Cardiac Action Potentials
-
Upload
teresa-martins -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Cardiac Action Potentials
-
02
3
4
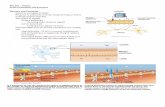
Slow Response
0 100 200 300
0 100 200 300
Diasto
lic Depo
larizat
ion
Threshold
CA PERMIABILITYK PERMIABILITY0mv
-60mv
-40mv
1 2
3
4
PLATEAU
K PERMIABILITY CA PERMIABILITY
PLATEAU
-90mv
0mv
Fast Sodium ChannelsResponsible for Depolarization
IK1 Inward Rectifying Potassium channel-High resting K+ Permeability
-Responsible for -90mv resting potential
ThresholdDiastolic Depolarization (DD) Decrease in K+ eux through Ikr + Iks channels -in Slow Response Fibers these progressivly close during DD Increase permeability to Sodium Sodium enters through If channels that open at -60mv Increase permeability to calcium L-type begin to open as membrane approaches threshold
Sodium Channel BlockerSlows rate of depolarizationSlows conduction VelocityTreats V-tach + A-b
Potassium Channel BlockerActs on IKr + IKsProlong the duration of APTreats: V-tach + A-Fib
Calcium Channel BlockerSuppresses activity of SA + AV node (Depolarization caused by calcium channels)-Slows rate of diastolic depolarization = slower HRTreats: Arrhythmias due to early and late afterpolarizaitonsAlsoDecreases cardiac contractility + SVR so used to treat Angina + Hypertension
Activation Gate
Inactivation GateInactivation
Gate
Activation
Gate
Na
Activation Gate
Inactivation Gate
Less than 1msLater Inactivation
Gate Closes
Activation Gate
Inactivation Gate
Fast sodium channelsopen and cause
Phase 0: Depolarization
Fast Sodium ChannelsReset to resting congurationas membrane potentialgoes from -50 -> -90mv
CC: pathological conditions existmembrane potentia does not repolarizeenough and inactivation gate does not reset, ber assumes SlowResponse characteristics
Inward rectifying Potassium ChannelCloses during Deplarization
Ik1 reopens at -40mvand contributes to lastphase of repolarization
K
Outward TransientRectifying Channel Ito1
Depolarization breiy opens these channel
They contribute to partialrepolarization (phase1)
K K
Outward Delayed Rectifying ChannelsIKr + Iks: Closed by depolarization
They determine the Beginning of Repolarization
Outward Delayed Rectifying Channels IKr + IKsClosed by depolarization
Ca
Ca
L-Type Calcium ChannelVoltage Gated, Opens at threshold
Open for a L-ong timeResponsible for plateau
Closes during repolarization
L-Type still open
L-Type Closes during Repolarization
K
K
Activation Gate
Inactivation Gate
K
Eective Refractory period last between Depolarization a half way through RepolarizationIt is caused by the INACTIVATION GATES of Fast Sodium Channels
IK1 Inward Rectifying Potassium channelare expressed at a much lower level in slow bersExplains -60mv resting potentialDO NOT OPEN IN SLOW FIBERS
Outward Delayed Rectifying Channels IKr + IKsContribute to DD in Slow Fibersby progressivle clossing
K KNa
Ca
If: Funny sodium ChannelsOpen when membrane reachesMaximum Negative potential(-60mv) and close approachingThreshold
Funny Sodium ChannelsClose at threshold
Fast Sodium ChannelsNon functional bc InactivationGate wont reset