CANCER COLON AND RECTUM (WARDAH).ppt
Transcript of CANCER COLON AND RECTUM (WARDAH).ppt
-
CANCER COLON AND RECTUM
-
DEFINITION A colorectal cancer may be benign or malignant. Benign means the tumor will not spread, while a malignant tumor consists of cells that can spread to other parts of the body and damage them.
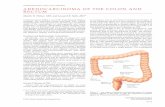
Colorectal cancer is a cancer affecting caecum, colon and rectum.
-
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONIron-deficiency anemiaRectal bleedingAbdominal painChange in bowel habitsIntestinal obstruction or perforationDiarrheaConstipationVomiting
-
ETIOLOGYInflammatory bowel disease - chronic inflammation of all or part of your digestive tract.
Genetic mutations
3. Polyps
-
RISK FACTOROlder ageMale genderHigh intake of fatAlcohol or red meatObesitySmokingLack of physical exercise
-
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Arise from dysplastic adenomatous polyps
The inactivation of a variety of tumour-suppressor and DNA repair genes
Along with simultaneous activation of oncogenes.
-
A selective growth advantage to the colonic epithelial cell
The transformation from normal colonic epithelium to adenomatous polyp
Colorectal Cancer
-
TREATMENT1. Surgery : colectomies for adenocarcinoma of the colon.
-
Colostomy- Part of the colon containing the cancer and nearby healthy tissue is removed, a stoma is created and a colostomy bag is attach to the stoma.
-
2. Radiotherapy and ChemotherapyChemotherapy for patient with node-positive disease.Radiation for patient with node-positive or transmural rectal cancer (pre or post op)Adjuvant therapy : chemotherapy (colon), radiation (rectum)
-
MEDICATION 1. Cetuximab (Erbitux)treatment of KRAS mutation-negative (wild-type), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-expressing, metastatic colorectal cancer
2. Bevacizumab (Avastin)for first-line and second-line treatment for metastatic colorectal carcinoma
-
INVESTIGATIONColonoscopy - Look for synchronous lesions, Alternative: air contrast barium enema (apple core lesion) + sigmoidoscopy.
2. PET scan (positron emission tomography) - helps to determine whether an abnormal area seen on another imaging test is a tumor or not.
3. CT scan - May be used if colorectal cancer has metastasized to other organs.
-
HEALTH EDUCATIONIncrease fibre in diet.
Decrease animal fat and red meat.
Decrease smoking.
Increase exercise and decrease BMI (body mass index).
Secondary prevention with screening.
-
NURSING CARE PLANNursing diagnosis : Risk for infection related to colostomy
Supporting data
Objective data : Subjective data :
Goal :
-
Nursing Intervention
Assess the condition of the patient such as all systems (e.g : skin, respiratory) for sign and symptoms of infection. R : Early recognition and intervention may prevent progression to more serious situation or sepsis.
2. Monitor vital signs especially temperature.R : Temperature elevation may occur (if not masked by corticosteroids or anti-inflammatory drugs) because of various factors, e.g : chemotherapy side effects, disease process, or infection. Early identification of infectious process enables appropriate therapy to be started promptly.
-
3. Screen or limit visitors who may have infections. Place in reverse isolation as indicated.R : Protects patient from sources of infection, such as visitors and staff who may have an upper respiratory infection (URI).
4. Emphasize personal hygiene.R : Limits potential sources of infection and or secondary overgrowth.
5. Reposition frequently, keep linens dry and wrinkle-free.R : Reduces pressure and irritation to tissues and may prevent skin breakdown (potential site for bacterial growth)
-
6. Promote adequate rest or exercise periods.R : Limits fatigue and encourages sufficient movement to prevent stasis complications, e.g : pneumonia and thrombus formation.
7. Stress the importance of good oral hygiene.R : Development of stomatitis increases risk of infection or secondary overgrowth.
8. Avoid or limit invasive procedures. Adhere to aseptic techniques.R : Reduces risk of contamination, limits portal of entry for infectious agent.
-
9. Administer antibiotics as indicated.R : May be used to treat identified infection or given prophylactically in immunocompromised patient.
10. Record and report the conditions of the patient to the doctor.R : For further intervention during hospitalization.
Evaluation :