Assignment 1 and 2
-
Upload
gopal-athani -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Assignment 1 and 2
Assignment AETT ZG612 Advances in Materials Plastics and Composites (Weight age 15%)
1. Derive an expression for finding major Poison’s ratio for a unidirectional composite.
2. Find the compliance matrix and hence the stiffness matrix for a Glass-Epoxy composite which has properties as given in Table-1:
Table-1 Material properties for Glass-Epoxy Composite
Constituent Volume Fraction ρ (Kg/m3) E (GPa) ν G(GPa)
Glass Fibers 0.58 2540 70 0.23 28.5 Epoxy 0.4 1200 3.5 0.35 1.30
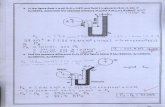
3. For the composite in Table-1, assume that the fibers are inclined at 450 with the loading axis. Calculate the elastic moduli in loading direction (Ex), perpendicular to loading direction (Ey) and in- plane shear modulus (Gxy) , Poisson ratio vxy and cross coupling coefficients (mx, my) for the orthotropic material. 4. With neat sketches, explain the difference between isotropic, anisotropic and orthotropic materials. 5. What do you mean by balanced orthotropic lamina? Plot the variations of major elastic constants for the balanced orthotropic lamina. 6. Discuss (with a neat sketch), the generalized Hook’s law for a three dimensional anisotropic material and write its matrix forms. Discuss and derive the different symmetries and considerations prevailing within the material and obtain the stiffness matrix for generally orthotropic material.
7. Based on the stiffness matrix for generally orthotropic material derived in Q.6 above, discuss the conditions for specially isotropic material, transversely isotropic and isotropic materials and obtain the stiffness matrix for the same.





![Assignment 2[1]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/558d404dd8b42aab4f8b46df/assignment-21-558dd8e883ea7.jpg)









![B2B Assignment No 2[1]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/577d349b1a28ab3a6b8e6f3c/b2b-assignment-no-21.jpg)



