Bronchial asthma pharmacology
-
Upload
reshmaulu -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
423 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Bronchial asthma pharmacology



Objectives What is bronchial asthma?
Etiology
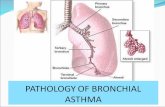
Pathophysiology of Asthma
Approaches to treatment
Phamacotherapy
Treatment plan
Drug delivery
Status Asthmaticus

Bronchial Asthma
300 million people
Adult 10-12 %
Children 15%

Bronchial Asthma
Definition: It is a syndrome
characterised by inflammation
and hyperresponsiveness of
tracheobronchial tree resulting
in reversible narrowing of air
tubes, mucosal oedema and
mucus plugging.

Etiology

Pathophysiology

Pathophysiology


Signs & Symptoms Dyspnoea
Wheezing
Cough
Limitation of activity

Approaches To TreatmentPrevention of Ag : Ab reaction
Neutralisation of IgE
Suppression of inflammation and hyperreactivity
Prevention of release of mediators
Antagonism of released mediators
Blockade of constrictor neurotransmittor
Mimicking dilator neurotransmittor
Directly acting bronchodilators

Drugs used in Asthma
Bronchodilators
• β2 agonists
• Methylxanthines
• Anticholinergics
Anti-inflammatory
agents
• Corticosteroids
• Chromones
• Lukasts
• 5-LOX inhibitor
• Antihistaminics
• 5-HT antagonists
Miscellaneous
• Mucolytics
• Antibiotics
• Monoclonal antibodies
• Desensitization
12

Bronchodilators
β2
agonistsSABA:
• Salbutamol
• Terbutaline
LABA:
• Salmeterol
• Formeterol
Methylxanthines
Theophylline
Anticholinergics
Tiotropiumbromide
Ipratropiumbromide
13

β2 sympathomimeticsACTIONS:
Bronchodilatation
Inhibits mediator release
Increase mucus clearance
β2 receptor stimulation
Increased cAMP
Relaxation of bronchial muscle

β2 Agonists
SABA
• Salbutamol, Terbutaline
• Maximum effect in 30 min
• Duration of action 4-6 hrs
• Used on ‘as needed’ basis
LABA
• Salmeterol, Formoterol
• Duration of action 12 hrs
• Used regularly

β2 agonists
ADRs
Muscle tremors
Palpitation,restlessness
Ankle edema
Throat irritation

MethylxanthinesTheophylline
Bronchodilatation
release of mediators
Narrow margin of safety
Ideal for night time symptoms
OTHER USES
COPD
Apnoea in premature infants
Mechanism of Action
adenylylcyclase
ATP
cAMP
5 AMP
Phosphodiesterase
Theophylline

Adverse effectsGastric pain, vomiting
Tremors, palpitation
Hypotension
Convulsions
Insomnia

Drug Interactions agents inducing metabolism
smoking
phenytoin
rifampicin
agents inhibiting metabolism erythromycin
OCPs
ciprofloxacin

AnticholinergicsIpratropium bromide, Tiotropium bromideACTIONS:
Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle
may increase mucociliary clearance
act in larger airways
less effective than sympathomimetics
suitable for prophylactic use
combination is useful
very few side effects - safe

Mechanism of Action

Anti-inflammatory Agents
Corticosteroids
Inhalational:
• Beclomethasone
• Flunisolide
• Budesonide
Systemic:
• Hydrocortisone
• Prednisolone
• Methyl prednisolone
Chromones
Cromolyn sodium
( MDI )
Nedocromil
22

Anti-inflammatory Agents (cont..)5-HT inhibitors & Antihistaminic
Ketotifen
(Oral )
Pizotifen
Lukasts ( Oral )
Zafirlukast
Montelukast
Pranlukast
Acolade
5-LOX inhibitors
Zileuton
(oral)
23

CorticosteroidsPrednisolone, BeclomethasoneADVANTAGES
more complete and sustained relief
improve airflow
Influence airway remodeling
retard progression of disease

Mechanism of Action

Inhaled v/s Systemic corticosteroidsINHALED SYSTEMIC
Beclomethasone, BudesonideTargeted drug delivery
Systemic side effects are less
Used as a prophylactic drug
Cannot be withdrawn abruptly – bronchial hyperreactivity
Prednisolone, HydrocortisoneSystemic side effects are marked
Used in chronic severe asthma
Can be tapered rapidly

Inhibits degranulation of mast cells
Restricted release of mediators
Inhibition of chemotaxis
CHROMONESSod cromoglycate, Nedocromil

Chromones contd…
Long term treatment - cellular inflammatory response
Ineffective during an attack
USES
prophylaxis in asthma
allergic rhinitis
allergic conjunctivitis

CHROMONES
Bronchospasm
Cough
Nasal congestion
Arthralgia
Rashes
ADRs

Leukotriene AntagonistsMontelukast and Zafirlukast
Prophylaxis of mild to moderate asthma
Alternatives to inhaled Glucocorticoids
Acceptable in children
Effective in aspirin induced asthma
Safe drugs
Mode of action
AntagoniseLTs
Inhibit receptors

Mechanism of Action

Anti IgE AntibodyOmalizumab



• Inhalational• Oral• Parenteral
Drug Delivery


Inhalational Drug Delivery SystemsMDI Dischalers Spacer
Rotahalers Nebulizer
37
Green[Salmeterol]
Orange[Fluticasone]
Blue[SABA]
Brown [budesonide]

Status AsthmaticusAcute severe life threatening form of asthma.
TREATMENT:
Hydrocortisone 100mg iv stat
Nebulized Salbutamol 2.5-5mg +Ipratropium bromide 0.5 mg
High flow O2 inhalation
Salbutamol/ Terbutaline 0.4mg im/sc
Intubation and mechanical ventilation
Antibiotics
Saline + sod. bicarbonate