Brian Coggins Lecture 4- Amino Acids and Protein Structure
-
Upload
shangnon-fei -
Category
Documents
-
view
5 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Brian Coggins Lecture 4- Amino Acids and Protein Structure

The Amino AcidsProtein Structure
BIOCHEM 301 SUMMER 2014Lectures 4 and 5
Wednesday, September 3, 2014Monday, September 8, 2014


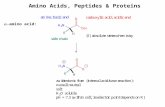
Amino Acids
(normal form)

Name Three-Letter Code
One-Letter Code
Alanine Ala AArginine Arg RAspartate Asp DAsparagine Asn NCysteine Cys CGlycine Gly GGlutamate Glu EGlutamine Gln QHistidine His HIsoleucine Ile ILeucine Leu LLysine Lys KMethionine Met MPhenylalanine Phe FProline Pro PSerine Ser SThreonine Thr TTryptophan Trp WTyrosine Tyr YValine Val V






FYI: Essential Amino Acids• Essential (humans do not make):
– Arg, His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp, Val
• Non-essential (humans make):– Ala, Asn, Asp, Cys, glu, Gln, Gly, Pro,
Ser, Tyr

Other Amino Acids• 4-hydroxproline found in collagen• ornithine and citrulline are N
metabolism intermediates

Sidechain pKa ValuesAmino Acid Sidechain pKa
Asp 3.6Glu 4.3His 6Cys 8Tyr 10Lys 10.5Arg 12.5

Expected Protonation State, pH 7?
Amino Acid Sidechain pKa
Protonated?
Asp 3.6 NoGlu 4.3 NoHis 6 NoCys 8 YesTyr 10 YesLys 10.5 YesArg 12.5 Yes

Sidechain pKa Values: Why?• Glu, Asp• Lys, Arg• Cys, Tyr• His• and what about Ser and Thr?

Perturbation of pKa Values• What factors could raise a sidechain
pKa from its normal value?• What factors could lower a sidechain
pKa from its normal value?

The Peptide Bond

Peptides

N- and C-Termini• First “residue” = N-terminus
– Has an amino group with pKa = 9• Last “residue” = C-terminus
– Has a carboxyl group with pKa = 2• Amino and carboxyl groups of all
other residues participate in peptide bonds and cannot protonate/deprotonate

Sequences and Residue Numbers
• Sequences are written using one-letter codes– Ex: MEGTNPEFDLVW...
• Residues are numbered from 1 at N-terminus, and identified using the amino acid type– Ex: L10
• Engineered mutations add one more letter– Ex: L10A means L10 is mutated to Ala

Peptides
The peptide bond has a partial double bond character.This helps to enforce the trans configuration.

Peptides

Catalyzed by Proline isomerase enzymes

Jane Richardson. “The Anatomy and Taxonomy of Protein Structure.” Advances in Protein Chemistry, 34 (1981).

Disulfides

Bovine insulin

The Alpha Helix

The Beta Sheet

An Antiparallel Beta Sheet
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase

A Parallel Beta Sheet
Flavodoxin

Everything Else• Loops or turns connect secondary
structural elements

Loops and Beta Sheets

Loops and Beta Sheets


Turns

The Ramachandran Plot(no Gly)(no Pro)

The Ramachandran Plot(Gly only)

Deriving the Ramachandran Plot
Crosshatchedregions are possible
The boundariesshow whichsteric clash makesa conformationimpossible

Motifs
Pyruvate kinase

Motifs
Helix-turn-helix motif binds DNA

Ways to Show Structures
Myoglobin
Heme in redHydrophobics in blue

Surface vs. Ribbon Diagrams

All-α, Mixed α/β, All-β
(a)Cytochrome b562(b)NAD-binding domain of lactic dehydrogease(c) Immunoglobulin light chain, variable region

Antiparallel Up/Down Alpha Helix Bundles

“Greek Key” Organization
Greek key =decorative elementin Greek andRoman mosaics

Antiparallel “Greek Key” Alpha Helix Bundles
Greek key =decorative elementin Greek andRoman mosaics

Parallel Alpha/Beta Singly Wound Barrels

Parallel Alpha/Beta Doubly Wound Sheets

Parallel Alpha/BetaDoubly Wound Sheets

Antiparallel Beta Greek Key Barrels

Antiparallel Beta “Jellyrolls”


Antiparallel Beta “Open-Face Sandwiches”

Dimers

Multimers

One Chain vs. Many Chains
Src protein: Four domains, one chain

Multimers• Example: hemoglobin
– Two “alpha” and two “beta” subunits– Symmetric– Four heme groups

GroEL/GroES

Protein Assemblies

Protein Assemblies

Protein Assemblies

Protein Assemblies

Virus Capsids
Tomato BushyStunt Virus

Virus Capsids
(a)Tomato bushy stunt virus (c) SV40(b)Poliovirus (d) Satellite tobacco necrosis virus

Proteins and Membranes
(1)Single alpha helix(2)Multiple alpha helices in a bundle(3)Beta barrel(4)Helix in the membrane horizontally(5)Anchored to a lipid(6)Anchored by sugars(7)Anchored by other membrane proteins(8)Anchored by other membrane proteins

Proteins and Membranes• Transmembrane region has exposed
hydrophobics

Alpha Helix Bundles

D Deng et al. Nature 000, 1-5 (2014) doi:10.1038/nature13306
Overall structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1.

Beta Barrels