the Myocardium
Skeletal muscle AP look and behave like neural cells
Due to the SLOW CLOSING OF Ca2+, Myocardium REPOLARIZES VERY SLOWLY
Plateau

Excitation-Contraction Coupling of Cardiac Muscle
SacrolemnaECF
ICF
SR
T-tubule
1
2
3
4
6
5
Contraction
2) VG Ca2+ channels open, CA 2+ Influx
3) Ca2+ influx triggers RyR channels on SR to open
Calcium Induced Calcium Release
4) Ca2+ pours out of SR Ca2+ Spark!
5) Sparks sum to create Ca2+ signal
1) Action Potential
6) Ca2+ binds Troponin, cross- bridge formation, Contraction!
Calcium Sparks Video
Ca2+
Ca2+
Ca2+ Spark
Ca2+ Signal
RyR
VG Ca2+ Channel
Sarcomere

Myocardium contraction is GRADED!
Amount of Ca2+ entering myocardium is proportional to contraction strength
Amount of Calcium INFLUX
Fo
rce
of
Myo
card
ium
Amount of Calcium INFLUX
# o
f C
ross
brid
ge
s F
orm
ed
Contraction
Ca2+
Ca2+
Ca2+ Spark
Ca2+ Signal

Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Myocardium vs. Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Myocardium
Ca2+ Plateau prolongs the refractory period…..summation cannot happen!Ca2+ Plateau prolongs the refractory period…..summation cannot happen!Guarantees that Cardiac Muscle Contract-Relaxes Rhythmically!!!!!Guarantees that Cardiac Muscle Contract-Relaxes Rhythmically!!!!!
Refractory

Don’t get CONFUSED!
• Pacemaker Potentials • Cardiac Muscle Excitation
Pacemaker EXCITATION >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>.Cardiac Muscle Excitation- Contraction

Heart’s Electrical Conducting System
SA = 100 min-1
AV node = 40 min-1
AV bundleBundle branchesPurkinje Fibers 10-30 min-1

Why do the SA pacemaker cells beat a higher frequency than AV, Bundle Branches & Purkinje?
SA NODE
AV NODE
SA Node has More Funny Current (Na+) channels

What about Bundle Branches and Purkinje (10-30 min-1)?
SA Node
Atrial Muscle
AV Node
AV Bundle
Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
Ventricular Muscle
Excitation involves Calcium PLATEAU
Huge Refractory Period
No Plateau Phase
Shorter Refractory Period

Ventricular Systole: Contraction Ventricular Diastole: Relaxation
Atria have Systole and Diastole TOO!

5
43
2
1 Late diastoleAtria & Ventricles
Atrial systole
Early Ventricular SYSTOLE
START
Late Ventricular Systole
Early Ventricular DIASTOLE.
S1
S2

Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle links
1) Electrical
2) Contractile
3) Pressure
4) Flow
through the heart!

High Ventricular Pressure ForcesAV Valves Shut
Low Ventricular Pressure Forces Aortic/Pulmonary Valves Shut

Valves respond to pressure!Guarantees One-Way Blood Flow
Relaxed ventricular muscle (diastole)
Low pressure in ventricle
AV valve flops openAortic Valve Shuts
Contracting ventricular muscle (systole)
High pressure in ventricle
AV valve forced shutAortic Valve Opens
Chordae Tendinae
Papillary Muscle

Isovolumetric CONTRACTION
Isovolumetric RELAXATION
Blood Flow through heart is driven by Pressure!

Blood Flow through Heart
R. AV Valve
L. AV Valve

Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle links
1) Electrical
2) Contractile
3) Pressure
4) Flow
through the heart!

Wiggers Diagram
1 2 3 4 5
1) No electrical activityAtrial & Ventricular Diastole Pressure is lowVolume is increasing
2) P-wave = Atrial Depol. Atrial Systole
Atrial Pressure Rises Ventricular volume increases
3) QRS = Atrial Repol, Ventricular Depol. Ventricular Systole, Atrial DiastoleVentricular Pressure rises dramaticallyAtrial Pressure risesVentricular Volume flat, then decreases
as AV closes and Aortic and Pulmonary Valves Open
4) T-wave = Ventricular Repol. Ventricular Diastole Pressure drops dramatically in ventricle
& rises in Atria Ventricular Volume decreases then is flat as aortic and pulmonary valves CLOSE
5) No electrical activity Atrial & Ventricular Diastole Pressure & Volume slowly rise as blood fills