Asthma Sagal Yusuf #1447. General Outliune Introduction Definition Types of Asthma Epidemology ...
-
Upload
bruno-osborne -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
7
Transcript of Asthma Sagal Yusuf #1447. General Outliune Introduction Definition Types of Asthma Epidemology ...

AsthmaSagal Yusuf #1447

General Outliune
Introduction
Definition
Types of Asthma
Epidemology
Pathogenesis

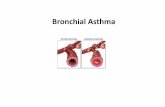
What is Asthma?
Chronic disease of the airways that may cause
Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing
Episodes are usualy associated with widespread, but variable, airflow obstruction within the lung that is often reversible either spontaneously or with treatment.


Pathogenetic Types of Asthma:
Extrinsic (Allergic/Immune) Typically develops in childhood (atopic)
70-80% child with asthma have other allergies Eczema Nasal allergies
Intrinsic (Non-Immune) Develops after age of 30yrs Not associated with allergies Often chronic and year-round conditions


Pathogenesis Allergens induce TH2 phenotype in CD4 T cells
of genetically susceptible individuals
TH2 cells secrete IL-4 (mediates class switch to IgE), IL-5 (attracts eosinophils), IL-10 (stimulates TH2 cells and inhibits TH1cells) and IL-13 (activates mast cells)
Re-exposure allergens leads to IgE-mediated activation of mast cells.

Early Phase Starts in 30-60 mins of exposure and lasts up
to 4-6 hours. Antigen + IgE on the mast cell in mucosa
Release of preformed histamine granules and generation of leukotrienes C4, D4 and E4 lead to broncho-constriction, inflammation and edema (early-phase reaction)
Stimulation of sub-mucosal vagal fibers leads to reflex smooth muscle contraction

Late Phase
Starts after 4-6 hours
Eosinophils play important role of the inflammation by attracting cytotoxic molecules IL-5, PAF, epithelial cells. Thus activate mast cells broncho-constriction



TRIGGERING FACTORS RESPIRATORY
INFECTIONS
Changed Temperatures (Cold Air)
Fog
Wood smoke; tobacco smoke
OCCUPATION
Emotions
Allergens (dust, pollen, etc)
Stress
Laughter
Anxiety
Exercise (dry, cold weather especially )

Early Warning Signs
Cough
Mood Changes
Change in facial appearance
Breathing changes
Verbal complaints
Itchy chin or neck
Itchy, watery, or glassy eyes
Runny nose Head stopped up Sneezing Dark Circles under
eyes Getting out of
breath Chest hurts

Asthma Flare Up Cough
Wheeze
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Retractions


Clinical Asthma Short, acute attacks:
Expiratory dyspnea Wheezing Dry cough
Curschman’s Spirals Thick stringy mucus, casts
Charcot Leyden crystals
Creola bodies (clusters of surface airway epithelial cells)

Cells Involved
Mast cells,
Eosinophils,
T-lymphocytes,
Macrophages,
Neutrophils,
Epithelial cells

Curschmann’s Spirals
Spiral shaped mucus plugs from the subepithelial mucus gland duct or bronchioles

Charcot-Leyden Crystals
Microscopic crystals Made up of
eosinophilic membrane proteins (lysophospholipase)

Epidemology
~300 million people with asthma around the world
Its projected that in 2025, another 100 million people will be affected
In the United States,
affects 25.7 million people, including 7.0 million children under 18
Asthma is a significant health and economic burden to patients
In 2010, 1.8 million people visited an ED for asthma-related care and 439,000 people were hospitalized because of asthma

Treatment Steroids and other Anti Inflammatory Drugs
Lifesaving Reducing swelling and mucus production in the airways Creates less sensitivity and reaction to triggers
Bronchodilators Relieve the symptoms of asthma by relaxing the muscles that
tighten within the airways, thus opening the airways. Rescue Inhalers: relieve the cough, wheezing and short breath To control all asthma need to combine with other medications
such as inhaled steroid for daily long term treatment

Continued…
Inhalers
Nebulizers Mouth piece or mask - mist
IV
Oral

Tips for USMLE on Asthma 1. If question mentions Curschmann’s spirals, think
asthma
2. If question mentions Charcot-Leyden crystals, think asthma
3. If question mentions creola bodies, think asthma
4. Status asthmaticus is an asthma attack that does not respond to pharmacologic agents and can be life threatening
5. If a 7-year-old boy suddenly complains to his mother that he can’t breath after playing with the new kitchen for the second time, think asthma

Famous Athletes with Asthma Paula Radcliffe--world record marathon runner
David Beckham
Jerome Bettis “The Bus” -- diagnosed 14yrs

References:
http://www.ginasthma.org/FAQs?faqid=2
http://www.score95.com/blog/blog/usmle-asthma/
http://www.asthma.org.uk/knowledge-bank-treatment-and-medicines-spacers
Kumar, Vinay, and Stanley L. 1915- Robbins. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier, 2007.