Biodiversity Unit 3: Salt - SEED Home | SEED School...
Transcript of Biodiversity Unit 3: Salt - SEED Home | SEED School...
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 1 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Biodiversity Unit 3: Salt Level 3&4 (Grade 3-6)
Unit Overview In order to complete some of the activities in this unit it is recommended that you contact Department of Primary Industries to assist with the provision of equipment and information. This unit is the first of two units that focus on salt, this introductory unit to salt can be delivered independently or to complement Unit 2. This unit will expose students to salt as a natural element, along with the historic and current uses of salt.
Background Salt is essential for our survival, our blood, sweat, and tears contain salt. Our bodies can not produce salt so we must consume it, but too much can cause us harm. Over thousands of years people have harvested and found different ways to use this natural product.
Bloom’s Taxonomy Activity Duration Page Key words and Definitions 2 Tuning In & Finding Out Growing Salt Crystals 1.5 hours 3 Tuning In & Finding Out Cubic Crystals 1 hour 4-5 Sorting Out History of Salt 2.5 hours 6 Taking Action Salty Sayings 1 hour 7-8 Salt around the World 1 hour 9-10 Uses of Salt 1 hour 1.5 hours (with
research time) 11
VELS links 12-16
Did you know? Salt is a colourless or white substance that is found in sea water and in deposits in the earth. Salt has been harvested for use by people since ancient times and was once considered as precious as gold. There are over 14000 known uses. for salt
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 2 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Keyword & Definitions The following keywords and definitions will be explored throughout this unit. In order for students to become familiar with the terminology the keywords and their definitions can be used as ‘words of the week’. Have students write out the keywords and definitions and put them up in the classroom or write them on the board for easy reference. Word Definition Brine Water containing a significant amount of salt. Cube Three-dimensional object formed of six equal squares. Evaporation Is the process when the sun heats up water and turns it
to vapour, this then goes in to the air. Liquid Substance in a condition in which it flows, that is a fluid
at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and whose shape but not volume can be changed.
Salt Is a mineral that is composed of Sodium Chloride. It is a colourless or white substance that is found in sea water and in deposits in the earth.
Sodium Chloride Are the two major components of salt, known as elements.
Solid An object that retains its size and shape under normal conditions.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 3 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity One: Growing Salt Crystals Adapted from the North Central CMA Environmental Education Resource: Salinity. Overview: This activity is designed to help students understand that salt can be dissolved in water, which like many elements that are found in water are not possible to see. This makes it difficult to know if water is salty just by looking at it. Students will explore the concept of evaporation, and solids and liquids. This hands-on activity exposes students to a method to determine if salt is present in water, along with the introduction of how salt might be harvested.
Duration: Part 1: Create a salty solution (30 minutes) Part 2: Monitoring (1.5 hours – during the following week)
Equipment:
Part 1 • Glass Jar • Table Salt • Pencil • Fine String • Button • Hot water • Tablespoon • Magnifying Glass • Warm area to place the sample Part 2 • Paper • Pen
Activity: Part 1 Create a salty solution 1. Divide the class into pairs, each pair should have 1 set of equipment. 2. To make the salty solution add 2 tablespoons of salt to half a cup of warm water. 3. Stir the mixture with a spoon. 4. When the salt has dissolved add 1 more tablespoon of salt. This time not all the salt will dissolve.
Some will settle on the bottom. You have made a very strong saline solution called ‘brine’. 5. Tie an end of the string to the pencil and tie the other end of the string to the button. Lay the
pencil across the top of the glass so that the button hangs down in the brine. 6. Put the glass in a warm place where it won’t be moved and leave for 4 or 5 days.
Part 2 Monitoring 1. Start your science report, writing the date, aim and as much of the method as you can. Make
notes or draw labelled sketches of your observations during this time. 2. Complete the results section of your science report by making detailed notes or sketches of your
observations of the glass after the 4 or 5 day period. Ask yourself: Where are the crystals and how are they grouped? What size and shape are they?
3. Write your discussion by considering: Why are some of the salt crystals above the water line? How did they get there? Why do salt crystals in the water cling to the string?
4. Write your conclusion by stating what you have discovered. 5. Publish your science report.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 4 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity Two: Cubic Crystals Adapted from the North Central CMA Environmental Education Resource: Salinity.
Overview: Now that students have been exposed to salt being a solid or a liquid, they can take a closer look to see that a perfect salt crystal is a cube. When salt is viewed under a microscope it is possible to see some of the broken, crushed and perfect crystals. If students have completed activity one, they can take a closer look at the salt crystals that have grown themselves. If salt crystals are not available images of salt can be sources from a number of web sites. http://www.3dham.com/microgallery/salt.html http://josepino.com/other_projects/?growing-salt This activity requires an understanding of the concept of 3D, and should be adjusted based on the student’s knowledge. Working in small groups might also be a better option.
Duration: Cubic Crystals (1 hour)
Equipment: • Salt • Magnifying glass or Microscope (or images of salt) • Cubes or blocks for model building • Activity Sheet 2.1 and/or graph paper
Activity:
1. Students are to view salt using a magnifying glass/microscope, to identify the shape of perfect
crystals (cubes). 2. Revise student’s knowledge of cubes, faces, edges and vertices. 3. Use a 3D model to explain visible faces and cubes hidden from view. 4. Provide the students with activity sheet 2.1. 5. Discuss the findings of the students as a class.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 5 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity Sheet 2.1 – Cubic Crystals
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 6 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity Three: History of Salt
Overview: Today salt is a cheap and widely used product, although salt was once considered as precious as gold. This activity allows students to explore how the value and uses of salt have changed, along with the cultural and economic significance of salt. Websites that provide information on the history of salt include: http://www.saltinstitute.org http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_salt
Duration: Part 1: Research History (1 hour) Part 2: Create timeline (1.5 hours)
Equipment: Part 1 • Information on the history of salt or access to the internet (students to research books/web, or
provide them with a print out from the above web sites). Part 2 • Roll of butches paper • White board markers
Activity: Part 1 Research History
1. Form small groups (4 students) and allocate each group a period in history. Examples of periods in history might include pre history, ancient history, and modern history (this can be divided up e.g., 200 – 1000, 1100 – 1700, 1800 – current)
2. Each group of students to research history of salt – internet, books or printout sources by teacher.
3. Each group should record the events associated with salt that occurred in there allocated period in history.
Part 2 Create Timeline 1. Following on from activity 1, provide each group with butchers paper to create a timeline for
their period in history. Explain what to include along the time line such as key dates and events.
2. Discuss as a class how the value of salt has changed, how the uses have changes and how different cultures have used salt.
Example of a timeline. Pre History Ancient History Modern History Current Year 4000BC 2000BC 1000AD 1500AD 1900AD
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 7 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity Four: Salty Sayings Adapted from the North Central CMA Environmental Education Resource: Salinity.
Overview: Salt has played such a significant part in history it has influenced our language. This activity involves students solving mathematical problems, with in turn gives them corresponding letters. These letters are then used to fill in the salty sayings. These salty saying highlight how salt has become part of our language.
Duration: Salty Sayings (1 hour)
Equipment: • Activity Sheet 4.1 Salty Sayings • Pencil
Activity:
1. Students are to solve the mathematic problems at the bottom of the page, take note of the corresponding letters.
2. Look for numbers that match the answers and insert the appropriate letter. 3. Discuss the correct answers and salty sayings as a class
Answers:
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt VELS 3&4 Page 8 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries February 2010
Activity Sheet 4.1 – Salty Sayings Solve the operations on the bottom of the page and take note of the letter beside the operation. Look for the numbers below that match your answer and insert the appropriate answer. Discover the salty sayings.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 9 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
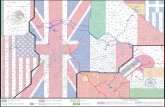
Activity Five: Salt around the World Overview: This activity will allow students to compare the amount of salt used in different countries. They will also be able to compare this usage over time by graphing the data.
Duration: Salt around the world (1 hour)
Equipment:
• World Atlas • Graph paper • Coloured pens or pencils • World salt usage data
Activity:
1. Provide students with a copy of the world map so they can identify the countries they will be talking about. Allow them to colour or label the countries.
2. Provide students with the data sheet and the materials to graph the salt usage of each country from 1991 through to 2007.
3. Discuss with the students which country uses the most/least salt and why this might be the case.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 10 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Sheet 5.1 – World salt usage Source: Salt Institute (www.saltinstitute.org)
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 11 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Six: Use of Salt Overview: There are over 1400 known uses for salt. This activity allows students to explore the wide range of uses for salt, including how it is used is not only in its raw form but also mixed with many other substances.
Web sites that contain information on uses of salt include: http://www.greenlivingtips.com/articles/274/1/Uses-for-salt.html http://www.bellybytes.com/articles/salt.shtml http://www.rd.com/advice-and-know-how/extraordinary-uses-for-salt/article24002.html http://www.lowsalt.info/serv03.htm
Duration: Part 1 Brain storming/web research (1 hour) Part 2 Advertising Poster (1 hour)
Equipment: Part 1
• Access to the internet • Black Board/White Board • Chalk/Board Markers
Part 2 • Cardboard • Coloured Pencils • Magazine • Scissors • Glue
Activity: Part 1 Brain storming Allow students 30 minutes to search the web sites listed above for information on the uses of salt. Brainstorm the uses of salt, listing the students suggestions on the board. Consider breaking it down into topics such as food, health, cleaning and farming. Use some information provided by the websites above if needed.
Part 2 Advertising Poster From the brain storming list each student should pick a use of salt or a product and create an advertising poster. The poster should promote the use, include any instructions, or benefits. Students should give a one minute talk to the class about their poster.
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 12 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
BIODIVERSITY UNIT 3: UNDERSTANDING SALT
LEVEL 4: VELS LINKS
Activity Description of Activity
Links to VELS LEVEL 3 Links to VELS LEVEL 4
1. Growing Salt Crystals
Part 1 • Creating a Salty
Solution
SCIENCE: Science at Work • Select and use simple measuring equipment, use
a range of appropriate methods to record observations and comment on trends.
Part 2 • Monitoring
SCIENCE: Knowledge and Understanding • Classify as solids, liquids and gases according to
observable properties Use appropriate scientific vocabulary to describe and explain observations and investigations ENGLISH: Writing • Students order information and sequence events
using some detail or illustrative evidence, and they express a point of view providing some information and support detail
• They meet the needs of audiences by including appropriate background information
SCIENCE: Knowledge and Understanding • Students explain change in terms of cause and
effect • They identify the characteristics of physical and
chemical changes • They describe how substances change during
reactions • COMMUNICATIONS: Listening, Viewing and
Responding: • Students develop interpretations of the content and
provide reasons for them. COMMUNICATIONS: Presenting: • Students summarise and organise ideas and
information, logically and clearly 2. Cubic Crystals SCIENCE: Knowledge and Understanding
• Classify as solids, liquids and gases according to observable properties
• Use appropriate scientific vocabulary to describe and explain observations and investigations
• Identify and describe structural features ICT: For Creating • With minimal assistance, student use ICT tools to
capture and save images ICT: For Communicating • Students locate information on an intranet, and
use a recommended search engine and limited
SCIENCE: Knowledge and Understanding • Students explain change in terms of cause and
effect • They identify the characteristics of physical and
chemical changes • They describe how substances change during
reactions ICT: For Communicating • Using recommended search engines, students
refine their search strategies to locate information quickly
• They evaluate the integrity of the located
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 13 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Description of Activity
Links to VELS LEVEL 3 Links to VELS LEVEL 4
key words to local information from websites MATHEMATICS: Space • Students recognise and name common three
dimensional shapes. They identify edges, vertices and faces
MATHEMATICS: Measurement, Chance and Data • Students estimate and measure volume MATHEMATICS: Working Mathematically • Students recognise the mathematical structure of
problems and use appropriate strategies to find solutions
ENGLISH: Reading • Student use several strategies to locate, select
and record key information from texts.
information based on its accuracy and the reliability of the web host.
MATHEMATICS: Measurement, Chance and Data • Students use metric units to estimate and
measure volume • They measure as accurately as needed for the
purpose of the activity COMMUNICATIONS: Listening, Viewing and Responding: • Students develop interpretations of the content and
provide reasons for them.
3. History of Salt Part 1 • Research History
HUMANITIES: Skills • Use a range of historical evidence to retell events ICT: For Communicating • Students locate information on an intranet, and
use a recommended search engine and limited key words to local information from websites
INTERPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT: Working in Teams: • Students cooperate with others in teams for agreed
purposes, taking roles and following guidelines established within the task.
HUMANITIES – HISTORY: Historical Knowledge and Understanding: • Students sequence events and describe their
significance in bringing about particular developments
Historical Reasoning and Interpretation: • Students use a range of secondary sources to
investigate the past • They use appropriate historical language and
concepts to develop historical explanations ICT: For Communicating • Using recommended search engines, students
refine their search strategies to locate information quickly
INTERPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT: Working in Teams: • Students work effectively in different teams and
take on a variety of roles to complete tasks or varying length and complexity
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 14 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Description of Activity
Links to VELS LEVEL 3 Links to VELS LEVEL 4
• They work cooperatively to allocate tasks and develop timelines
• Students accept responsibility for their role and tasks.
Part 2 • Create Timeline
HUMANITIES: Skills • Develop simple timelines to show events in
sequence ICT: For Communicating • Students locate information on an intranet, and
use a recommended search engine and limited key words to local information from websites
MATHEMATICS: Working Mathematically • Students recognise the mathematical structure of
problems and use appropriate strategies to find solutions
• Students apply number skills in a timeline context ENGLISH: Reading • Student use several strategies to locate, select
and record key information from texts. • Students interpret the main ideas and purpose of
texts ENGLISH: Writing • Students order information and sequence events
using some detail or illustrative evidence, and they express a point of view providing some information and support detail
HUMANITIES – HISTORY: Historical Knowledge and Understanding: • Students sequence events and describe their
significance in bringing about particular developments
Historical Reasoning and Interpretation: • Students use appropriate historical language and
concepts to develop historical explanations MATHEMATICS: Working Mathematically • Students recognise and investigate the use of
mathematics in real and historical situations COMMUNICATIONS: Presenting: • Students summarise and organise ideas and
information, logically and clearly
4. Salty Sayings • Salty Sayings MATHEMATICS: Number • Students devise and use written methods for
whole number problems of addition and subtraction involving numbers up to 999
ENGLISH: Reading • Students infer meaning from material presented
ENGLISH: Reading: • Students analyse texts and support interpretations
with evidence drawn from the text • Students analyse information and imagery,
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 15 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Description of Activity
Links to VELS LEVEL 3 Links to VELS LEVEL 4
5. Salt around the World
• Salt around the world
HUMANITIES: Skills • Identify the location of places on a simple map • Explain some of the differences between different
types of historical evidence, and frame questions to further explore historical events
MATHEMATICICS: Measurement, Chance and Data • Students interpret tables • Students use a column or bar graph to display
results MATHEMATICS: Working Mathematically • Students use computer software to organise and
present data ENGLISH: Reading • Students interpret the main ideas and purpose of
text
HUMANITIES – GEOGRAPHY: Geospatial Skills: • Students use atlases to accurately describe the
location of places MATHEMATICICS: Measurement, Chance and Data • Students present data in appropriate displays MATHEMATICS: Working Mathematically • Students recognise and investigate the use of
mathematics in real and historical situations COMMUNICATIONS: Presenting: • Students summarise and organise ideas and
information, logically and clearly • Using provided criteria, they evaluate the
effectiveness of their own and others’ presentations
6. Uses of Salt Part 1 • Brainstorming
ICT: For Communicating • Students locate information on an intranet, and
use a recommended search engine and limited key words to local information from websites
ENGLISH: Reading • Students infer meaning from material presented
ICT: For Communicating • Using recommended search engines, students
refine their search strategies COMMUNICATIONS: Presenting: • Students summarise and organise ideas and
information, logically and clearly
Part 2 • Advertising Poster
ENGLISH: Reading • Students infer meaning from material presented • Student use several strategies to locate, select
and record key information from texts. ENGLISH: Speaking and Listening • Student vary their speaking and listening for a
small range of contexts, purposes and audiences THE ARTS: Creating and Making • Students create and present works in a range of
art forms that communicate experiences, ideas,
DESIGN, CREATIVITY AND TECHNOLOGY: Investigating and Designing: • Students generate and communicate alternative
design ideas in response to a design brief and use words, labelled sketches and models to demonstrate that they are aware of environmental and social constraints
COMMUNICATIONS: Presenting: • Students summarise and organise ideas and
information, logically and clearly • They identify the features of an effective
Biodiversity Unit 3: Understanding Salt Page 16 of 16 Created by Department of Primary Industries, November 2009
Activity Description of Activity
Links to VELS LEVEL 3 Links to VELS LEVEL 4
concepts, observations and feelings • They refine their work in response to feedback and
self-evaluation
presentation and adapt elements of their own presentations to reflect them
• Using provided criteria, they evaluate the effectiveness of their own and others’ presentations
THE ARTS: Creating and Making • In their arts works, students communicate ideas
and understandings about themselves and others, incorporating influences from their own and other cultures and times.

























![SALT-OVERLY SENSITIVE5 Mediates Arabidopsis Seed Coat … · SALT-OVERLY SENSITIVE5 Mediates Arabidopsis Seed Coat Mucilage Adherence and Organization through Pectins1[W][OPEN] Jonathan](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5e3585e8c9781e4b2f69c445/salt-overly-sensitive5-mediates-arabidopsis-seed-coat-salt-overly-sensitive5-mediates.jpg)