Bilaminar Embryo
-
Upload
manan-shah -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of Bilaminar Embryo
-
8/4/2019 Bilaminar Embryo
1/3
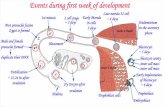
Bilaminar Embryo (Second Week of Development)
1. Rule of Twoa. Trophoblast has two layers
b. Blastocyst cavity transformed twicec. Two unique cavities are formed twice
d. Two populations of extraembryonic mesoderm arise (somatic &splanchnic)
e. Embryonic disc is bilaminar
2. Implantation of the Blastocysta. Begins on day 6 and is completed during the second week of development
b. Differentiation of syncytiotrophoblast maintains the ovarian corpose
luteum (hCG this hormone is basis of pregnancy test)3. Maternal uterine response to implanation is dermed decidual reaction
a. Mothers body protects and changes to accommodate the embryo
b. Protect the baby from the recognition by the mothers immune system4. Blastocyst is NOT recognized by the maternal immune system as an allograft5. Day 7.5
a. Inner cell mass divides into an epiblast and a hypoblast
b. Synsytiotrophoblast produces hCG and other cytokines to maintainpregnancy
c. Trophoblast now known as the cytotrophoblast, which fuses at some point
to be the synsytioum which pushes out Td. The space outside is known as endometrial stroma (stroma = connective
tissue) goes through changes is called the maternal decidual reaction
i. Decidual cells tell the fibrolasts (spindly cells) to line up in
columns to form more of an epithelium and become loaded withthings like glycogen. As theyre overtaken by the invading mass
of synsitious cells, they will be phagocytized and the glycogen will
be used as nutrition by the invading cells.ii. Blob nothing can stop it = synsetious trophoblast
e. Epiblast = embryonic stem cells (epiblast cells can become anything in a
petri dist)f. Amnioblast (derived from the epiblast and will form the amnion)
g. Amnion (membrane around cavity will come around to enclose the
entire fetus)h. Hypoblast (low cuboidal cells also known as primitive endoderm
because this is where gut cells will form eventually)i. Blastocyst cavity
j. Maternal closing plug - may cause some bleeding due to the invasion ofthis tissue into (confused for a period)
6. Formation of amniotic cavity
a. Appearance of amnioblastsb. Fluid will accumulate this is continuous with epiblast
c. Concurrent epiblast modifications (embryonic disc formation)
-
8/4/2019 Bilaminar Embryo
2/3
d. Contact with cytotrophoblast
7. Day 9.0
a. One of the characteristics of the hypoblast cells is that they will migratearound the epiblast and the hollow area is called the primitive yolk sac
(exocoelomic cavity)
i. Meckehs Diriticulum in the gut when in adults primitive yolksac doesnt go away
b. Exoxoelomic Cavity
i. Transforms the blastocyst cavity forming the primary yolk sac lined by extraembryonic endoderm which is derived from the
hypoblast
ii. Divides the conceptus into two fluid filled sacs
8. Day 12a. Endoderm cells and extraexmbryonic coelom forms
b. The synsetio trophoblast will start eating a lot of these blood vessels use
the oxygen and nutrition, etc, which may close bleeding
i. This is necessary for growth (nutritions)ii. So lakes (lacunae) provide open spaces for the blood to percolate
as it provides oxygen, sugar and nutritioniii. The yolk cavity undergoes a transition from a big single structure
to a reduplication as the chorionic cavity expands, the secondary
yolk sac becomes smaller
iv. Spaces that are forming within the extraembryonic mesoderm formchorionic cavity which persists throughout pregnancy
v. Chorionic membrane will form fingers which will go into these
lacunae, and it will form mechanism for blood vessels to comethrough
c. Chorionic Cavity (sac)
i. Mesoderm appears in a specific locationii. Formation of loose (hydrated) reticular connective tissue
iii. Division of extraembryonic mesoderm into somatic and splanchnic
mesodermiv. Extraembryonic coelom (chorionic cavity)
v. Establishment of chorion
d. Definition of Chorion
i. The chorion is a multilayered structure consisting of:1. somatic layer of extraembryonic mesoderm
2. cytotrophoblast
3. syncytiotrophoblastii. The chorion contributes to the fetal portion of the placenta,
including the villi
9. Day 13 (implanted blastocyst)a. Two cell layers (epiblast and hypoblast)
b. Two cavities the amniotic cavity and the secondary yolk sac
c. The chorionic cavity itself is formed
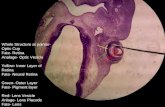
10. Day 13 (human conceptus) learn this picture
-
8/4/2019 Bilaminar Embryo
3/3
a. One other thing that adds itself to the lakes of blood endometrius in the
adult are filled with secretory gland, which secrete into the lacunae the
mixture of blood and lymphb. Very quicky, the primary villi have to become invested because organs
need to start forming
11. Summary of implantationa. Zona pellucida degenerates (day 5) - hatching
b. Blastocyst adheres to endometrial epithelium
c. Trophoblast generates cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast (day 7)d. Endometrial stroma undergoes decidual reaction
e. Blood filled lacunae appear within the synctiotrophoblast and will fill with
blood (day 9)
f. Endometrial defect filled w closing blood (day 10)12. Most ectopic pregnancies are within the beginning of the fallopian tube
13. Origins of uteroplacental circulation
a. Lacunar networks form within the syncytiotrophoblast
b. Lacunae fill with maternal blood and contents of ruptured urine glands(embryotroph)
c. Oxygenated blood delivered by spiral arteriesd. Poorly oxygenated blood removed by endometrial veins
e. Primary villi form (cytotrophoblast core)
f. Release of hCG into the maternal circulation to prevent menstruation and
maintain pregnancy14. Molar pregnancy
a. Trophoblast grows but there is no fetus
15. Hydatidiform molea. Hyperplastic trophoblast
16. Prechordal Plate (day 14)
a. Some cells in the anterior region of the hypoblast are different from all theother cells in that region
b. They are different because they are larger and more adhesive and these
are important because they place an end point to gastrulationc. The head region of the embryo will develop near the precordal plate, and
some of the migrating cells will go around it (induces the formation of the
head region, heart, etc)
d. Bascially a patch of primitive endoderm that signals the future site of theoropharyngeal membrane. It helps us organize the head region of the
embryo.
17. Summary ORIGIN F EMBRYONIC TISSUESa. MEMORIZE THIS
b. Proliferation, differentiation, and migration of extra-embryonic
trophoblastc. Maternal uterine endometrial tissue response to implantation
d. Formation of yolk sac and extraembryonic coelom
e. Formation of amnion and amniotic cavity
f. Formation of bilaminar embryonic disc