C09 Pedigrees
Transcript of C09 Pedigrees

Bio 103 - Introduction to Biology
Chapter 9: Patterns of InheritancePedigrees
Background: Geneticists cannot study people in the same way in which they study other organisms. Since humans choose their own mates, geneticists cannot conduct breeding experiments to determine how human traits are inherited. In addition, humans have a long life span. As a result, it takes many years to produce several generations. Finally, most human families have small numbers of offspring, too few to verify the outcomes of crosses predicted by probability.
To overcome these problems, geneticists use special techniques. Three of the most common methods used are:a. pedigree analysisb. population samplingc. twin studies
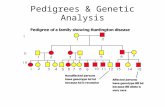
In this worksheet we will limit our study to pedigree analysis. A pedigree is a record that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations. It is like a family tree but more specific because it represents more than just names of individuals. By analyzing pedigrees, one can learn how the character and location of a genetic trait is distributed within families. When genotypes are known then predictions can be made about potential genetic problems. Pedigrees are based on the observable phenotypes; for in them are the clues to genotypes. Below is a sample pedigree. Try to determine if the trait indicated in the pedigree is dominant or recessive. Is the trait autosomal or sex linked? Use the key to better understand the symbols. Using the letters M for normal allele and m for muscular dystrophy, try to assign each individual two alleles. Base your letters on the phenotypes indicated in the pedigree.
The pedigree shown above is one for a disorder called Duchenne muscular dystrophy in which the muscles grow progressively weaker. The disease is caused by a recessive gene found on the X chromosome. Traits found on the X chromosome are called sex linked and will be more common in the male than the female.
1 success = preparation + execution

Objectives: To learn how to evaluate and use pedigrees to solve genetic problems.
Procedure: Examine the following pedigree. Based on the given phenotypes, fill in as many of the alleles as possible. Use the small c for Cream and large C for Dark fur color.
PEDIGREE 1: FUR COLOR IN VOLES; SEGREGATION AND DOMINANT/RECESSIVE ALLELES
Analysis:
1. Which fur color is dominant? What evidence do you see to support your conclusion?
2. What symbol is used to represent a female in pedigrees?
3. List each genotype, 1 through 14, for each individual within the pedigree.
2 success = preparation + execution