Assessment of the Renal/Urinary System. Anatomy and Physiology Review Kidneys Ureters Urinary...
-
Upload
esther-arnold -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
3
Transcript of Assessment of the Renal/Urinary System. Anatomy and Physiology Review Kidneys Ureters Urinary...
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology ReviewReview
KidneysKidneys UretersUreters Urinary bladderUrinary bladder Urethra Urethra
Function of the Urinary Function of the Urinary SystemSystem
The primary function of the urinary The primary function of the urinary system is to maintain homeostasissystem is to maintain homeostasis
Regulate fluids and electrolytesRegulate fluids and electrolytes Eliminate waste productsEliminate waste products Maintain BP Maintain BP Involved with RBC productionInvolved with RBC production Involved with bone metabolismInvolved with bone metabolism
Kidneys Kidneys
PairedPaired Located retroperitoneally on the posterior Located retroperitoneally on the posterior
wall of the abdomen from T12-L3wall of the abdomen from T12-L3 The average adult kidney weighs 4.5ozThe average adult kidney weighs 4.5oz The right kidney sits lower in the abdomen The right kidney sits lower in the abdomen
due to liver placementdue to liver placement An adrenal gland sits on top of each An adrenal gland sits on top of each
kidneykidney
Kidney AnatomyKidney Anatomy
Each kidney has two partsEach kidney has two parts The renal medulla is the inner portionThe renal medulla is the inner portion
consists of renal pyramids which are collecting consists of renal pyramids which are collecting ducts that drain into renal pelvisducts that drain into renal pelvis
Once urine leaves the renal pelvis the Once urine leaves the renal pelvis the composition or amount of urine does not composition or amount of urine does not changechange
The Cortex is the outer portionThe Cortex is the outer portion contains nephronscontains nephrons
NephronNephron
Each kidney has approximately 1 million Each kidney has approximately 1 million nephronsnephrons
If the function is less than 20% If the function is less than 20% replacement therapy is usually initiatedreplacement therapy is usually initiated
The nephron is responsible for the initial The nephron is responsible for the initial formation of urineformation of urine
KIDNEY FUNCTIONSKIDNEY FUNCTIONS Urine formationUrine formation Excretion of waste products Excretion of waste products Regulation of electrolytesRegulation of electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balanceRegulation of acid-base balance Control of water balanceControl of water balance Control BPControl BP Regulation of RBC productionRegulation of RBC production Synthesis of vitamin D to active formSynthesis of vitamin D to active form Secretion of prostaglandinsSecretion of prostaglandins Regulation of calcium and phosphorus balanceRegulation of calcium and phosphorus balance
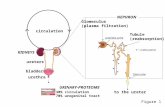
Urine FormationUrine Formation Urine is formed in the nephrons in a three step processUrine is formed in the nephrons in a three step process
Glomerular filtrationGlomerular filtration Tubular reabsorptionTubular reabsorption Tubular secretionTubular secretion
Glomerular Filtration produces ultrafiltrate which enters Glomerular Filtration produces ultrafiltrate which enters the tubules the tubules
Selective reabsorption of H2O & solutes occurs in Selective reabsorption of H2O & solutes occurs in tubulestubules
Selective secretion of solutes occurs in tubulesSelective secretion of solutes occurs in tubules 99% of ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed into the bloodstream99% of ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed into the bloodstream 1000-1500mL of urine is produced each day1000-1500mL of urine is produced each day
Excretion of Waste Excretion of Waste ProductsProducts
The kidney is the body’s main excretory organThe kidney is the body’s main excretory organ The major waste product of protein metabolism is The major waste product of protein metabolism is
ureaurea 25-30g are produced and excreted daily25-30g are produced and excreted daily
Other waste products include:Other waste products include: CreatinineCreatinine PhosphatesPhosphates SulfatesSulfates Uric acidUric acid Drug metabolitesDrug metabolites
Regulation of Regulation of ElectrolytesElectrolytes
In normally functioning kidneys the amount of In normally functioning kidneys the amount of electrolytes excreted per day is equal to the amount electrolytes excreted per day is equal to the amount ingestedingested
SodiumSodium Linked to blood volume and pressureLinked to blood volume and pressure Significant effects on osmotic pressureSignificant effects on osmotic pressure 90% of Na in ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules 90% of Na in ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules
and loops of Henleand loops of Henle Aldosterone causes kidneys to reabsorb sodiumAldosterone causes kidneys to reabsorb sodium
PotassiumPotassium The kidneys excrete more than 90% of K intake to maintain a The kidneys excrete more than 90% of K intake to maintain a
normal serum balancenormal serum balance Aldosterone causes the kidneys to excrete potassiumAldosterone causes the kidneys to excrete potassium
Regulation of acid-base Regulation of acid-base balancebalance
Normal serum pH is 7.35-7.45Normal serum pH is 7.35-7.45 Normal urine pH is 4.6-8Normal urine pH is 4.6-8 Kidneys 3rd line of defense in acid-base balanceKidneys 3rd line of defense in acid-base balance
respiratory & other buffer systems respond more rapidlyrespiratory & other buffer systems respond more rapidly kidneys require several hours to a day or more to kidneys require several hours to a day or more to
readjust balancereadjust balance Reabsorb bicarbonate from ultrafiltrateReabsorb bicarbonate from ultrafiltrate Excrete large quantities of acid in the urine Excrete large quantities of acid in the urine
(phosphoric and sulfuric acids) by buffering with (phosphoric and sulfuric acids) by buffering with ammoniaammonia
Control of water balanceControl of water balance The human body is made up of 60% waterThe human body is made up of 60% water Regulated by Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or Regulated by Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or
vasopressinvasopressin Secreted by the posterior pituitary in response to Secreted by the posterior pituitary in response to
serum osmolalityserum osmolality ADH increases reabsorption of water to return ADH increases reabsorption of water to return
serum osmolality to normalserum osmolality to normal Decreased water intake stimulates ADH releaseDecreased water intake stimulates ADH release ADH controls volume & concentration of urine by ADH controls volume & concentration of urine by
regulating permeability of distal tubule to H2Oregulating permeability of distal tubule to H2O
Control BPControl BP The kidney secrets the hormone renin when The kidney secrets the hormone renin when
there is a decrease in BPthere is a decrease in BP Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin
II Angiotensin I converts to angiotensin IIAngiotensin I converts to angiotensin II Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor and Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor and
causes BP to increasecauses BP to increase Increase in BP stops the excretion of reninIncrease in BP stops the excretion of renin The adrenal cortex also releases aldosterone The adrenal cortex also releases aldosterone
in response to increasing serum osmolality or in response to increasing serum osmolality or poor perfusion to increase BPpoor perfusion to increase BP
Regulation of RBC Regulation of RBC productionproduction
The kidneys release erythropoietin when The kidneys release erythropoietin when they sense a decrease in oxygen in the they sense a decrease in oxygen in the bloodblood
Erythropoietin stimulates the bone Erythropoietin stimulates the bone marrow to produce RBCsmarrow to produce RBCs
Vitamin D SynthesisVitamin D Synthesis
The kidneys convert inactive vitamin D to The kidneys convert inactive vitamin D to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Vitamin D is necessary for calcium Vitamin D is necessary for calcium balancebalance
Ureters Ureters
• • 1 ureter per kidney1 ureter per kidney
• • Long fibromuscular tubes that connect Long fibromuscular tubes that connect each kidney to the bladdereach kidney to the bladder
• • Enter bladder at an oblique angle to Enter bladder at an oblique angle to prevent flow blockageprevent flow blockage
• • Propel urine to bladder through Propel urine to bladder through peristalsisperistalsis
Bladder Bladder Hollow, muscular organ behind the pubic boneHollow, muscular organ behind the pubic bone Anatomic capacity is 1500-2000mLAnatomic capacity is 1500-2000mL Wall of the bladder contains four layersWall of the bladder contains four layers
Adventitia—Outer layer/connective tissueAdventitia—Outer layer/connective tissue Detrusor—smooth muscleDetrusor—smooth muscle Submucosal layer—loose connective tissueSubmucosal layer—loose connective tissue Mucosal lining—Inner layer/impermeable to waterMucosal lining—Inner layer/impermeable to water
Bladder neck forms Internal sphincter which is Bladder neck forms Internal sphincter which is composed of smooth musclecomposed of smooth muscle
Urethra Urethra Female = 4 cm. (1.5”), Opens anterior to the Female = 4 cm. (1.5”), Opens anterior to the
vaginavagina Male = 20 cm. (8”) 3 sectionsMale = 20 cm. (8”) 3 sections
prostatic = 1”, superior end joins bladder & prostatic = 1”, superior end joins bladder & internal involuntary sphincter; dilatable at internal involuntary sphincter; dilatable at this point & larger; has 2 ejaculatory ductsthis point & larger; has 2 ejaculatory ducts
Urination Urination approximately 150-350 mL of urine triggers approximately 150-350 mL of urine triggers
stretch receptors & stimulates afferent nerves stretch receptors & stimulates afferent nerves sending signal to CNSsending signal to CNS
Functional Capacity of bladder is 350mLFunctional Capacity of bladder is 350mL The efferent pelvic nerve stimulates the The efferent pelvic nerve stimulates the
bladder to contract, relaxing the urethral bladder to contract, relaxing the urethral sphincter. The decrease in urethral pressure sphincter. The decrease in urethral pressure and contractions of the detrusor muscle opens and contractions of the detrusor muscle opens the proximal urethra and leads to flow of urinethe proximal urethra and leads to flow of urine
reflex action however external sphincter can be reflex action however external sphincter can be contracted with voluntary controlcontracted with voluntary control
TERMINOLOGYTERMINOLOGY Micturation—Urination Micturation—Urination Frequency—Frequent voiding >every 3hoursFrequency—Frequent voiding >every 3hours Urgency—Strong desire to voidUrgency—Strong desire to void Hesitancy—Delay or difficulty in initiating Hesitancy—Delay or difficulty in initiating
voidingvoiding Nocturia—Excessive urination at nightNocturia—Excessive urination at night Oliguria—Output <400mL/dayOliguria—Output <400mL/day Anuria—Output <50mL/dayAnuria—Output <50mL/day Polyuria—Increased volume of urine voidedPolyuria—Increased volume of urine voided Hematuria—RBCs in urineHematuria—RBCs in urine Dysuria—Painful or difficult voidingDysuria—Painful or difficult voiding Enuresis—Involuntary voiding during sleepEnuresis—Involuntary voiding during sleep Incontinence—Involuntary loss of urineIncontinence—Involuntary loss of urine
Renal/Urinary System Changes Renal/Urinary System Changes Associated with AgingAssociated with Aging
Reduced renal blood flow causing kidney Reduced renal blood flow causing kidney loss of cortical tissue by 80 years of ageloss of cortical tissue by 80 years of age
Thickened glomerular and tubular basement Thickened glomerular and tubular basement membranes, reducing filtrating abilitymembranes, reducing filtrating ability
Decreased tubule lengthDecreased tubule length Nocturnal polyuria and risk for dehydrationNocturnal polyuria and risk for dehydration Decreased glomerular filtration rateDecreased glomerular filtration rate
Diagnostic TestsDiagnostic Tests
Blood TestsBlood Tests Serum Creatinine (0.5 – 1.2 mg/dl)Serum Creatinine (0.5 – 1.2 mg/dl) Blood Urea Nitrogen (10-20 mg/dl)Blood Urea Nitrogen (10-20 mg/dl) BUN/Creatinine Ratio (12:1 to 20:1 mass)BUN/Creatinine Ratio (12:1 to 20:1 mass)
Urine TestsUrine Tests Urinalysis Urinalysis Urine for C&SUrine for C&S Composite (e.g., 24hr) urine collectionsComposite (e.g., 24hr) urine collections Creatinine Clearance TestCreatinine Clearance Test Urine ElectrolytesUrine Electrolytes Osmolality (plasma; urine)Osmolality (plasma; urine)
Diagnostic Tests (cont)Diagnostic Tests (cont) Bedside sonography; Bladder scanners Bedside sonography; Bladder scanners Radiographic ExaminationsRadiographic Examinations
Kidneys, Ureter, and Bladder X-rayKidneys, Ureter, and Bladder X-ray Intravenous UrographyIntravenous Urography Computed TomographyComputed Tomography Cystography and CystourethrographyCystography and Cystourethrography
Other Renal Diagnostic TestsOther Renal Diagnostic Tests Renal Arteriography (Angiography)Renal Arteriography (Angiography) Renal BiopsyRenal Biopsy Renography (Kidney Scan)Renography (Kidney Scan) UltrasonographyUltrasonography
Diagnostic Testing: Diagnostic Testing: Nursing ImplicationsNursing Implications
Anticipate anxiety, discomfort and Anticipate anxiety, discomfort and embarrassmentembarrassment
Promote relaxation, comfort and privacy Promote relaxation, comfort and privacy as ableas able
Provide teaching Provide teaching
Assessment TechniquesAssessment Techniques
Family history and genetic risk Family history and genetic risk assessmentassessment
Demographic data and personal Demographic data and personal historyhistory
Diet historyDiet history Socioeconomic statusSocioeconomic status Current health problemsCurrent health problems
Physical AssessmentPhysical Assessment
InspectionInspection AuscultationAuscultation PalpationPalpation PercussionPercussion Assessment of the urethraAssessment of the urethra
Blood TestsBlood Tests
Serum creatinineSerum creatinine Blood urea nitrogenBlood urea nitrogen Ratio of blood urea nitrogen to serum Ratio of blood urea nitrogen to serum
creatininecreatinine
UrinalysisUrinalysis
Color, odor, and turbidityColor, odor, and turbidity Specific gravitySpecific gravity pHpH GlucoseGlucose Ketone bodiesKetone bodies ProteinProtein LeukoesteraseLeukoesterase Cells, casts, crystals, and bacteriaCells, casts, crystals, and bacteria
Other Urine TestsOther Urine Tests
Urine for culture and sensitivityUrine for culture and sensitivity Composite urine collectionsComposite urine collections Creatinine clearance—best indication Creatinine clearance—best indication
of overall kidney functionof overall kidney function Urine electrolytesUrine electrolytes Osmolarity, blood/plasma osmolarity, Osmolarity, blood/plasma osmolarity,
urine osmolarityurine osmolarity
Others Diagnostic TestsOthers Diagnostic Tests
Bedside sonography/bladder Bedside sonography/bladder scannersscanners
Computed tomographyComputed tomography Kidney, ureter, and bladder x-raysKidney, ureter, and bladder x-rays Intravenous urographyIntravenous urography
Bowel preparationBowel preparation Allergy informationAllergy information FluidsFluids
Cystography and Cystography and CystourethrographyCystourethrography
Instilling dye into bladder via urethral Instilling dye into bladder via urethral cathetercatheter
Voiding cystourethrogramVoiding cystourethrogram Monitoring for infectionMonitoring for infection Encouraging fluid intakeEncouraging fluid intake Monitoring for changes in urine output Monitoring for changes in urine output
and for development of infection from and for development of infection from catheter placementcatheter placement
Renal Arteriography Renal Arteriography (Angiography)(Angiography)
Possible bowel preparationPossible bowel preparation Light meal evening before, then nothing by Light meal evening before, then nothing by
mouthmouth Injection of radiopaque dye into renal Injection of radiopaque dye into renal
arteriesarteries Assessment for bleedingAssessment for bleeding Monitoring of vital signsMonitoring of vital signs Absolute bedrest for 4 to 6 hoursAbsolute bedrest for 4 to 6 hours Serum creatinine measured for several Serum creatinine measured for several
days to assess effects of testdays to assess effects of test
Renal BiopsyRenal Biopsy
Percutaneous kidney biopsyPercutaneous kidney biopsy Clotting studiesClotting studies Preprocedure carePreprocedure care Follow-up careFollow-up care
Assessment for bleeding for 24 hoursAssessment for bleeding for 24 hours Strict bedrestStrict bedrest Monitoring for hematuriaMonitoring for hematuria Comfort measuresComfort measures
RenographyRenography
Small amount of radioactive material, a Small amount of radioactive material, a radionuclide, usedradionuclide, used
Procedure via intravenous infectionProcedure via intravenous infection Follow-up care:Follow-up care:
Small amount of radioactive material may be Small amount of radioactive material may be excreted.excreted.
Maintain standard precautions.Maintain standard precautions. Client should avoid changing posture rapidly Client should avoid changing posture rapidly
and avoid falling.and avoid falling.
Other Diagnostic TestsOther Diagnostic Tests
UltrasonographyUltrasonography Cystoscopy and cystourethroscopyCystoscopy and cystourethroscopy
Procedure is invasive.Procedure is invasive. Consent is required.Consent is required. Postprocedure care includes monitoring Postprocedure care includes monitoring
for airway patency, vital signs, and urine for airway patency, vital signs, and urine output.output.
Monitor for bleeding and infection.Monitor for bleeding and infection. Encourage client to take oral fluids.Encourage client to take oral fluids.
Retrograde ProceduresRetrograde Procedures
Retrograde procedures go against the Retrograde procedures go against the normal flow of urine.normal flow of urine.
Procedure identifies obstruction or Procedure identifies obstruction or structural abnormalities with the instillation structural abnormalities with the instillation of dye into lower urinary tract.of dye into lower urinary tract.
Monitor for infection.Monitor for infection. Follow-up care is the same as for a Follow-up care is the same as for a
cystoscopic examination.cystoscopic examination.
Urodynamic StudiesUrodynamic Studies
Studies that examine the process of Studies that examine the process of voiding include:voiding include: Cystometrography Cystometrography Urethral pressure profileUrethral pressure profile ElectromyographyElectromyography Urine stream testUrine stream test
Stress IncontinenceStress Incontinence
Expected Outcomes: to have fewer episodes of stress Expected Outcomes: to have fewer episodes of stress incontinence or a decreased amount of urine lost with incontinence or a decreased amount of urine lost with each episode.each episode.
Interventions:Interventions: NonsurgicalNonsurgical
Drug therapyDrug therapy Behavioral interventions (diet and exercise)Behavioral interventions (diet and exercise) Vaginal Cone therapyVaginal Cone therapy Other: behavior modification, psychotherapyOther: behavior modification, psychotherapy
SurgicalSurgical Vaginal, abdominal or retropubic proceduresVaginal, abdominal or retropubic procedures
Urge Urinary Urge Urinary IncontinenceIncontinence
Expected Outcomes: to use techniques to prevent Expected Outcomes: to use techniques to prevent or manage urge incontinenceor manage urge incontinence
Interventions:Interventions: Drug Therapy (Chart 73-9, p. 1691)Drug Therapy (Chart 73-9, p. 1691) Diet TherapyDiet Therapy Behavioral InterventionsBehavioral Interventions
Bladder trainingBladder training Habit trainingHabit training Exercise therapyExercise therapy Electrical stimulationElectrical stimulation
Reflex Urinary Reflex Urinary IncontinenceIncontinence
Expected outcomes: to achieve continence by Expected outcomes: to achieve continence by keeping urine volume in the bladder within keeping urine volume in the bladder within normal limits, preventing bladder overdistention.normal limits, preventing bladder overdistention.
Interventions:Interventions: Drug TherapyDrug Therapy Behavioral InterventionsBehavioral Interventions
Bladder Compression (CredBladder Compression (Credéé, Valsalva), Valsalva) Intermittent Self-Cathererization (Clean tech.)Intermittent Self-Cathererization (Clean tech.)
Functional Urinary Functional Urinary IncontinenceIncontinence
Expected outcome: to use methods of urine Expected outcome: to use methods of urine containment or collection that ensure dryness containment or collection that ensure dryness until the underlying cause of the incontinence is until the underlying cause of the incontinence is treated.treated.
Interventions:Interventions: Applied devicesApplied devices ContainmentContainment Urinary catheterization Urinary catheterization
(intermittent or indwelling)(intermittent or indwelling)