C H A P T E R 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates.
-
Upload
cynthia-jenkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of C H A P T E R 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates.

C H A P T E R 6C H A P T E R 6
Government Influence on Government Influence on Exchange RatesExchange Rates

Chapter OverviewChapter Overview
A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
B. A Single European CurrencyB. A Single European Currency
C. Government InterventionC. Government Intervention
D. Intervention as a Policy ToolD. Intervention as a Policy Tool

Chapter 6 ObjectivesChapter 6 Objectives
This chapter will:This chapter will:A. Describe the exchange rate system used A. Describe the exchange rate system used
by various governmentsby various governmentsB. Explain how governments can use direct B. Explain how governments can use direct
intervention to influence exchange intervention to influence exchange ratesrates
C. Explain how governments can use C. Explain how governments can use indirect intervention to influence indirect intervention to influence exchange ratesexchange rates
D. Explain how government intervention in D. Explain how government intervention in the foreign exchange market can affect the foreign exchange market can affect economic conditionseconomic conditions

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
1. Fixed Exchange Rate System1. Fixed Exchange Rate System
a. Bretton woods Agreementa. Bretton woods Agreement
b. Smithsonian Agreementb. Smithsonian Agreement
c. Advantages of a Fixed Exchange Rate c. Advantages of a Fixed Exchange Rate SystemSystem
d. Disadvantages of a Fixed Exchange d. Disadvantages of a Fixed Exchange Rate SystemRate System

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
2. Freely Floating Exchange Rate System2. Freely Floating Exchange Rate Systema. Advantages of a Freely Floating a. Advantages of a Freely Floating
Exchange Rate SystemExchange Rate System1.) a country is more insulated from the 1.) a country is more insulated from the
inflation of other countriesinflation of other countries2.) a country is more insulated2.) a country is more insulated
from unemployment problems in other from unemployment problems in other countriescountries

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
b. Disadvantages of a Freely Floating b. Disadvantages of a Freely Floating Exchange Rate SystemExchange Rate System
can adversely affect a country that has high unemployment.

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
3. Managed Float Exchange Rate 3. Managed Float Exchange Rate SystemSystem
a. Criticism of a Managed Float a. Criticism of a Managed Float SystemSystem

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
4. Pegged Exchange Rate System4. Pegged Exchange Rate Systema. Limitations of a Pegged Systema. Limitations of a Pegged Systemb. Creation of Europe’s Snake b. Creation of Europe’s Snake
ArrangementArrangementc. Creation of the European c. Creation of the European
Monetary System (EMS)Monetary System (EMS)d. Demise of the European d. Demise of the European
Monetary SystemMonetary System

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
5. Currency Boards5. Currency Boards
a. Exposure of a Pegged Currency a. Exposure of a Pegged Currency to Interest Rate Movementsto Interest Rate Movements
b. Exposure of a Pegged b. Exposure of a Pegged Currency to Currency to Exchange Rate Exchange Rate MovementsMovements

A. Exchange Rate SystemsA. Exchange Rate Systems
6. Dollarization6. Dollarizationa. ta. the replacement of a foreign currency withU.S.
dollars.
b. This process is a step beyond a currency board because it forces the local currency to be replaced
by the U.S. dollar.
c. Although dollarization and a currency board both attempt to peg the local currency’s value, the
currency board does not replace the local currency with dollars.
7. Classification of Exchange Rate 7. Classification of Exchange Rate Arrangements Arrangements

B. A Single European Currency B. A Single European Currency
1. Membership1. Membership
2. Impact on European Monetary 2. Impact on European Monetary PolicyPolicy
a. European Central Banka. European Central Bankb. Implications of a European b. Implications of a European
Monetary PolicyMonetary Policy
3. Impact on Business within Europe3. Impact on Business within Europe

B. A Single European CurrencyB. A Single European Currency
4. Impact on the Valuation of 4. Impact on the Valuation of Businesses in EuropeBusinesses in Europe
5. Impact on Financial Flows5. Impact on Financial Flows
6. Impact on Exchange Rate Risk6. Impact on Exchange Rate Risk
7. Status Report on the Euro7. Status Report on the Euro

C. Government InterventionC. Government Intervention
1. Reasons for Government 1. Reasons for Government InterventionIntervention
a. Smooth Exchange Rate a. Smooth Exchange Rate MovementsMovements
b. Establish Implicit Exchange b. Establish Implicit Exchange Rate Rate boundariesboundaries
c. Respond to Temporary c. Respond to Temporary DisturbancesDisturbances

Exhibit 6.2Exhibit 6.2
Effects of Effects of DirectDirect Central Bank Intervention Central Bank Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Marketin the Foreign Exchange Market

C. Government InterventionC. Government Intervention
2. Direct Intervention2. Direct Intervention
a. Reliance on Reservesa. Reliance on Reserves
b. Nonsterilized versus Sterilized b. Nonsterilized versus Sterilized InterventionIntervention
c. Speculating on Direct c. Speculating on Direct InterventionIntervention

Exhibit 6.3Exhibit 6.3
Forms of Central Bank InterventionForms of Central Bank Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Marketin the Foreign Exchange Market

C. Government InterventionC. Government Intervention
3. Indirect Intervention3. Indirect Intervention
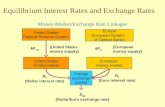
a. Government Adjustment of a. Government Adjustment of Interest RatesInterest Rates
b. Government Use of Foreign b. Government Use of Foreign Exchange ControlsExchange Controls

D. Intervention as a Policy ToolD. Intervention as a Policy Tool
1. Influence of a Weak Home Currency 1. Influence of a Weak Home Currency on the Economyon the Economy
2. Influence of a Strong Home 2. Influence of a Strong Home Currency on the EconomyCurrency on the Economy

Exhibit 6.4Exhibit 6.4
Impact of Government Actions on Exchange RatesImpact of Government Actions on Exchange Rates