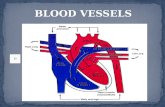
Blood vessels: Plumbing of the people Chapter 20 A&P.
-
Upload
lesley-cameron -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Blood vessels: Plumbing of the people Chapter 20 A&P.
Types of Blood VesselsArteryArterioleCapillaryVenulesVeins
• Stretch out for 100,000 km or 60,000 miles!
Structure of Blood Vessel Consists of three layers:1. Tunica adventitia/externa-
“coming from outside”; outermost layer; fibrous connective tissue; prevents tearing
2. Tunica media- “middle coat”; smooth muscle tissue and elastic tissue; change b.v. diameter
3. Tunica intima/interna- “innermost coat”; endothelium tissue; smooth lining; helps make up semilunar valves in veins
Lumen – central blood-containing space
1. Arteries distribute; use precapillary sphincters to regulate flow
2. Capillaries transport essential materials to and from cells by diffusion
3. Veins collect; use capacitance or stretch to catch all blood; sinuses- reservoirs of blood
Blood pressure: Hydrostatic force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel
1.Arterial blood pressure- highest; from cardiac output (heart rate & contractions) and peripheral resistance (blood viscosity & diameter of arterioles)
2.Capillary blood pressure- lowest; thin walls for diffusion and filtration
3. Venous blood pressure- medium; from pressure gradient of skeletal muscle contractions & total blood volume
Circulation Routes:1. Systemic- WHOLE BODY; blood flow from left ventricle to all parts of
body and back to right atrium2.Pulmonary- LUNGS; blood flow from right ventricle to lungs, get O2,
release CO2, and go back to left atrium3.Hepatic Portal- DIGESTION; blood flow from digestive organs into
liver 1st through hepatic portal vein blood leaves liver through hepatic vein into inferior vena cava. Liver can remove excess glucose and store it as glycogen; also it can detoxify blood (alcohol).
4.Fetal- FETUS; gets O2 and food through diffusion from mother’s blood and receives it from placenta through umbilical arteries and veins; ductus venosus allows blood to by-pass fetal liver; also by-passes lungs; foramen ovale opens from right atrium into left atrium in septum; ductus arteriosus lets blood enter aorta from pulmonary artery; No maternal blood actually mixes with the fetus. After birth, lungs function and extra vessels are not needed.
Circulation Routes
1. Systemic- WHOLE BODY; blood flow from left ventricle to all parts of body and back to right atrium
Circulation Routes
2.Pulmonary- LUNGS; blood flow from right ventricle to lungs, get O2, release CO2, and go back to left atrium
Circulation Routes 3.Hepatic Portal-DIGESTION• blood flow from digestive organs into liver 1st
through hepatic portal vein blood leaves liver through hepatic vein into inferior vena cava.
• Liver can remove excess glucose and store it as glycogen; also it can detoxify blood (alcohol).
Circulation Routes
4.Fetal- FETUS• gets O2 and food through
diffusion from mother’s blood and receives it from placenta through umbilical arteries and veins
• ductus venosus allows blood to by-pass fetal liver; also by-passes lungs
• foramen ovale opens from right atrium into left atrium in septum
• ductus arteriosus lets blood enter aorta from pulmonary artery
• No maternal blood actually mixes with the fetus
• After birth, lungs function and extra vessels are not needed.
The aorta branches into 3 main arteries:
1. Brachiocephalic
2. Subclavian
3. Carotid
VI. Blood vessels of the body
Arteries: Veins:
Carotids – C, I, E Jugular – I, E
Brachiocephalic Brachiocephalic – R, L
Abdominal aorta Vena Cava – I, S
Iliac – C, I, E Iliac – C, E
Femoral Femoral
Popliteal Popliteal
Arcuate Dorsal venous arch
Subclavian – R, L Subclavian – R, L
Aorta Hepatic Portal/ Hepatic
Palmar arch Digital
Pulmonary Pulmonary
Plantar arch Plantar arch
Splenic Splenic
Renal Renal
Axillary Axillary
Mesenteric – S, I Mesenteric – S, I
Tibial – A, P Tibial – A, P
Brachial Brachial
Radial Radial
Ulnar Ulnar
Coronary Coronary