Cancer Nlec
-
Upload
vaughncarlisle -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Cancer Nlec
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
1/39
CANCER
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
2/39
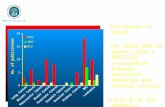
DEATH
MALE- lung
- prostate
- colorectal
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
3/39
DEATH
FEMALE
- lung
- breast
- colorectal
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
4/39
DEFINITION
Disease process that begins when an
abnormal cellis transformed by the
genetic mutation of the cellular
DNA.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
5/39
METASTASIS
- spread of cancer cells from the
primary tumor to distant sites
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
6/39
PATTERNS OF CELL GROWTH
HYPERPLASIA
- increase in the number of cells of a
tissue
METAPLASIA
- conversion of one type of nature cell
into another type of cell
DYSPLASIA- bizarre cell growth resultingin cells
that differin size, shape, or arrangement
from other cells of the same type of tissue.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
7/39
PATTERNS OF CELL GROWTH
ANAPLASIA
- cells that lack normal cellular
characteristics and differin shape, and
organization with respect to their cells oforigin
NEOPLASIA
- uncontrolled cell growth that follows
no physiologic demand
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
8/39
MANAGEMENT
GOALS:
CURE
CONTROL
PALLIATION
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
9/39
DETECTION AND PREVENTION
PRIMARYPREVENTION:
- Life style changes.
- Stop smoking
-
Limit alcoholintake- Eat healthy diet
- Be physically active
- Avoid sun exposure- Chemoprevention
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
10/39
CHEMOPREVENTION
ASPIRIN
TAMOXIFEN
FINASTERIDE
COX-2 INHIBITORS
CALCIUM
BETA CAROTENE
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
11/39
SECONDARY PREVENTION
Cost effective routine screening test
Screening should be based on
individuals age, sex, family history
a. TESTICULAR CA: most common bet.
20 and 34
- recommends annual screening
beginning at 15 yo
b. PROSTATE CANCER
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
12/39
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
13/39
STAGING
T primary tumor
Tx
T0
Tis
T1, T2, T3, T4
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
14/39
STAGING
N presence or absence of regional lymph
node involvement
Nx
N0N1, N2, N3, N4
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
15/39
STAGING
M absence or presence or distant
metastasis
Mx
M0M1
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
16/39
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
DIAGNOSIS:
1. BI OPSY: usually performed to obtain a
tissue sample for analysis of cells
suspected to be malignant.
a. EXCISIONAL
b. INCISIONAL
c. NEE DLE
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
17/39
PROCEDURE
1. PRIMARY: involves the removal of
a malignant tumor and a margin of
adjacent normal tissue
a. Local
b. Wide
c. Electrosurgery
d. Cryosurgery
e. Laser
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
18/39
PROCEDURE
2. SALVAGE SX: additional tx option
that uses an extensive surgical
approach to treat local recurrence of
cancer
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
19/39
PROCEDURE
3. PROPHYLACTIC SURGERYikely to develop
cancer
- Involves removing nonvital tissues or organs
that are likely to develop cancer
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
20/39
PROCEDURE
4. PALLIATIVE
- attempt to relieve complications
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
21/39
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Provide information about the procedure,
possible findings, post-op limitations,
changes in normal body functions.
Provide emotional support/
Provide patients comfort
Post-op teachings
Educate on plans for discharge, homecare, and follow up
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
22/39
RADIATION THERAPY
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
23/39
TYPES
1. BRAC HYTHERAPY
- Deliver high dose of radiation to a localized
area with direct tumor access.
a. INTERSTITIAL
b. INTRACAVITARY
2. TELETHERAPY: external beam irradiation
uses a device located at a distance from the
pt.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
24/39
UNITS FOR MEASURING RADIATION
EXPOSURE
GRAY: unit to measure absorbed dose
ROENTGEN: standard unit of
exposure
RADIATIONDOSE EQUIVALENT
(rem): unit of measure that relates to
biologic effectiveness.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
25/39
ACUTE ADVERSE EFFECTS
Fatigue and malaise
Skin: develop reaction as soon as
2wks
G I: N/V diarrhea
ORAL: changes in taste, dryness,
xerostomia
Bone marrow suppression
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
26/39
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
RISK FOR IMPAIRED SKININTEGRITY
- Dont apply lotion, ointment on the site
- Discourage vigorous rubbing, friction or
scratching
-Avoid tight fitting clothing
- Avoid exposure to sunlight
- Dont apply adhesive tape
- Avoid shaving
- Use luke warm water only and mild soap
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
27/39
RADIATION
Time: exposure to radiation is directly
proportional to the time spent within a
specific distance to the source
Distance: amount of radiation reaching
a given area decreases as resistance
increases
Shield: sheet of absorbing material
placed between the radiation source
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
28/39
CHEMOTHERAPY
Use of antineoplastic agents in an
attempt to destroy tumor cells by
interfering with cellular functions
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
29/39
PRINCIPLES
1. THE INTENT IS TO DESTROYAS MANY
TUMOR CELLS ASPOSSIBLE.
2. CANCER CELLSDEPEND ONTHE SAME
MECHANISMS FOR CELL DIVISION
THAT ARE FOUND INNORMAL CELLS.
3. CHEMOTHERAPYIS UTILIZED IN
DIFFERENT CLINICAL SETTING.
4. CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS CANBE
EFFECTIVE ONONE OF THE FOURPHASES OF THE CELL CYCLE.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
30/39
CELL CYCLE
G1: RNA and protein synthesis
S phase:DNA component doubles for
the chromosomes in preparation to cell
division
G2: short time period; Protein and
RNA synthesis occurs
M phase: extremely short pd; the cell
actually divides into two identical cells G0: resting not active in the cell
cycle
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
31/39
CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENT
1. CELL CYCLE SPECIFIC
- Destroy cell that are actively reproducing by
means of the cell cycles
2. VI NCA/PLANT ALKALOIDS
3. CELL CYCLEDNONSPECIFIC- Actindependently of the cell cycle have
prolonged effect on cells, leading to cellular
damage or death.
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
32/39
ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION
ORAL
IV
INTRATHECAL
IM
INTRA-ARTERIAL INTRACAVITARY
INTRAVESICAL
TOPICAL
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
33/39
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
MINIMIZE EXPOSURE VIA
INHALATION
-wrap gauze or alcohol pads around the
neck of ampules
- Wrap gauze on injection sites when
removing syringes in IV ports
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
34/39
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
MINIMIZE EXPOSURE VIA SKIN
CONTACT
- Wear gloves
- Handwashing
-
Wear gown- Eye and face shield
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
35/39
ADVERSE EFFECTS
Alopecia
Anorexia
Fatigue
N/V
Mucositis
Anemia
Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
36/39
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
PREVENT INFECTION
PREVENTINGBLEEDING
MINIMIZINGFATIGUE
PROM
OTIN
GNUTRITI
ON
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
37/39
PAIN MANAGEMENT
TYPES:
1. Somatic
2. Neutropathic3. Visceral
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
38/39
PHARMACOLOGICMGT.
NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS:
- NSAID
-Acetaminophen
- Corticosteroids
-anti convulsants- Ant idepressants
OPIOID
-
8/6/2019 Cancer Nlec
39/39
NURSING MGT
ASSESSPAINREPEATEDLYAT EACH
VISIT.
USE A PAIN INTENSITYSCALE
ASSESS RELIEF FROM MEDICATIONAND
D
URATION
OF RELIEF. ADMINISTER DRUGS ORALLY
WHENEVER POSSIBLE
ADMINISTER ANALGESICS RTC
RATHER THANPRN.